Pancreas Physiology Flashcards
acute
rapid onset, sharp, severe, a short course.
ACUTE Exacerbation / ACUTE ON CHRONIC
To aggravate, increase severity.
acute on chronic
A long term (chronic) problem with an acute flair up
allograft
same species cadaver donor
amylase
It is secreted by the pancreas, salivary glands, fallopian tubes and bowel. Normally found in small amounts in the blood (serum) and urine. Serum levels will typically double or more in cases of acute pancreatitis. (inflammation of pancreas)
breaks down carbohydrates
Increases seen in pancreatitis, carcinoma of pancreas
labs: Serum, Urine
annular pancreas
what is its etiology (cause)?
Pancreatic tissue surrounds the 2nd portion of the duodenum, often causing GI obstructive problems.
A problem with the fusion of the ventral and dorsal buds of the embryonic pancreas.
Are pancreas transplants orthotopic?
No, Non-orthotopic. Placed along the iliac wing within the pelvis
•
Good protection from pelvis
Good vascular anastomoses
Good exocrine anastomosis
cholecystokinin
stimulates secretion of pancreatic enzymes and bile. It is released by cells in the duodenum
chronic
Long, drawn out, long duration, slow progress.
Do the pancreatic exocrine products pass through the ampulla of Vater?
yes
documentation
Minimum views
Head, body, tail (trans)
Head (long)
Measurements
Head (trans, long)
Body
Tail
Additional views
To better visualize
Ductal dilation
Positive finding
ectopic pancreatic tissue
the most common congenital anamoly of the pancreas
Ectopic pancreatic tissue is susceptible to pancreatitis and pancreatic tumors. There is an abundance of acini cells in this tissue,
These ectopic tissues would be prone to secrete insulin, glucagon and somatostatin.
What hormones are found in the enteric (intestines) system of the pancreas aka endocrine hormones?
gastrin, secretin and cholycysokinin
What 3 hormones are made by the Islets of Langerhans?
glucagon, insulin and somatostatin
exacerbation
to increase the severity
What do Acini cells do?
produce exocrine enzymes aka digestive juices. Approx. 2 litres per day that contain Enzymes and Sodium Bicarbonate
Gastrin
stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by cells in the stomach, duodenum, and pancreas
glucagon
Glucagon is a hormone secreted/released by the alpha cells (islets of langerhans). It increases blood glucose levels by causing the liver to release some glucose and glycogen. Glycogen is converted into glucose by glucagon.
process Glycogen (Starch) to Glucose
Glucose Lab: serum
Helps determine glucose metabolism disorders
Tumor of the islet of Langerhans
How is fibrocystic pancreatic disease acquired?
What glands does it affect?
it is a hereditary disorder affecting acini cells more than islet cells.
exocrine glands causing their secretions to become thick and appears bright on US like that of an older person in that has fat has replaced the large of pancreatic tissue.
how many anstomoses are there in a transplanted pancreas?
arterial – Donor AO or CA to external iliac artery
venous – Donor PV to external iliac vein
duodenal – exocrine functions to jejunum or bladder
iatrogenic
Caused by a physician. Typically through actions or therapy. Can be both positive and negative consequences.
A patient developed a hematoma after the biopsy. (a negative)
A patient is cured of pain after a procedure. (a positive)
If you can’t see the pancreas and you have manipulated the probe, what else can you do?

Give patient H2O-Simethicone which fills the stomach with H2O allowing for an acoustic window.
–
Simethicone is an anti-foaming agent that decreases the surface tension of gas bubbles, causing them to combine into larger bubbles in the stomach that can be passed more easily by burping.
•
Pass on giving H20-Simethicone if the patient has pancreatitis
Additional exams following US, i.e. Upper GI, Abd. CT etc…
In cases of acute pancreatistis, ________ serum levels will double in 24 hours of pancreatic damage?
When will they begin to drop?
amylase
1-2 days
Indications for pancreas exam (8)
Epigastric pain
–
Abd. pain radiating to back
–
Abd. distension with hypoactive bowel sounds
–
Acute pancreatitis
–
Chronic pancreatitis
–
Biliary dz.
–
Abnormal labs – pancreatic enzymes
–
Pancreatic neoplasm
insulin
islets of langerhans Beta cells
convert Glucose to Glycogen
Is it common to have the Td oblique to the patient in order to see the entire pancreas from head to tail?Yes
Yes, head is inferior to tail.
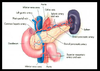
lipase
Increases in serum levels are an indication of pancreatic cellular damage. Serum levels of Amylase and Lipase increase when pancreatic damage has occurred. Amylase levels begins to drop after a day or two, whereas Lipase levels are elevated for longer period of time depending on the amount of parenchymal damage.
breaks down fat
Lab: serum
Helps determine amount of pancreatic damage
nucleases
Not an enzyme
Nucleic acids: The most common nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are universal in living things, as they are found in all cells and viruses.
patient positioning
Think about where fluid and gas will be in these different positions
–
Supine: Easiest position for most patients but often inadequate for viewing the pancreas
–
Rt lat decub vs. Lt lat decub: A RLD will be better to fill the c-loop
–
Upright: I find this position to be very useful. Gravity pull liver inferior making a better window, fluid pools in the inferior portion of the stomach and gas will rise.

Probe manipulations
PRESSURE: Firm pressure to move gas
Rotate: Don’t forget… head is inf. to tail
Tilts: sometimes a tilt is just the thing to improve an image
secretin
stimulates secretion of a bicarbonate-rich fluids from the pancreas. It is released by cells in the duodenum
serum levels of ___ will rise when pancreatic cellular damage has occured.
These serum levels are elevated for a longer period of time than ___ levels once pancreatic damage has occured.
lipase
amylase
sodium bicarbonate
neutralizes acid rich environment foudn in duodenum
Increases the ph environment from and acid environment to a more neutral environment. As the chyme (partially digested food) leaves the stomach and enters the duodenum it is very acidic and the sodium bicarbonate help to neutralize the environment. Digestive enzymes work better, more effectively in a more neutral environment.
somatostatin
islets of langerhans Delta cells;
Alpha and Beta inhibitor. least abundant of all endocrine and islet cells.
sonographic appearance of pancreas (prep, echogenicity, duct)
Difficult to visualize
2o Location
•
Prep. is important – NPO 8-12 hrs for adult
Echogenicity / Texture – Slightly more echogenic than liver, Fine, homogeneous in texture
–
Pancreatic Duct– anechoic are with parallel lines echogenic line. single echogenic line – if duct is collapsed
T/F diabetic’s are given insulin b/c they need to have the blood glucose levels decreased.
True
T/F pt’s how are hypoglycemic have too much glucose in their blood?
False, too little.
T/F the duct of wirsung is the main duct for the tranportation of endocrine hormones int he pancreas.
true.
tail to head oreintation
tail superior and posterior to head

True or False, Blood sugar regulation depends only on the hormones secreted from the healthy pancreas.
False
trypsin, carboxypeptidase and chymotrypin
enzymes produced by acini cells to break down protein
What are the pancreatic parenchyma functions (2)?
Exocrine system – digestion of carbs, fats and proteins via digestive enzymes produced by Acini cells
Endocrine system - produces hormones that regulate blood sugar levels via the cells called the Islets of Langerhans (insulin, glucagon, somatostatin)
How does the pancreas appear on US? Why?
bright due to the thick secretions
What group of ppl are eligible for pancreas tranplants?
diabetic patients - –
Poor native pancreas Endocrine function
Normal native pancreas exocrine function
Often will have Kidney and Pancreas together
•
Retinopathy
Neuropathy
Nephropathy
US Evaluation & Vascular flow assessment
Check for: Fluid collections,Guided tissue biopsy, Rejection, Anti-rejection toxicity, Necrosis
What is helping you visualize the pancreatic tail in this image (note: it helps to haeve the pt stand up to get htis image?
Are there any other acoustic windows in this image?
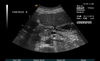
fluid in the stomach
lt lobe of the liver
What is the arrow pointing to in this long image of the pancreas?

distal common bile duct
What is the name of the material that leaves the stomach after digestion?
chyme, it has a low pH
What is the relationship b/t pH and acids and bases?
To increase pH is to go from a low number to a higher number, and acid to a base. To decrease the acidity you would need to increase the pH.

What is the Td orientaiton in this imagE?

Longitudinal
What type of anstomoses are common with pancreas transplant?
End to Side for artery and vein
•
Donor Celiac Axis anastomosed to Recipient iliac artery
Donor PV anastomosed to Recipient iliac vein
Donor Duodenum anastomosed to Bladder or middle of the small bowel (Jejunum)

where do endocrine hormones go?
into the bloodstream
where do exocrine enzymes go?
into the bladder or jejunum of the sm bowel.
Where is the uncinate process in relation to the PV confluence?
posterior
Why is a long image of the pancreatic head important?

it makes the sonographer look @ the inferior border of the pancreatic head. 60-70% of pancreatic cancer occurs in the head.
xenograft
different species cadaver donor


