Radiology Flashcards
Turn me over!









Point to them!




























whatis the abnormality?


What is the pathology here?

Both SBO and LBO
Name this pathology

Calcified Gall stone
What can you see here? What is the likely cause?

Cholecystectomy clips - and air in the Biliary tree. The most likely cause is recent laprop surgery.
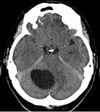
what does this image show?

Dilated Colon - Sigmoid Volvulus
This occurs in cases of long-standing chronic constipation where patients develop a large, elongated, relatively atonic colon, particularly in the sigmoid segment. It is often referred to as acquired or idiopathic megacolon. In sigmoid volvulus, a large sigmoid loop full of faeces and distended with gas twists on its mesenteric pedicle to create a closed-loop obstruction. If uncorrected, venous infarction leads to perforation and faecal peritonitis.