Placenta previa & abruption Flashcards
(30 cards)
What is the definition of placenta previa
When the placenta implants in the lower uterine segment

What are the clinical features of placenta previa
Painless vaginal bleeding
Malpresentation of fetus
Soft & non-tender uterus
Tachycardia
Hypotension
What type of vaginal bleeding occurs in placenta previa
Painless
What is the main management strategy for placenta previa
C-section
What is the 1st line investigation for placenta previa
USS
What are the investigations for placenta previa
USS
MRI
What is a potential complication of placenta previa
Post-partum haemorrhage
What are the risk factors for placenta previa
High parity
Multiple pregnancies
Smoking
Previous C-section
How is placenta previa graded
By how much of the internal cervical os is covered
Graded from 1 -> 4
What are the 4 grades of placenta previa
Grade 1 -> ICO is not covered but placenta is low-lying
Grade 2 -> ICO is marginally covered
Grade 3 -> ICO is partially covered
Grade 4 -> ICO is completely covered
ICO= internal cervical os
What must you do prior to a C-section for placenta previa
USS
(don’t wanna do an Adam Kay bro)
What are the treatments for placenta previa
C-section
Tranexamic acid
Prostaglandin pessaries
IV oxytocin
What is the definition of placenta abruption
The seperation of the placenta from the inner uterine wall before birth, resulting in a revealed or concealed haemorrhage
What are the 3 different types of placenta abruption
Revealed
Concealed
Mixed

What is the difference between a revelaed and concelead placenta abruption
Revealed
When the haemorrhage casued by the placenta abruption escapes through the cervical os, so the haemorrhage is apparent externally
Concealed
The heamorrhage occurs between the placenta and the uterine wall
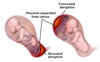
What are some of the signs of a concealed placenta aburption that are usually not be present in a revealed abruption
Increased fundal height
Increased uterine volume
In concealed placenta aburptions, blood can sometimes penetrate the uterine wall and cause some bruising to the uterus
What is this called?
Coucelaire uterus
(cou-ve-laire)

What can sometimes form in the uterus after a placenta abruption
A retroplacental clot
What is the classic signs of placetna aburption
Heavy vaginal bleeding that is late in pregnacny
What are the clinical features of placetna abrutpion
Heavy vaginal bleeding late in pregnancy
Abdominla pain
Uterine contractions & tenderness
Lower back pain
What investigation should you always do for a placenta abruption and what would you expect to see on it
USS
Would see a haematoma
What are the risk factors for placenta abruption
Old maternal age
Multiple pregnancies
Smoking
Pre-eclampsia
Past history
Cocaine
Why is cocaine a risk factor for placenta abruption
As it is a vaso-constrictor
What is placenta abruption associated with
Placenta previa
Pre-term labour
Chorioamnioinitis (inflammation of the chorion)


