PHYS 2 The Menstrual Cycle Flashcards
Major differences between male and female repro systems?
long lol

stages in ovarian cycle and endometrial cycle corresponding to hormone levels

puberty marks the transition to?
puberty in girls involves? (3)
what are each?
____arche

gonadotropin levels throughout the life of a female

menstrual cycle comprises parallel ____ and ____ cycles?
O- what phases?
E- what phases?

oocyte maturation:
production of a ____ female gamete capable of ______ by a ______
begins in?
follicles mature in ____ from _____ to _____ follicles

primordial follicle to secondary follicle?

development of what marks what dependency?

growing antral follicles
early antral are dependent on what for growth? large antral follicles?

other cells (around antral follicles)
become?
remain in?

dominant follicle
at the end of monthly cycle what happens? this is dependent on? # can be as high as? with older age?
at end of selection? when does this occur?
what makes rapidly growing follicles undergo atresia until one is left?
so which follicle is chosen?

dominant follicle during periovulatory period
when is this period? how long does it last?
at same time same time as ovulation change in what functio of what two cells? AKA
this culminates in the formation of? whihc is capable of producing?
LH surge induces what structural changes in dominant follicle?

dominant follicle periovulatory period
before ovulation follicle presses against? forming?
LH surge induces release of? from where? this causes?
at end what becomes continuous with what?

dominant follicle during periovulatory period
what cells detach from what cells? this fees what? within?
in resposnse to LH paracrine factors oocyte releases? (2)
this does what?

dominant follicle periovulatory period
basal lamina of _____ cells is what? blood vessels and ______ can push into ______ cells?
granulosa cells produce _______ to increase ______ to new corpus luteum. ex of angiogenic factors?

this is programmed to live for how long? unless?
this is detected in what tests?
if rescued corpus luteum of pregnancy will remain for how long?


what is this?
predominant process in?
can occur when?
during this what cells undergo apoptosis?
what persists? this does what? by retaining what?


fate of the ovarian reserve in women
number of follicles at different stages?
what else can happen?

summary of folliculogenesis
steps?
(3)

ovarian cycle
first phase: ______
what is released and stims what?
begins with onset of? and end of day of?
what stims endometrium to undergo rapid and continuous growth?
coincides with what phase? rapid rise in ovarian ______ triggers surge of wich causes?

ovarian cycle
second phase:________
follicle transforms into?
what cells produce what (2) wihc stimulate what?
begins on day of? and ends at?
coincides with what phase?

hypothalamic neurons?
this binds to receptors where? resulting in synthesis/release of? thest stim what to sythesize/secrete what? ovaries can also produce?
ovarian steroids and peptides exert _______ feedback on what?


cellular events that result in synth and secretion of gonadotropins
GnRH binds to? which undergos what pathway? this stimulates which PK? this stims transcription through? whats synthesized? then up to release?

GnRH is released in what manner?
early in follicular phase gonadotrophs are?
later in follicular phase?
what allows this to happen?

FSH and LH stim ovarian cells to secrete?
before ovulation LH and FSH act on? which cell has which receptors? what production needs both?
after ovulation what acts to do what?

ovaries also produce what? not estrogen and progesterone.
I- produced by what cells? what specifically stims these cells to release it? what also stims release? when? action of I?
A- produced where? action?

feedback of axis: ovarian steroids
type of feedback?
negative
net effect?
concentrations for feedback to happen?
both types of feedback

feedback on axis: ovarian steroids
positive
when does this happen?
levels of what cause this? what changes to switch from negative to positive?
how long to reach these levels? this promotes what event?

feedback of axis: inhibins and activins
+/-? what specific actions?
intraovarian action

cyclic hormonal changes during menstrual cycle
what 3 positive feedback induces LH surge?
as what begins LH and FSH do what?
this is caused by?
as these levels fall what happens?

cyclic hormonal changes during menstrual cycle
during luteal phase what is rising/falling?
during late luteal?

cyclical changes (hormonal) menstrual cycle
after onset of mentruation the HP axis goes to?

estrogens and progestins
estrogen is derived from what structures? (3)
in women primarily?
Ovarian can synthesize what de novo?
ovaries have what enzyme? this does what?
estrone? mediated by?
liver does what?
more important progestin?

during follicular phase major product of follicle is?
in follicular phase what synthesizes this? whereas in luteal phase?
this hormone requires what cells to be made? (in the two different phases)
what is lacking in each cell making this a need?

during the luteal phase the major products of the corpus luteum are the? although?
what steps only important during luteal phase?

hormones and functional changes of endometrium
endometrial cycle with ovarian cycle?

hormonal reg basal body temp during menstrual cycle
what lowers? when?
what raise? when? day its highest?
if pregnancy does not occur? coincides with?

endometrial cycle
1._______
what is it? estrogen/progesterone levels?
as this happens endometrium? resulting in?
this moment is defined as?

endometrial cycle
2._______
what happens? endometrium? when?
stroma? all this is stimulated by? secreted by?

endometrial cycle
2._______
(continuation)
levels of what rise early in follicular phase? this causes what to endometrium? it also induces synthesis of?
the other female sex hormone has what action here? although? stimulates what?

the endometrial cycle
3.________
what is it? corresponds to what phase?
early: characterized by? stimulated by?
mid/late: what increases? what else happens? hormone promotes what to happen in what cells? this cell does what?

oral contraceptive pill
combinations?
taken how long out of cycle?

OCP
effectiveness due to?
(2)
- net effect is suppressed secretion of? this causes what? contraceptive hormone doses aren’t high enough for what to happen?
- this inhibits how?

disorders of menstruation
relatively common/uncommon?
include?
(4)
what are each?

endometriosis?
affects what age group?
what is it?
each month? this causes?
clin presentation?

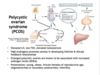
PCOS
most common cause of?
manifest during?
characterized by abnormal? clinically manifested by?

PCOS
elevated/low what?
high what causes atresia and disrupt feedback?
enlarged PCO associated with?
presentation?
turner syndrome?
most common cause of?
half of cases result from?
what happens? type of this?
because of ovarian failure many individuals have?

menopause
defined as occuring?
occurs at what average age?
due to reduction in? we have low levels of?
this means what?
can occur due to?

menopause
signs and symptoms?
treatments focus on? examples?



