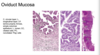
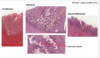
HIST 2 Female Development and the Female Reproductive Tract Flashcards
oogenesis
begins when?
primary oocytes in what arrest at?
remain inactive during?
at puberty what happens?

the menstrual cycle
two coexisting events during menstrual cycle?
O- what happens?
U- what happens?

The ovary
4 main functions?
ovary has two main supporting _______?
(2)

each lined by? type? subjacent to it?
structure can be broken down into?
(2)
outer- is what?
inner- is what?
OSE will form? (2)


Folliculogenesis
ovarian cycle consists of three phases:
- what changes?
2.
3.
disclaimer: stages vary in texts so use what?

follicles
located where?
contain what?
what surround this? does what?
early stages of oogenesis occur when?
oocytes at birth remain at?
puberty?

follicle maturation pictures and corpus luteum formation/degeneration
happen at the same time?

Terms to know (define)
Primary oocyte:
follicular cells:
granulosa cells:
zona pellucida:
Theca: Interna/externa
secondary oocyte:

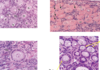

folliculogenesis
1st as a what?
number? size? surrounded by?
these are recruited for?
2nd as a what?
when do they stop being 1 and become 2?basal lamina separates what? what begins to assemble?



what start to proliferate in these? what begins to organize?
into?
TI- adjacent to? produces?
TE- what is it?
what develop among granulosa cells? AKA??
contain? derived from? reach what? how?


what reaches its max size?
what segregates granulosa cells?
3 structures important? locations and function?
Theca:
externa- formed a? continuous with?
interna: well-_______, cell types w/ _______



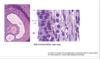
Ovulatory phase
whats a stigma?
what causes rupture?
released gamete:
then does what? still need to do what?
enters?
what will repair OSE damage following follicle rupture?

Luteal phase: ________
after ovulation what happens? becomes part of?
4 steps:
- breakdown of?
- blood vessels? forming?
- ___ cells —> ______ cells
- ____ cells —-> ______ cells


right picture
upper- produce?
lower-secrete? express? essential for?


Luteal phase: ______
if fert occurs: (2) what happens? under what control? this comes from where?
if fert does not occur: what happens? when? regression of? forms?
what replaces what?

what is this?
forms where?
mostly what tissues? with some? over time?
involution of CL does not involve?