PHYS 1 Male reproductive physiology Flashcards


genetic sex? determined by?
5 weeks? 6-7? 9?
gonadal sex?
phenotypic sex?

gonadotropin secretion over lifetime
which is higher when?

puberty initiated by?
these cause what secretion?
GnRH analogue administered intermittently then?
if long acting?

CNS and nutritional status may alter what?
what else?
(2)
the molecule. highest when?

Anatomy of male repro tract
testes- functions? (2)
scrotum- function?
epididymis- function?

anat of male repro tract
vas deferens- functions (2)
seminal visseicles- functions?
prostate gland- functions?

anat of male repro tract
seminiferous tubule- epithelium formed by? with? other cells present? where?
Leydig cells- are where?
adult testis- mainly what structures?

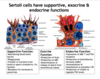
General functions of sertoli/leydig cells
sertoli- (3)
leydig- (1)

testes secrete what male sex hormones?
(3)
most abundant?
some tissues this is converted to?

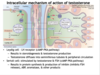
Testosterone (_)
synthesized and secreted by?
testes lack?
which means?
they do have?
which does what? end product is? not? like in?
Testosterone is concentrated where? by?

more on T
active in all tissues?
in some tissues? like in?
what enzyme converts to this?
circulating T bound to?

Leydig cells are main what cells in testis
get cholesterol from?
store it as?
free cholesterol generated by?
cholesterol then transferred to? via?
cholesterol then converted to?

production of estrogen in the male
how much?
where is it high?
source is what cells? (product of?)
potential important role in what process?
large amounts formed from what (2) in other tissues especially?

biosynthetic pathway of androgens
mitochondrial- rate-limiting step? enzyme?
then what?