Peripheral Nerves COPY Flashcards
(242 cards)
Radial nerve origins
C5-8
Pass through upper, middle and lower trunks then posterior cord of brachial plexus
Radial nerve anatomy in upper arm
As it winds around the humerus or proximal to this it innervates the tricpes.
After course in spiral groove it supplies brachioradialis and ECRL and brevis.
Bifurcates into a superifical (sensory) and deep (motor) branches

Muscles supplied by proximal branches of radial nerve
Triceps
Brachioradiailis
ECRL
ECRB
Superficial branch of radial nerve
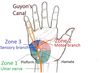
In forearm, passes distally into the hand where it supplies skin of the radial aspect of the dorsum of the hand and dorsum of first four fingers.

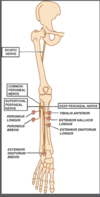
Deep branch of radial nerve
Passes deep through the fibrous arch of supinator (arch of Froshe) to enter the posterior compartment of forearm
Continuous in this compartment as the purely motor posterior interosseous branch
Innervates
Supinator
Extensor digitorum
Extensor digit mini
ECU
Abductor pollicis longus
Extensor pollicis longus
Extensor pollicis brevis
Extensor indicies

Forearm muscles dupplied by posterior interosseous nerve
Supinator
Extensor digitorum
Extensor digiti minimi
ECU
Abductor pollicis longus
Extensor pollicis longus
Extensor pollicis brevis
Extensor indicis
Supinator function
Forearm supinator
Test with resisted supination
Extensor digitorum
Extensor of 2nd to 5th metacraophalangeal joints
Extensor digiti minimi function
Extensor if fifth MCP
ECU function
Ulnar extenor of the wrist
APL function
Abductor of carpometacarpal joint of thumb
EPL function
Extension of thumb interphalangeal joint
EPB function
Extensor of the MCPJ of thumb
Extensor indicies function
Extensor of index finger
Saturday night palsy
AKA radial nerve palsy
Classically associated with a drunkard who falls asleep with arm hyper abducted across a park bench
Site of compression is in the region of the spiral groove
Why is the triceps preserved in radial nerve palsy (Saturday night palsy)
Because branches of the tricpes originate proximal to spiral groove
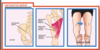
Wrist drop
Inability to extend fingers at MCPJ
Supinator weakness
Triceps spared
Absent sensation first dorsal interosseuous
Radial nerve palsy
Compression in the spira groove of humerus/humeral fracture

Why is weakness of supination only partial in Radial nerve palsy
Because it may be accomplished with either biceps or supinator
Posterior interosseous nerve syndrome
Most common syndrome caused by compression at the arcade of Frohse (fibrous arch at the origin of supinator) which may pathologically constrict nerve
Inability to extend fingers at MCPJ, absence of wrist drop and normal sensation
Supintaor spared as branches are given off proximal to PIN entering the arcade of Frohse
Why is wrist drop absent in PIN palsy
The ECR is presreved
The ECU is innervated by PIN so there may be radial deviation of the hand on extension
Why is there no senosry deficit in PIN syndrome
It is purely motor
Inability to extend fingers at MCPJ
No wrist drop but radial deviation on extension of wrist
Presrved sensation
Preserved supinator and triceps
Posterior interosseus nerve syndrome
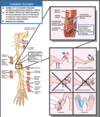

Arcade of Frohse associated with PIN syndrome/supinator syndrome
Roots of median nerve
C6 to T1
Pasing through upper middle and lower trunks and the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus