Cranial nerves Flashcards
(365 cards)
Cranial nerve 0
Nervus terminalis
Function of nervus terminalis
Lies alongside the olfactory bulb.
Serves as a conduit along which a population of neurones migrates from the olfactory placode into the pre-optic area and hypothalamus.
These neurones are essential for reproductive function in both sexes

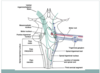
Components of the nuclei for CNs innervating the extraocular muscles.
Contain both motor neurones and internuclear neurones, with axons that contact the motor neurons for muscles that move the opposite eye in the same direction.
Location of oculomotor nucleus
Periaquedctal grey matter of the midbrain, ventral to the aqueduct at the level of the superior colliculus.

Passage of oculomotor nerve fibres within the midbrain.
Myelinated axons from each nucleus curve ventrally through the tegmentum and emerge from the medial side of the cerebral peduncle in the interpeduncular fossa.

Passage of oculomotor fibres after leaving the midbrain
Pass in the subarachnoid space, the lateral wall of cavernous sinus and the SOF.
What happens to the oculomotor nerve in the orbit?
Superior divison:
SR, LPS
Inferior division:
MR, IR, IO, Ciliary ganglion via short ciliary nerves

Arrangement of motor units in the oculomotor nucleus
The motor neurones for individual muscles are localised in distinct subnuclei.
The small sizes of the motor units (6 muscle fibres supplied by one neurone) indicate the level of precision required for co-ordinated eye movement in binocular vision
Location of the EW nucleus?
Situated dorsal to the main oculomotor nucleus.
Function of the EW nucleus
Preganglionic parasympathetic
Passage of EW neurones
Accompany the other oculomotor neurones into the orbit where they terminate in the ciliary ganglion behind the eye.
How do post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres of the EW reach their targets
Pass through the short ciliary nerves to the eyeball where they supply the sphincter pupllae muscle of the iris and ciliary muscle
Through which structure do oculomotor and EW fibres run in the tegmentum of the midbrain?
Pass through the red nucleus.
Location of the trochlear nucleus
Immediately caudal to the oculomotor nucleus at the level of the inferior colliculus.
Passage of the trochlear nerve fibres after leaving their nucleus.
Small bundles of fibres curve around the periaqueductal grey matter with a caudal slope and decussate in the superior medullary velum.

Where do trochlear nerve fibres leave the brainstem?
The only nerve to emerge from the dorsum.
The slender nerve emerges immediately caudal to the inferior colliculus.

Function of SO
Depress, inwardly rotate and abduct the eyeball.
Location of the abducens nerve
Situated beneath the facial colliculus in the pons in the floor of the fourth ventricle.

What is the relationship of the facial nerve to the abducens nucleus?
A bundle of facial nerve fibres known as the internal genu curves over the nucleus, contributing to the facial colliculus.

Passage of motor neurones of the abducens
Gives rise to axons that pass through the pons in a ventrocaudal direction, emerging from the brainstem at the junction of the pons and the pyramid.
Interneurons of the abducens
Axons cross into the contralateral MLF and travel rostrally to the oculomotor subnucleus that supplies the contralateral rectus muscle.

Saccadic eye movements
Quick movements of the eyes in altering direction of gaze
Fr. saccader- to jerk
Optokinetic movements
Frequent saccades, made when the image on the retina is continuously changing.
Vergence movements
Both eyes looking medially to look at a near object or laterally to look into the distance.