Overview and Embryology COPY Flashcards
Efferent neurone columns
3
Somatic
Branchial
Visceral
Arrangement of efferent cell columns from M->L
SBV
Somatic
Branchial
Visceral
Afferent neurone columns
Special visceral
General visceral
Special somatic
General somatic
Arrangement of afferent cell columns from M-> L
VG VS, SG, SS
Visceral General
Visceral special (taste)
Somatic general
Somatic special (hearing, vestibular)
To what do the colours correspond

Blue- sensory
Orange- intermediant visceral (i.e. autonomic)
Red motor
Pure corticospinal tracts in humans
Thought to be exceedingly rare due to close proximity to other corticofugal tracts (corticoreticular, corticopontine, reticulospinal, vestibulospinal).
Thought to result in deficits in delicate fractionate movement and Babinski
Fucntion of ventral rami of spinal nerves
Innervates limbs and anterior skin and muscles of trunk
Function of dorsal rami of spinal nerves
Postvertebral muscles and skin of back
nAChR
Inotropic receptor
mAChR
Metabotropic receptor (GPCR)
Formation of the cerebelleum
Forms from dorsolateral thickenings of metencephalon which overgrow the root of the fourth ventricle (rhombic lips)
These lips fuse in the midline to form the cerebellar vermis.
Peripheral neuroblasts contribute to cerebellar cortex, central-> deep nuclei

Origin of tectal nuclei
Neuroblasts from the alar plates migrate into the tectum to form the superior and inferior colliculi
Origin of central gray matter around aqueduct
Neurobalsts of the alar plates
What are the three major commissures beign to develop in the lamina terminalis
Anterior commissure
Hippocampal commissure
Corpus callosum
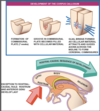
Describe the development of the corpus callosum
7th week
The dorsal aspect of the lamina terminalis thickens into the commissural plate which becomes thickened with cellular material that forms a glial bridge across the groove
Develops in rostral to caudal fashion.
The exception is the rostral most portion of the corpus callosum- rostrum and anterior genu which develop last
What might cause violation of the corpus callosal front to back development
Secondary destructive processes might damage the corpus callosum after it is already formed
How does the presentation of corpus callosum agenesis occur?
Due to front to back development, then developmental arrest will normally result in an intact genu with a partially or completely formed body and small or absent splenium or rostrum.
Small or absent genu but intact splenium and rostrum in corpus callosal agenesis suggests?
Secondary destructive process
What is the corpus callosum abnormality which is an exception to the front to back and secondary destructive lesion
The callosal abnormality associated with holoprosencephaly in which the corpus callosum demonstrates and intact splenium in the absence of a genu or body.

Agenesis of the corpus callosum
Cardinal features of corpus callosum agensis
Hypogensis of the corpus typically produces an intact genu and body with absent splenium and rostrum.
Other patterns suggest secondary destructive process

Associated anomalies, corpus callosum agenesis?
Dandy-Walker
Disorders of neuronal migration, organisation
Encephaloceles
Symptoms of callosal agenesis
Seizures, mental retardation.
Commonly also related to associated brain abnormalities
Aicardi’s syndrome

X-linked disorder
Infantile spasms, callosal agenesis or hypogensis, chorioretinopathy
Abnormal EEG












































































