Path - CNS infectious dz Flashcards
What is the difference between cerebritis and intraparenchymal abscess?
cerebritis is focal inflammation and infection, without capsule
abscess has a capsule
What is the general morphology associated with cerebral abscesses?
capsule is hyperemic (reddish), firm and gray (when mature)
liquefied, tan green, purulent center
What is the general morphology of cerebritis?
involved brain is hyperemic, more poorly defined than with abscess. No capsule
What does the micriscopic view of an abscess and cerebritis have?
- central cavity with necrosis and neutrophils
- collagenous capsule (abscess only)
- exuberant granulation tissue
- surrounding area of gliosis and edema
- macrophages (halo cells)
What makes up the dense fibrotic capsule of a brain abscess? What stain should be used to visualize this?
Reticulin fibers from perivascular fibroblasts
reticulin stain
Where would I find the organisms responsible for an abscess or cerebritis?
within necrotic areas, not capsule or surrouding gliotic brain
What is usually from direct extension from skull bones, middle ear, or air sinuses, but can be from hematogenous spread of bacteria from lung infection?
subdural absecess/empyema
Are epidural abscesses more common in the brain or in the spinal cord?
spinal cord; epidural space does not normal exist in the cranium
Suppurative inflammation from spread of organisms from osteomyelitis or vertebral tuberculosis to the epidural space can lead to…
Epidural space in the spincal column is usually filled with
spinal epidural abscess
fat
inflammatory process of leptomeninges and CSF within the subarachnoid space
meningitis
What will the CBC of someone with acute pyogenic meningitis usually have?
peripheral blood leukocytosis, usually with neutrophilia and left shift
severe inf may cause leukopenia
possible thrombocytopenia
combo leukopenia and thrombocytopenia correlate with a worse prognosis
What labs should you get to work up meningitis?
- CBC
- Coag studies
- chemistry studies
- blood cultures
- LP
What are contraindications for an LP?
no absolute contraindications
use caution if evidence of increased ICP, could cause herniation?
What are CSF findings in acute bacterial meningitis?
- hazy, cloudy, frank pus
- high opening pressure
- increased leukocytes - neutrophils
- increased protein
- decreased glucose
- increased lactate
Why is glucose low in acute bacterial meningitis?
consumed by inflammatory cells, not so much the organisms
What would I find microscopically looking at acute bacterial meningitis? grossly?
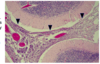
- micro
- acute inflammatory infiltrate (neutrophils) in subarachnoid space
- arrowheads are pointing to inflamed meninges in cerebellum
- gross
- creamy purulent exudate covering teh cerebral hemispheres and settles along the base of teh brain, around the cranial nerves and the openings of the fourth ventricle

What are possible sequelae of meningitis?
cranial nerve deficits
ischemic infarction (invasion of leptomeningeal vessels)
hydrocephalus (after the purulent exudate fibroses and clogs the fourth ventricle)
meningitis with no recognizable organism in culture or gram stain and no pus in CSF is considered … and is usually/…
acute aseptic meningitis
viral
Would you rather have bacterial meningitis or acute aseptic meningitis?
acute aseptic - less fulminant, is self-limiting
Does bacterial or aspetic meningitis have associated mental status changes?
bacterial
What is the MCC of acute aseptic meningitis?
non-polio enteroviruses
What are the morphologic findings of acute aseptic meningitis?
leptomininges/subarachnoid and perivascular spaces by lymphocytes (sparse or uneven distrib)
NO involvement of brain parenchyma
What are typical CSF findings of aseptic meningitis?
- increased WBCs (less than bacterial)
- low number neutrophils and only for 48 hours
- protein moderately increased
- glucose normal
- negative stains and cultures
What is a parenchymal infection of the brain?
viral encephalitis









