Paediatric Upper & Lower GI Disorders - Crohn's, IBD, UC Flashcards
Incidence of Crohn’s Disease in Scottish Children - how is it changing?
increasing

what are the Presenting Features of CD and UC and how do they differ between one another?
In UC, most have diarrhea, rectal bleeding and abdominal pain
Blood diarrohoea more than a couple weeks = think about UC
CD almost always shows up on blood tests whereas UC is a bit more difficult as blood tests often more normal

how is a diagnosis of IBD made?
- History & Examination
- Intestinal symptoms (Not a lot of signs normally)
- Extra-intestinal manifestations
- Exclude infection
- Family History
- Growth and sexual development (particularly for CD)
- Nutritional status (take weight and height and plot on growth chart, not single one off measurement but longitudinal measurement)
what is shown here?

ERYTHEMA NODOSUM:
See it commonly
More so in CD
what can happen to the mouth in IBD?
Oral changes:
ulcers
rounded edge

what Laboratory investigations can be done to make a diagnosis?
Full blood count & ESR (Do blood tests, particularly point you to CD):
- Anaemia
- Thrombocytosis
- Raised ESR
Biochemistry:
- Stool calprotectin (the key these days)
- Raised CRP
- Low Albumin (particularly in CD, tends to be due to leaking protein in gut and passing it out in stool, tends to be that more so than a nutritional problem)
Microbiology:
•No stool pathogens
Differences between adult and paediatric IBD rates
Children’s tend to be more severe and more extensive
IBDU - know they have IBD but cant say which one it is

Differences to adult UC:
how common in Proctitis in adults and children?

Paediatric:
4% < 5 years
17% 5 – 17 years
Adult = 40%
Proctitis most typical in adults
Differences to adult UC:
how common in L sided colitis adults and children?
Paediatric = 14%
Adult = 40%
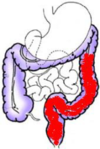
Differences to adult UC:
how common in Pancolitis adults and children?
Paediatric = >60%
Adult = 20%
In paeds closer to 80%
Much more severe and extensive phenotype
In children use more biologics
Differences to adult Crohn’s Disease
how common in isolated ilial in adults and children?
Paediatric = 6%
Adults = 36%
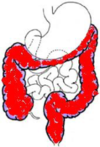
Differences to adult Crohn’s Disease
how common in Ileocolonic in adults and children?
Paediatric = 45%
Adults = 50%

Differences to adult Crohn’s Disease
how common in Upper GI/panenteric in adults and children?
Paediatric = 51%
Adults = ?%
far less frequent in adults

what are some definitive investigaitons that could be done for IBD?
Radiology (especially Crohn’s disease):
- MRI
- Barium meal and follow-through (younger kids)
Endoscopy:
- Colonoscopy & Upper GI endoscopy
- Mucosal biopsy
- Capsule enteroscopy
- Enteroscopy
we struggle to get a look into the small bowel

what is shown here?
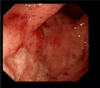
Ulcerative colitis
Colonoscopy
Severe bloody stools
Abdomen pain
Sloopy muco pus, contact bleeding, white dots are crypt abscesses (on histology crypt is full of puss)
what is shown here?

Crohn’s disease
Typical ulcers (looks like slime of snail)
what is shown here?

Could be either ……
These are the ones we put in the IBDU category
histopatholigy - Pathology very helpful
what is shown here?

2 left you can see granuloma and you know you have CD – don’t see in all children with CD
Right is UC – disordered crypts, pus in crypts, great increase in inflammatory cells
what are the Aims of Treatment?
- Induce and maintain remission
- Correct nutritional deficiencies
- Maintain normal growth and development:
Growth is what makes management harder in children than adults
Inflammation and steroid use will affect growth and slow it
Try avoid steroids and get disease under control
Kids have more extensive and severe disease
what are the methods of treatment?
- Medical - Anti-inflammatory, Immuno-suppressive, Biologicals ( Infliximab)
- Nutritional (Nutritional therapy particularly for CD) - Immune modulation, Nutritional supplementation
- Surgical
Sometimes have to use surgery, use it for UC if we cant bring it under control, we do colectomies, pouch surgery
In CD its never curative so do as limited surgery as we can
what is “Bottom-up” treatment for Crohn’s disease?
Start with gentle treatment
2nd step is things like immunomodulation that stops the inflammation coming back again
You can do surgery before biologics sometimes



