Neuro Flashcards
MDx? EDx? What will you see histologically?

MDx: focal extensive meningitis
EDx: bacterial meningitis
Histologically will see lots of degenerative neutrophils
This is craniosynostosis (failure of bones to fuse). What will this condition cause? What effect does it have on the brain?

Congenital hydrocephalus
Will cause thinning of cerebral coritcal tissue
[acquired hydrocephalus after bones fuse]

MDx? Etiology? Pathogenesis?

MDx: arthrogryposis
Etiology: BVD, Schmallenberg virus (in utero infection)
Pathogenesis: tendons contract due to calf not moving in uterus
[picture: chondrodysplasia (shortening of limbs) with arthrogryposis]

This cerebrum has collapsed. What things could make this happen? If this was a calf what would be in your DDx?
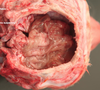
Element of hydrocephalus
Improper development on the cerebrum
Infection
In calves - BDV
MDx? Why? Which species is this most common in?

MDx: meningioma
This is shelled out, if it was not shelled out would think astrocytoma or oligodendroma
Most common in cats
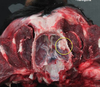
Whats wrong with this cerebrum?

Focal area of discoloration that is causing asymmetry of the cerebrum.
This is a cerebral abcess caused by a tooth puncture in a cat fight
[cryptococcus also causes brain abscesses but will be more protruded]

MDx? Is this a functional neoplasia?

MDx: pituitary carcinoma
Non functional -tumor is invasive and destroying functioning tissue
This is a spinal cord from a horse that is experiencing dysphagia (can’t swallow [lol]). What is your number 1 DDx?

Grass sickness
This is a dysautonomia –> ganglia degeneration (chromatolysis)
This is a spinal abcess. What kind of degeneration does this cause? What condition would suspect in dogs and horses? Calves?

Wallarian degeneration
Dogs and horses: Wobbler’s
Calves: salmonella
Spinal cord of a horse
MDx? Etiology?
MDx: cauda equina neuritis
Etiology: EHV-1



