Microbiology (All Topics) Flashcards
Respiratory infections:
Outline the main features of Pneumonia and Bronchitis
Pneumonia:
- Mortality is 5 to 10%
- 20 to 40% are hospitalised
- 30 to 50% are Commuinity Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)

Respiratory infections:
Outline the symptoms and microscopitc findings of:
- S.Pneumonia
- H.Influenza
- M.Catarrhalis
- S.Auerus
- K.Pneumonia

Respiratory infections:
Outline the symptoms and features of:
- Legionella pneumophilia
- Mycoplasma pneumonia
- Chlamydia pneumonia
- Chlymydia psittaci
- Bordatella pertussis
- TB
- Coxiella Burnetti
Coxiella Burnetti:
- Domestic/farm animals
- Aerosol
- Diagnose with serology
- Treat with macrolides
Macrolide > Clarithromycin
Tetracycline > Doxycyline

Respiratory infections:
Outline the resipiratory tract infections associated with:
- HIV
- Neutropenia
- Bone Marrow transplant
- Splenectomy
- Cystic fibrosis

Respiratory infections:
Outline the daignosis of respiratory tract infections

Respiratory infections:
Outline the Antibiotics used for Community (Classical and Atypical) and Hospital Aquired Pneumonia

Respiratory infections:
What is the simplistic antibiotic framework for respiratory tract infections?
To simplify:
Just Gram positive:
- Amoxicillin
- Flucloxacillin
- Vancomycin
Mostly Gram positive, little gram negative:
- Coamoxiclav
- Cefuroxime
Clearly both:
- Cafotaxime
- Meropenem or Piperacillin & Tazobactam
Mostly Gram negative, little gram positive:
- Ciprofloxacin
Just Gram negative:
- Cefazidime
- Gentamicin
Atypical Pneumonia:
- Clarithromycin/doxycyline

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What is the definition of Pyrexia of Unknown Origin?

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
- What is the approach to Neutropenic fever?
- What are the other key points to consider in PUO?

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What are the main causes of fever in the returning traveller?

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What are the Severity & Liver stage, Length of Rhythm, Blood film and treatment of P.Malaria

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What are the symptoms, investigations and management options for Typhoid?
Antibiotics:
- Cotrimidazole, Chloramphenicol or ampicillin
- (Multi-drug resistance) >> 3rd gen cephalosporin or azithromycin

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What are the Severity & Liver stage, Length of Rhythm, Blood film and treatment of P.Vivax

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What insect carries malara?

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What are the Severity & Liver stage, Length of Rhythm, Blood film and treatment of P.Ovale
P.Malaria

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What are the Severity & Liver stage, Length of Rhythm, Blood film and treatment of P.Falciparum

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What are the major features of sever or complicated Malaria?
IS PHARAOS:
- I: Impaired concoiusness/Seizures
- S: Shock
- P: Pulmonary oedema or ARDS
- H: Hypoglycaemia (<2.2mmol)/Haemoglobinueria
- A: Anaemia (Hb <8)
- R: Renal imapairement
- A: Acidosis (ph <7.3)
- O: Other indications
- S: Spontaneous bleeding/DIC

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What are the investigations for P.Falciparum?

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What is the treatment for P.Falciparum?

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What are the common signs of P.Falciparum?

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What are the symptoms of P.Falciparum?
Uncommon signs:
DDACC
- Diarrhoea
- Dark Urine
- Abdrominal pain
- Confusion
- Cough

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What is the definition of Classical PUO and give some examples
PUO Definition:
>38.3⁰C fever on several occasions persisting >3/52 without diagnosis despite >1/52 of intensive Ix

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What is the definition of Healthcare associated PUO and give some examples

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What is the definition of Neutropenic PUO and give some examples

PUO & Fever in the returning traveller
What is the definition of HIV Associated PUO and give some examples

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are the subtypes of the Microorganisms that causes Gastrointestinal Infections?
-
Anaerobic:
- Clostridia
- Botulinum
- Perefringes
- Difficile
- Clostridia
-
Aerobic:
- Bacillus Cerus
- Staph.Aureus
-
Lactose Fermenters:
- Gram negative Enterobacteriacae
- E.Coli
- ETEC
- EIEC
- EHEC
HUS
EPEC
-
Non-lactose Fermenters:
-
Salmonella
- Typhi
- Paratyphi
- H2S Producers
- Yersinia enterocoli
-
Salmonella
-
Miscellaneous:
- Vibrosis
- Cholera
- Parahaemolyticus
- Vulnificus
- Campylobacter jejuni
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Vibrosis
-
Protozoa:
- Entamoeba Histolytica
Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Clostridia Botulinum Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Clostridia Perfringes Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Clostridia Difficile Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Bacillus cereus Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Staph. Auerus Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of E.Coli Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Salmonella Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Enteritides Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Shigella Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Yersinia enterocoli Gastrointestinal Infections?
“CEMENTR”
- Cold enrichment: prefers 4 Degrees C
- Enterocolitis
- Mesenteric adenitis
- Erythema Nodosum
- Nectotising gramulomas
- Transmitted via animal comtaminated food
- Reactive arthritis

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Cholera Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Parahaemolticus and Vulinficus Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Campylobacter jejuni Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Lysteria Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Entamoeba Histolytica Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Giardia lamblia Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
. What are clinical symptoms and treatment of Cryptosporidium Parvum Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are clinical symptoms of Mycobacteria Gastrointestinal Infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What are the clinical features of Viral Gastrointestinal Infections?
“RAPHEN”
- Rotavirus
- Adeovirus
- Polio
- Hep A
- Eenterovirus
- Norovius

Gastrointestinal Infections
What is the board classification of Gastroenteritis?

Hospital acquired infections:
What is the definition of a hospital acquired infection?

Hospital acquired infections:
What is the transmission route range of symptoms/risk factors pathology and management of Clostridium Difficile?

Hospital acquired infections:
What is the resistance profile of E.Coli?
What are the main risk factors and causative organisms of UTI?

Hospital acquired infections:
What are the causative organisms of Bacteraemia?
What are the causative organisms of Surgical site infections?

Neonatal and Childhood infections:
What are the key congenital infections, their investigations and management?

Neonatal and Childhood infections:
What are the risk factors, symptoms, investigations and management of early onset sepsis in neonatal infections?

Neonatal and Childhood infections:
What are the risk factors, symptoms, investigations and management of late onset neonatal infections?

Neonatal and Childhood infections:
What are the key organisms in Childhood infections, Paediatric Bacterial Meningitis, Respiratory tract infections and UTIs?

CNS Infection and Meningitis:
What is the subclassifications of meningitis and the causative organisms?

CNS Infection and Meningitis:
What is the aetiology, presentation, diagnosis and management of bacterial meningitis?

Viral Hepatitis:
What are the principles of CSF interpretation?

Viral Hepatitis:
What is the transmission, diagnosis and management of:
- Hep A
- Hep B
- Hep C
What is the transmission route of Hepatitis D and E?
Hepatitis D: RNA Virus that can only infect Hepatitis B patients
Hepatitis E: RNA Virus, transmitted by feacooral route. Common in india.

Viral Infections in Pregnancy:
What is the aetiology, presentation, diagnosis and management of Parovirus B19 in Pregnancy?

Viral Infections in Pregnancy:
What is the aetiology, presentation, diagnosis and management of Rubella in Pregnancy?

Viral Infections in Pregnancy:
What is the aetiology, presentation, diagnosis and management of Influenza and Measles in Pregnancy?

Vaccines:
What are the types of vaccine available?

Pandemic Flu:
What is/are:
- Antigenic drift
- Antigenic shift
- Pathogenesis
- Causes of severe outcomes of flu
- Antivirals for Influenza

Infective Endocarditis:
What is the history of Infective Endocarditis?

Infective Endocarditis:
What are the examination findings for Infective Endocarditis?

Infective Endocarditis:
What are the Investigations for Infective Endocarditis?

Infective Endocarditis:
What is the Dukes Criteria for Infective Endocarditis?

Infective Endocarditis:
What are the Infective Agents in Infective Endocarditis?

Infective Endocarditis:
What is the treatment for Infective Endocarditis?

Infective Endocarditis:
What are the indications for surgery in Infective Endocarditis?

Infective Endocarditis:
What precautions need to be taken in a patients suspected of Infective Endocarditis?

Wound, Bone and Joint Infections:
Describe the aetiology, organisms, presentations and management of Surgical site infections

Wound, Bone and Joint Infections:
Describe the aetiology, organisms, presentations and management of Septic Arthritis

Wound, Bone and Joint Infections:
Describe the aetiology, organisms, presentations and management of Osteomyelitis

Wound, Bone and Joint Infections:
Describe the aetiology, organisms, presentations and management of Prosthetic Joint Infection

Urinary Tract Infection:
What are the common organisms, presentations and management of Urinary Tract Infections?

Fungal Infections
Who are particularly vulnerable to fingal infections?
Why can they be difficult to diagnose?
What is the classification of fungal infections?

Antifungals
What are the targets and indications of:
- Polyene
- Azole
- Terbinafine
- Flucytosine
- Echinocandin

Fungal Infections
What are the key superficial fungal infections and how are they diagnosed?

Herpes Infections
What are the symptoms of the following:
- Asymptomatic CMV
- Congenital CMV
Congential: LIMITED JHCC:
- Late progressive sensorineural deafness
- IUGR
- Microcephaly
- Impaired IQ
- Thrombocytopenia
- Encephalitis
- Death
- Jaundice
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Chorioretinitis
- Cytomegalic inclusion disease (13%)

Herpes Infections
What is/are the aetiology, investigations and treatment of Cytomegalovirus?
Investigtions: STICHH
-
Serology
- Immunocompromised: limited diagnostic value
- Immunocompitent: CMV IgM & IgG (IgG low avidity in first infection)
- Tissue
- Immunoflourescence
- Cell culture
- Histopathology
-
Heterphile Antibodies
- Paul Bunnel monospot: clumping of sheep RBCs

Herpes Infections
What are the symptoms investigations and management of Roseola infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the features of oral HSV1/HSV 2 infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the symptoms of Encephalitis from HSV1/HSV2 infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the symptoms of skin infections from HSV1/HSV2 infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the symptoms of Varicella Zoster infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the symptoms, investigations and management of Shingles infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the features of:
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Burkitt’s lymphoma
Alongside Nasopharyngeal Ca and Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease, these are the possible causes of EBV.

Herpes Infections
What are the features of HHV8 infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the features of Neonatal HSV1/HSV2 infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the symptoms of the following:
- CMV Mononucelosis
- Immunocompromised CMV
Immunocompromised CMV: “GRAPH/GRAF B”
- GI: colitis
- Retinitis (Retinitis=AIDS)/Radiculopathy
- Addisons disease
- Pneumonitis (in BMT patients)
- Hepatitis
- Fever
- Bone Marrow supression

Herpes Infections
What are the features of ocular HSV1/HSV 2 infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the features of genital HSV1/HSV 2 infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the investigations of skin infections from HSV1/HSV2 infections?
ELISA= HSV-2 IgG enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay

Herpes Infections:
What is the management of skin infections from HSV1/HSV2 infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the investigations for Varicella Zoster infections?

Herpes Infections
What is the management of Varicella Zoster infections?
Pregnancy:
- Can give Aciclovir within 24hrs of exposure
- IVIG VZV can be give up to 10 days post exposure

Herpes Infections
What are features of Varicella Zoster infections in pregnancy?

Herpes Infections
What is Mollarets Meningitis?

Herpes Infections
What are the CT/MRI findings in Encephalitis from HSV1/HSV2 infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the CSF findings in Encephalitis from HSV1/HSV2 infections?

Herpes Infections
What is the management of Encephalitis from HSV1/HSV2 infections?

Herpes Infections:
What are the features of:
- Nasopharyngeal Ca
- Post transplant lymphoproliferative disease
Alongside Infectious mononucleosis and Burkitt’s lymphoma, possible causes of EBV

Fungal Infections
What are the symptoms, investigations and management of Candida infections?

Fungal Infections
What are the symptoms, investigations and management of Crypotococcus infections?

Fungal Infections
What are the symptoms, investigations and management of Aspergillus infections?

Herpes Infections
What are the classifications of Herpes infections?
Herpes Infection Classifications:
-
Epitheliotropic
- CMV
- Infected cells swell (hence megavirus)
- Roseola virus
- CMV
-
Neurotropic
- HSV1 & HSV2: dsDNA. No animal reservoir. Persistent latent phase in DRG. Lytic infection of fibroblasts + epithelial cells. Transmitted via muco-cutaneous contact
-
VZV:dsDNA. Droplet spread. Viral replication in LNs, then in liver + spleen then vesicular rash (rash ~48hrs after infection). 14/7
- Shingles
- Chickenpox
-
Lymphocytic
- EBV
- HHV8
Fungal Infections
What are the key deep fungal infections and how are they diagnosed?
Diagnosed: clinical details, lab results and imaging
Main types:
- Candida
- Aspergillus
- Cryptococcus
Gastrointestinal Infections
What is/are the incubation period, duration and comments of E.Coli infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What is/are the incubation period, duration and comments of Shigella infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What is/are the incubation period, duration and comments of Salmonella (nontypoidal) infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What is/are the incubation period, duration and comments of Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What is/are the incubation period, duration and comments of Bacillus Cereus infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What is/are the incubation period, duration and comments of Staph Aureus infections?

Gastrointestinal Infections
What is/are the incubation period, duration and comments of Vibrio Cholera infections?

Antimicrobial Agents:
Outline the main targets of Antimicrobial Agents and their Classes

Antimicrobial Agents:
What are the main narrow and broad spectrum antibiotics?

Antimicrobial Agents:
What are the four mechanisms of action of antibiotic resistance?

Antimicrobial Agents:
What are the typical Infective Organisms and Antibiotics for the following infections:
- Skin
- Pharyngitis
- Community acquired pneumonia
- Hospital acquired pneumonia
- UTI
- Spesis
- Colitis

Reference Table of Common Bugs:
What is the reference table for common bugs?

Antimicrobial Agents
Outline the process of Bacterial wall synthesis

Antimicrobial Agents
Outline the mechanism of action of RNA synthesis inhibitors

Anitmicrobial Agents:
Outline the mechanism of action of Nitrofurantoin

Anitmicrobial Agents:
Outline the mechanism of action of Glycopeptides

Anitmicrobial Agents:
Outline the mechanism of action of Beta Lactams

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Beta Lactams?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Glycopeptides?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Aminoglycosides?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Tetracyclines?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Macrolides?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Chloramphenicol?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Oxazolidinone?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Fluoroquinolones?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Nitroimidazoles?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Rifamycin?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Polymyxin?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Cyclic lipopeptide?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Sulfonamides?

Antimicrobial Agents
What is/are an example and the indication for Diaminopyrimidines?

Prion disease:
What is the definition of Prion Disease?

Prion disease:
What is the Prion Disease, Aetiology and Course of Sporadic CJD?
1

Prion disease:
What is the Prion Disease, Aetiology and Course of Acquired Variant CJD?

Prion disease:
What is the Prion Disease, Aetiology and Course of Acquired Iatrogenic CJD?

Prion disease:
What is the Prion Disease, Aetiology and Course of Inherited Prion Disease?

Zoonoses
What is the who definition of Zoonoses?

Zoonoses
What is are the symptoms, investigations and management of Rabies?

Zoonoses
What is the aetiology of Bubonic and Pneumonic Plague?
What are the investigations and treatment?

Zoonoses
What are the transmission routes, symptoms and management of Leptospirosis?

Zoonoses
What are the symptoms of Anthrax?

Zoonoses
What are the symptoms of Q fever?

Zoonoses
What are the symptoms of Q fever?

Zoonoses
What are the transmission routes and symptoms of Cutaneous Leishmania?

Zoonoses
What are the transmission routes and symptoms of Diffuse cutaneous Leishmania?

Zoonoses
What are the transmission routes and symptoms of Muco-cutaneous Leishmania?

Zoonoses
What are the transmission routes and symptoms of Visceral Leishmania?

Zoonoses
What are the diseases caused by Rats?

Zoonoses
What are the diseases caused by Cats?

Zoonoses
What are the diseases caused by Dogs?

Zoonoses
What are the diseases caused by Small Ruminants?

Zoonoses
What are the diseases caused by Cattle?

Zoonoses
What are the diseases caused by Swine?

Zoonoses
What are the diseases caused by Birds?

Zoonoses
What are the diseases are Water Sports associated?

Zoonoses
What are the diseases that are Water borne?

Zoonoses
What are the diseases that are Food associated?

Zoonoses
What is the microbiology and transmission of Brucellosis?

Zoonoses
What are the symptoms and complications of Brucellosis?

Zoonoses
What are the investigations for Brucellosis?

Zoonoses
What is the treatment of Brucellosis?

Zoonoses
What is/are the aetiology and symptoms of Lyme Disease?

Zoonoses
What is/are the investigations and management of Lyme Disease?

Prion Disease
What is the aetiology/definition of Prion disease?

Prion Disease
What is/are the genetics and differentials of Prion Disease?

Prion Disease
What is normal PrP structure and how is it affected in Prion disease?

Prion Disease
What is CJD treatment?

Prion Disease
What are the following findings in Sporadic CJD?:
- EEG
- MRI
- CSF
- PNRP
- Genetics
- Western Blot
- Post Mortem

Prion Disease
What are the following findings in Variant CJD?:
- EEG
- MRI
- CSF
- PNRP
- Genetics
- Western Blot
- Post Mortem

Prion Disease
What are the following findings in Iatrogenic CJD?:
- EEG
- MRI
- CSF
- PNRP
- Genetics
- Western Blot
- Post Mortem

Prion Disease
What are the following findings in Inherited Prion Disease?:
- EEG
- MRI
- CSF
- PNRP
- Genetics
- Western Blot
- Post Mortem

Zoonoses
What are the diseases caused by Mice?
“BELL H”
- Bartonella
- Ehrlichina
- Lyme borreliosis
- Lymphocytic choriomenigitis
- Hatan vurus (fleas)

Prion disease:
What is the Prion Disease, Aetiology and Course of Acquired Kuru CJD?
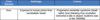
Pandemic Flu:
What is the causative virus of flu?
What are the 3 anti genetically different flus?

Pandemic Flu:
What is a natural reservoir of Influenza A?
What is H5N1?
What are the ideal situations for flu to grow?

Pandemic Flu:
What are the RNA segments?
What is the effect of neuraminidase?
What is the effect of haemogglutimin?

Pandemic Flu:
What is Antigenic drift?

Antivirals:
What is the mechanism of action of for:
- Acyclovir
- Ganciclovir
What are the symptoms of CMV?

Antivirals:
What is used if there is resistance to Ganciclovir?

Antivirals:
What is the machoism of action of Cidofovir?
What is the effect of Foscarnet & Cidofovir?

Antivirals:
What is the treatment of Herpes Simplex Infection (HSV)?

Antivirals:
What is the treatment for CMV in BMT?

Antivirals:
What is the treatment for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) based on?

Antivirals:
What is is the treatment for Respiratory Viruses?

Opportunistic Viral Infections:
Who is affected by opportunistic viral infections?
What are the types of immunodeficiencies?

Opportunistic Viral Infections:
What are the stages of PCR?

Opportunistic Viral Infections:
What are the 3 origins of opportunistic viral infections?

Opportunistic Viral Infections:
What are the most important characteristics of VZV?

Pandemic Flu:
What is Antigenic shift?
HA = Haemagglutinin
NA = Viral Neuraminidase

Pandemic Flu:
What is the pathogenesis of Influenza?

Pandemic Flu:
What is are the causes of sever outcomes in Flu?

Pandemic Flu:
What are the antivirals used in Flu?

Antivirals:
What are the goals in Hepatitis B treatment?

Antivirals:
What are the drugs given in Hepatitis B treatment?
Nuceloside Analogues: “LEATT”
- Lamivudine
- Entecavir
- Adefovir dipivoxil
- Telbivudine
- Tenofovir (Inhibitor of reverse transcriptase, the rest are inhibitors of viral polymerase)
Preferred 1st line: “PET”
- PegINF alpha 2a
- Entecavir
- Tenofovir

Antivirals:
What are the treatment goals in Hepatitis C treatment?

Antivirals:
What are the drugs given in Hepatitis C treatment?

Antivirals:
What are the genotypes affecting outcomes in Hepatitis C treatment?

Opportunistic Viral Infections:
What are the most important characteristics of VZV?

Opportunistic Viral Infections:
What are the most important characteristics of CMV?

Opportunistic Viral Infections:
What are the most important characteristics of EBV?

Opportunistic Viral Infections:
What are the most important characteristics of HHV8?

Opportunistic Viral Infections:
What are the most important characteristics of HHV6?

Opportunistic Viral Infections:
What are the most important characteristics of Adenovirus?

Opportunistic Viral Infections:
What are the most important characteristics of Measles?

Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the microbiology Mycobacteria
Microbiology of Mycobacteria:
- Gram positive
- Aerobic
- Acid alcohol fast
- Cell wall with long chain (mycolic) acids, as well as glycolipids which is Thick, waxy and with complex immunogenics
- Nonmotile rod shaped bacteria
- Relatively slow growing for bacteria
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Exaplain how the host’s immune response shapes the clinical outcome
- (Different types of disease with worse immune response going down)
- Healthy contact (LTBI)
- Lymph node
- Localised Extraplumonary
- Pulmonary (localised)
- Pulmonary (widespread)
- Meningeal
- Miliary
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the presentation of TB
Presentation:
- Cough in 80%
- Haemoptysis in 6 to 40%
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Malaise
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the classification of Mycobacteria

Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the first line treatment of TB
- 6 month treatemnt, RIPE for 2 months then just Rifampicin and Isonazid for 4 months
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What are the main types of investigation for TB?
Types of TB Investigations
- Imaging CXR/CT
- Sputum microscopy
- Cultures
- Histology
- Mantoux test:
- Interferon gamma release assay (IGRA)
- Nuclear Acid Amplification test (NAAT)
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the features of Extrapulmonary TB
Extrapulmonary TB:
-
Lymphadenitis:
- Known as scrofula or King’s disease
- Cervical Lymph nodes are most common
- Abscesses and sinuses
-
GI:
- Swallowing of tubercules
- Dominant form in children
-
Peritoneal:
- Ascitis or adhesive
-
Genitourinary:
- Can present with just epydidimytis
-
Bone:
- Spinal TB most common
-
MIliary:
- Millet seeds on CXR
- Progressive disseminated haemtogenous TB
- Increasing due to HIV
-
Caridac:
- Pericarditis
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the pathopysiology, investigations and treamtent of Spinal TB
Pathophysiology:
- Haematogenous spread
- Initial discitis
- Vertebral destruction and collapse
- Anterior extension
Investigations:
- MRI/CT
- Biopsy/Aspirate
Treatment:
- 12 months of anti-TB
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the main types of Non Tuberculous TB
Two types of NTMs:
-
Slow growing
- M.Amvium
- M.Marinum
- M.Ulcerans
-
Rapidly growing
- M.Abscessus, M.Chelonae. M.Foruitum
- Skin and soft tissue infections
- In hospital settings, isolated from blood cultures
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the features of TB Vaccination
- BCG= Bacille Calmette-Guerin
- Live attenuated vaccine
- Only given to babies in areas of >10/100,000, since 2005
- Efficacy is 70 to 80%
- Doesn’t work well in adults
- Treatment with biologics, Infliximab: Anti TNF, screens for latent TB before giving the vaccine.
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the 3 types of Leprosy
3 Types:
-
Paucibacilliary: Tuberculoid leprosy
- Few bacilli
- Large and vigorous cell mediated immune response
- Develop peripheral neuropathy > lose limbs
-
Multibacilliary: Lepromatous leprosy
- Heavy bacterial loads
- Smaller cell response
- Develop lumps and bumps
-
Boarderline (BB)
- Multiple plaques
EMQ Buzzwords: Thickened sural nerve, Shaved outer eyebrows
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the presentation of TB in HIV

Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the features of Primary TB
- Multiplies at the pleual surface (Ghon focus)
- Rarely can get allergic reactions such as erythema nodosum
- Taken to a lymph node (primary complex)
- Granulomata is the characteristic lesion with Langhan’s giant cells
- Can be asymptomatic, especially in children
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the features of Post Primary TB
Post Primary:
- Reactivation is over 5 years since last infection
- 5 to 10% lifetime risk
- Upper lobes affected
- Classic lesion = caseating granuloma
- healing = fibrosis and calcification
- Risk factors:
- immunosupression,
- alcoholism,
- malnutrition,
- aging
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the resistance of TB
Resistance:
- Mono= 1 drug only
- MDRTB= Rifampicin and Isonazid
- XDRTB= Rifampicin and Isonazid + Injecatables and Quinolones
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What are the side effects of Rifampicin?
Side effects:
- Organge sectrations
- Induce cP450
- Hepatoxtoicity
- Increased transmaminases
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What are the side effects of Isoniazid?
Side effects:
- Peripheral neuropathy (give B6/pyridoxine)
- Hepatotoxicity
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What are the side effects of Ethambutol?
Side effects
- Optic Neuritis
- Visual disturbances
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What is the treatment for TB Meningitis?
TB Meningitis Treatment:
- RIPE for 4 months
- R and I for 8-10 months
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What is is 2nd line treatment for TB?
2nd Line treament for TB:
-
Injectables
- Capreomycin
- Kanamycin
- Amikacin
-
Quinolones
- Moxifloxacin
- Cycloserine
- Ethionamide/Protionamide
- PAS
- Linelozid
- Clofazamine
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What is the treatment for latent TB?
Latent TB treatment:
- 6-9 months of Isoniazid
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What is used for T Prophylaxis?
Just Isoniazid
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What are the features of Sputum Microscopy and Cultures for TB?
-
Sputum Microscopy
- Zeihl Neelson/Auramine staining
- Gram +ve rods, acid fast
-
Cultures:
- Sputum:
- on 3 different occasions
- Bronchoalveolar lavage
- Urine
- Gold standard = Pus in lowenstein jensen medium
- Can take 6 weeks (more like 1 to 3 though)
- Sputum:
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What are the features of the Mantoux for TB?
-
Mantoux test:
- Inject 2 units of tuberculin to check previous exposure
- Looking for induration not erythema!
- Poor sensitivity
-
Positive result if:
- >5mm in immunocompromised pateint
- >10mm if recent immigrant
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What are the features of the IGRA and NAAT?
Interferon Gamma Release Assay:
- Episilot quantification
NAAT:
- PCR-line probe analysis. tests for sensitivities
Tuberculosis and Other Mycobacteria
What are the symptoms of TB Meningitis?
- Subacute presentation
- (Classic TB) weight loss, fever, night sweats
-
Signs of meningism:
- Headache
- Neck stiffness
- Personality changes
- Reduced GCS
- Focal Neurological deficit
Tuberculosis and Other Mycobacteria
What are the investigations for TB Meningitis?
- CT: Tuberculomata
- LP: Lymphocytic
Tuberculosis and Other Mycobacteria
What are the treatment for TB Meningitis?
- 12 months of Anti-TB treatment
- Steroids
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What are the featutres of M.Avium?
-
Children:
- Pharyngitis/cervical adenitis
-
Pulmonary
- Underlying lung disease
-
Disseminated
- Cytotoxics, lymphoma
-
AIDS:
- Disseminated infection.
- Mycobacteraemia
- consider in HIV pateints with longstanding diarrhoea
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What are the featutres of M.marinum?
- Also called Fish tank granuloma
- Single or in clusters papules/plaques
- Swimming pool/aquarium owners
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What are the featutres of M.Ulcerance?
- Insect transmission (tropics/Australia)
- Early: painless nodules
- Usually slowly progressive leading to ulceration
- Seldom fatal, hideous deformity
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
How is the TB vaccine contraindicated in HIV pateints?
- BCG is contraindicated in HIV pateints
-
HIV -ve
- latent TB > active
- risk is 5 - 10% lifetime risk
-
HIV +ve
- latent TB > active
- risk is 5 - 10% YEARLY RISK
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What is the incubation period, transmission route and main damage site in Leprosy?
- Incubation 2-10 years
- Poor transmission via nasal secretion
- Most damage is secondary effects to nerves
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What is the treatment of Leprosy?
- Rifampicin
- Dapsone
- Clofazimine (if multibacliliary)
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
What are the key manifestations of Leprosy?
-
Skin
- Depigmentation, macules, plaques, nodules, trophic ulcers
-
Nerves
- Thickened nerves, sensory neuropathy
-
Eyes
- Keratinitis, Irdocyclitis
-
Bones
- Periositis nasecptic necrosis
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the features of “Progressive” Primary TB
- Progressive primary
- Rarely, focus or node ulcerates into bronchus
- causing
- pneumonia
- cavity formation
- bronchiectasis
- consolidation
- collapse
Tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria
Outline the features of Miliary TB
-
Miliary TB:
- progressive, disseminated haematogenous spread with rich foci
Sexually transmitted Infections
-
Which diseases present with:
- discharge
- ulceration
- rashes, lumps/growths
- How do you distinguish genital ulcers?
-
TB CCG (Tuberculosis in a Clinical Comissioning group)
-
__Candida=“Cottage cheese” discharge
- Vulvitis
- itch
- Trichomonas = Offensive yellow/green, frothy discharge
- Vulvoganginitis
- Strawberry cervix
- Bacterial vaginosis= Offensive, thin, white/grey, “fishy” discharge
-
__Candida=“Cottage cheese” discharge
- CHLD
- GMPS (Grumps, without the r or u)

Sexually transmitted Infections
What are the features and main types of investigation of Syphilis?
Main types of Investigations:
- Non Treponemal
- Treponemal

Sexually transmitted Infections
What are the features, diagnosis and treatment of Trichomoniasis?

Sexually transmitted Infections
What are the features, diagnosis and treatment of Bacterial Vaginosis?

Sexually transmitted Infections
What are the features, diagnosis and treatment of Candidiasis?

Sexually transmitted Infections
What are the features, diagnosis and treatment of Molluscum contagious?

Sexually transmitted Infections
What are the features, diagnosis and treatment of Genital warts?

Sexually transmitted Infections
What are the main viral STI?

Sexually transmitted infections
Outline the features of primary Syphilis

Sexually transmitted infections
Outline the features of secondary syphilis

Sexually transmitted infections
Outline the features of tertiary syphilis and latent syphilis

Sexually transmitted infections
Outline the treatment of Syphilis

Sexually transmitted Infections
What are the miscroscopic features, symptoms and diagnosis of Chancroid?

Sexually transmitted Infections
What are the miscroscopic features, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of Donovanosis?

Sexually transmitted Infections
What are the enteric pathogens (oro/anal contact)?

Sexually transmitted infections
What are the microscopic features, subtypes, complications and epidemiological features of Chlamydia?

Sexually transmitted infections
What are the investigations and management options for Clamydia?

Sexually transmitted infections
What are the microscopic features, investigations and treatment for Gonorrhoea?

Sexually transmitted infections
What are the features of uncomplicated and complicated Gonorrhoea for men and women?

Sexually Transmitted Infections
What are the microscopic features and classifications of Lympho Granuloma Venerum (LGV)?
- Early LGV (first stage): 3 - 12 days
- Early LVG (second stage): 2-25 weeks
- Late LGV
- Current LGV Outbreak

Sexually Transmitted Infections
What are the investigations and management for Lympho Granuloma Venerum (LGV)?

Sexually Transmitted Infections
What are the Non Treponemal tests of Syphilis?

Sexually Transmitted Infections
What are the Treponemal tests of Syphilis?

Sexually Transmitted Infections
What are the features of Early LGV (first stage)?

Sexually Transmitted Infections
What are the features of Early LGV (second stage)?

Sexually Transmitted Infections
What are the features of Late LGV?

Sexually Transmitted Infections
What are the features of Current LGV infection?



