L42. Nasal Cavity and Nasopharynx Flashcards
What are the main boney parts of the external nose?
- Frontal bone
- Frontal proxess of the maxilla
- 2 nasal bones
These all articulate together to form the bridge of the nose

What is most of the external nose composed of?
Cartilage
Describe the cartilaginous components of the external nose
- Made up of lateral cartilages making up the bulk of the external nose
- Septal cartilage runs in the midline of the lateral cartilages and articulates with the back of the nasal cavity bones (creates two nasal cavities)
- The Alar cartilages create the shape of the nostrils
(Alar fibrofatty tissue makes up the rest of the nostrils on the lateral side)s

What are the skeletal boundaries on the lateral wall of the nasal cavity?
(there are 6 bones involved - draw them)
- The sphenoid bone (its body and the descending pterygoid plates) forms the posterior nasal cavity
- The ethmoid bone forms the roof of the nasal cavity
- The frontal bone and nasal cartilages corm the anterior part
- The maxilla forms a majority of the wall
- The Palatine bone forms the rest of the roof and closes in the posterior part
- The inferior concha is boney projection (its own bone)

What are the skeletal boundaries making up the medial wall of the nasal cavity?
(there are 5 major aspects - draw this)
- The ethmoid bone and its cribiform plate make up the roof
- The septal cartilage of the external nose makes up the anterior
- The floor is still made up of the maxilla and palatine bones
- The posterior wall is still body sphenoid bone (note the pterygoid only forms the lateral wall)
- The vomer is a separate boney process that closes off the entire nasal septum (separating it entirely into two)

There is a space between the septal processes and the lateral wall of the nasal cavities.
What is it called and what is the function?
The posterior nare
It is the opening where air goes in and out
(there is an anterior nare which is the external opening of the nose)

What is in very close relation to the nasal cavity at the level of the ethmoid bone?
Describe how this is significant in Bad breaks of the nose
The ethmoid bone is very intimately related to the CNS especially the meninges
Bad breaks of the nose that involve the ethmoid bone may lead to infection (meningitis), bleeds of the CNS or rhinorrea
What is Rhinorrea?
Damage to the meninges by an ethmoid bone fracture (or something similar) that causes leakage of the CSF into the nasal cavity
What is the nasal cavity lined with?
What is the exception?
Lined by a highly vascular mucous membrane except for the very front vestible which is lined by skin and hair.

What is a common pathological implication of this highly vascular mucous membrane?
Rupture of these vessels (most commonly by having penetrating objects) is the most common cause of epistaxis (nose bleeds)
Why is this vasculature network so important to the nasal cavity?
Because the warmth from these anastomosing network is used to warm up and humifity the air (cold air can cause spasm of smooth muscles in the respiratory tract)
Describe the two major sections of the vascular mucous membrane lining the nasal cavites
- The superior third of the mucous membrane is the olfactory area
- The rest of the membrane is respiratory epithelium

Describe the olfactory epithelium of the superior third of the mucous membrane
The olfactory epithelium contains filaments for sensory nerves up through the cribiform plate where they synapse in the olfactory bulb with the secondary order neurons (olfactory nerves; CN I)

Describe the respiratory epithelium of the nasal cavity, what is its major function?
It is lined by pseudostratified, columnar, ciliated epithelium and is continuous with the remainder of the airways
These cilia beat actively in the direction towards the anterior part of the nasal cavity to move mucuos towards the nose to be removed
What are the turbinate bones of the lateral wall?
They are three bones/projections that are also lined by mucosa that protrude into the nasal cavity.
- Superior concha
- Middle concha
- Inferior Conca

What bones do the turbinates/choncae stem from?
The superior and the middle conchae are projections off the ethmoid bone
The inferior conchae is its own bone
What role do the conchae play in inflammation and congestion?
They occupy a lot of space in the nasal cavity and thus cause the nasal cavity to be relatively susceptible to being blocked

There is a space underneath each of the conchae. what is it called and what do they contain?
They are called meatuses (singular meatus)
The contain openings for the paranasal sinuses

What is a paranasal sinus?
Spaces in bone that are formed by outpouches/diverticuli of the bone of the nasal cavity
What are the four paranasal sinuses?
- Frontal
- Sphenoid
- Ethmoid
- Maxillary
Each one is associated with the bones of the nasal cavity

How are the paranasal sinuses formed?
They outpouch and grow into the bones very early in life (within the first few months after birth). As they develop they take with it mucosa to line the bone.
Describe drainage of the sinuses and risks of infection (sinusitis), relate this to their location in the skull
The openings of the paranasal sinuses (in the meatuses) allos for the migration of bacteria into the sinus and cause infection and inflamamtion.
The inflammation causes pressure on a highly innervated mucosa causing lots of pain.
All except the maxillary sinus sit high above the nasal cavity and drain down easily while the maxillary opening is high up on the medial wall so drainage is much harder for this to occur

The maxillary sinus is susceptible to infection from an additional source (other than the nasal cavity). Describe what is meant by this
The nasal havity has a thin inferior shelf of bone that delineates it from the roots of the upper teeth. Thus problems with tooth extractions and any infection of the teeth may ascend into the maxillary sinus from the oral cavity
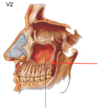
Label the following diagrams:


Roughly, where are the locations of the openings of each of the paranasal sinuses?
They exit out as superiorly as they possibly can.
Frontal exists in the middle meatus very anteriorly, ethmoid in the middle (and some superior) meatus, maxillary just under it also in middle meatus, and sphenoid near the superior meatus

Describe the link between the lacrimal gland and the nasal cavity
The lacrimal gland produces tears to lubricate the eye. These secretions are collected in the corner of the eye draining into a lacrimal sac (in the medial side of the orbit)
This sac is drained by the nasolacrimal gland into the nasal cavity by the anterior region of the inferior meatus to be removed by the nose

What is a simple method to remember the vessels of the nasal cavity?
Divide the nasal cavity into quadrants
- Posterior
- Superior
- Inferior
- Anterior

Describe the blood supply to the posterior quadrant of the nasal cavity (both the medial and lateral walls)
They derive blood from the sphenopalatine artery
This is a large and high pressure artery and damage to it (usually by trauma of the vessel or nearby boney processes or by inhaled chemicals) causes high pressure nose bleeds.

Describe the blood supply to the inferior quadrant of the walls of the nasal cavity
They are supplied by the branches of the greated palatine artery
This artery runs along the roof of the mouth supplying it and then it projects up through a small hole in the maxilla into the inferior aspect of the nose

Describe the blood supply to the superior quadrants of the nasal cavity
They are supplied by the ethmoidal arteries which are branches of the opthalmic artery

Describe the blood supply to the anterior quadrants of the nasal cavity
The anterior quadrant is supplied differently on the medial side to the lateral side.
- On the lateral wall, the quadrant is supplied by the lateral branches of the facial artery
- On the medial wall, the quadrant is supplied by the labial branches (from the upper lip)

What and where is Kiesselbach’s plexus?
(or Little’s area) is in the anteroinferior part of the nasal septum. It is the site where the four arteries anastomose to form a vascular plexus
Anterior ethmoidal artery, Sphenopalatine artery,
Greater palatine artery, and septal branch of the superior labial artery
It is a very weak area prone to damage

Describe the nerve supply of the nasal cavity
It is derived entirely from branches of the trigeminal nerve.
- Anterosuperior part is innervated by V1 especially the nasociliary nerve and ethmoidal nerves
- Posterioinferior half is recieved from V2 especially the nasopalatine nerve

Where does the pharynx span from and to?
What are the three major sections of the pharynx?
From the base of skul to the level of C6 (lower border of the cricoid cartilage)
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharynx

What is the function of the constrictor muscles? What structure do they form around the larynx?
They contract sequentialy to force a bolus of food down the pharynx towards the oesophagus.
They are a set of muscles that wrap around either side of the pharynx and join in the back in a muscular sling-like organisation
What are the three main constrictor muscles of the pharynx? Describe their origins
- Superior constrictor muscle: attaches to the buccinator muscle
- Middle constrictor muscle: attaches to the hyoid bone
- Inferior constrictor muscle: attaches to thyroid cartilage and cricoid
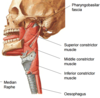
Describe the union of either side of the pharynx of each of these muscles
They connect to their counterpart in the midline in the back at the median raphe

Where is the start of the nasopharynx?
What are the superior and inferior borders?
What are the posterior and lateral walls formed by?
It begins directly posterior to the posterior nare
- The superior border is formed by the sphenoid bone
- Inferior border formed by the soft palate and the uvula
- The posterior wall is made up by the superior constrictor muscles
- Lateral wall is formbed by mucosa of some muscles
Where are the pharyngeal tonsils/adenoids? What is their significance to inflammation?
In the roof of the nasopharynx
They are a cluster of lymphoid tissue sitting just under the mucosa.
They can be chronically inflammed and cause obstruction of the posterior nare causing sleep problems especially. Obstruction also prevents sound from reaching resonance centre chambers.

What is the main connection to the auditory tube in the nasopharynx?
There is a cartilagenous auditory tube which maintains the pressure in the middle ear (it is in the lateral wall of the nasopharynx) with muscles associated with it

What is the salpingopharyngeus muscle?
It is an internal pharyngeal muscle that attaches to the cartilagenous part of the auditory tube attaching to the muscular wall of the pharynx.
Contraction of this muscle pulls on the medial aspect of the auditory tube and this is important when it becomes blocked (so serves to drain contents out - this is why you get blocked ears when you have a cold)


