L10. Anatomy of the cranial cavity Flashcards
What is the pericranium?
A thin layer of connective tissue (the periostium) surrounding the skull
What is the superior sagitall sinus? Where does it lie
An endothelial lined space in the root of the falx cerebri (dural enclosure).
It runs in the root/origin of the attachment of the falx cerebri superificially.

Where does venous blood come from entering the superior (and inferior) sagittal sinus?
Collecting venous blood from the brain (cerebral veins), the diploe via diploic vein and some of the venous drainage from the scalp by the emissary vein.

What is the inferior sagital sinus?
What drains into it?
An endothelial lined sinus that is present in the small split forming the falx cerebri projecting down between the hemispheres
Cerebral blood, emissary blood and dipoloic blood

Describe the formation of the Straight sinus
The falx cerebri meets and attaches to the tentorium cerebelli. At this point, the inferior sinus joins the great cerebral vein and straightens out and becomes the straight sinus.

Describe the path of the straight sinus
From the point of contact of the inferior sagittal sinus with the intersection of the falx and tentorium, the straight sinus goes back following the intersection towards the inside aspect of the EOP
Describe the interaction between the straight sinus and the superior sagittal sinus
They meet (either mix their contents or come into contact) at the EOP and then diverge into a left and right components.
This point of contact is called the confluence of sinuses
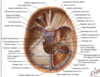
Describe the development and path of the transverse sinuses
From the confluence of sinuses, there is aleft and right division and the development of transverse sinuses in the root/origin of the attachment of the tentorium cerebellum, tracking along of the posterior wall of the posterior cranial fossa.
What happens to the transverse sinuses when they reach the petrous part of the temporal bone (ie. the edge of the posterior fossa)
When it reaches the petrous part, they snake out as an S shaped becoming the sigmoid sinus
Describe the path of the sigmoid sinus
It snakes down from the petrous bone towards the centre and through the jugular foramen (with cranial nerves IX, X and XI) and out to become the jugular vein.

Describe the trend of the venous sinuses as they track down towards jugular foramen to become the jugular vein
The vessels become bigger as it goes, as it collects venous blood as it goes.
What is the cavenous sinus?
A pair of sinuses sitting on the lateral aspect of the body of sphenoid.
It forms very important in connections (receiving and draining) blood from cerebral, opthalmic and emissary veins of the face. Running through or in the lateral wall of the sinus are those heading for the superior orbital fissure.

What collection of arteries supply the skull and meninges of the head?
A network of many small meningeal arteries
What is the largest and most important meningeal arterial supply?
The middle meningeal artery.
Describe the origin of the middle meningeal artery
The external carotid artery breaks into the superficial temporal artery nd the maxillary artery (deeply situated). Branching off this is the middle meningeal artery.
Through what foramen does the middle meningeal artery enter the cranial cavity?
Foramen spinosum
What happens just after the entrance through the foramen spinosum to the middle meningeal artery?
It spans out to an anterior and posterior branches that grooves the internal surface of the skull.
Where does the anterior division of the middle meningeal artery run along?
What is the importance of this?
Directly internal to the pterion in the extradural space (thin bone area)
Common cause of extradural haemorrhage.

Venous blood often haemorrhages into the subdural space. Explain this.
Subdural haemorrhage (often as a result of a fall)
Tearing often occurs where cerebral vein into the sinus - this is an oozing of blood into the subdural space.
Sometimes this can stop and calcify causing no symptoms, sometimes when the clot calcifies and become an epileptic focus. Large enough one will compromise consciousness.



