L38. Hearing Flashcards
Describe hearing loss severity to the loss of different frequency detection
A loss of low frequency detection is regarded moderate relative to normal while a loss of high frequency sound is indicative of severe/profound hearing loss

What is the symptom described by patients beyond mild hearing loss?
Lots of difficulty discriminating words
What is being detected by humans in terms of sound energy to characterise:
- Pitch
- Loudness
- Timbre/Tone/Resonance
- Pitch = Wavelength/frequency
- Loudness = amplitude
- Resonance = Waveform
Recall the anatomy of the auditory system in terms of the chambers and the major components that make up hearing (draw a diagram)

Describe the general path of sound energy waves picked up by the auricle through to the neural signal sent through to the auditory cortex of the brain
- Sound energy waves picked up by auricle
- Sound energy converted into mechanical energy at the tympanic membrane
- The tympanic membrane transmits this energy through the three ossicles and then to the oval window
- The oval window is the interface for mechanical vibrations being converted into energy vibrating through fluid
- Fluid movement is sensed by specialised hair cells in the cochlear
- Hair calls convert this movement into a neural signal to be transmitted to the brain
What is the main nerve carrying this information to the auditory cortex?
The vestibulocochlear nerve CN VIII (through the cochlear division of the nerve)
What is one of the important functions of the auricle?
To localize sound particularly in the vertical domain
What normally happens to sound travelling through air as it reaches a fluid interface? (And thus what does the ear have to overcome?)
Normally sounds passing from air to fluid become dampened significantly as over 90% of the sound energy is reflected at the interface.
Thus the apparatus of the ear has to overcome this loss of energy
What is impedance matching? What structure(s) of the ear are important for this?
Impedance is the level of resistance through a circuit.
Impedance matching is matching the waves of sound in air to the movement of sound in fluid (ie. matches the impedance of air to the impedance of fluid within the ear)
The ossicles are important for this
Describe how the ossicles of the ear achieve impedance matching
The size of the tympanic membrane is very large relative to the oval window (20:1) this means that there is a large pressure difference generated between them through the ossciles.
The lever action of the ossicles of 1:3:1 generates a force difference
There pressure and force at the oval window is about 200 fold greater than that of the hitting the air at the tympanic membrane
Describe the spiral arrangement of the cochlea in relation to the ganglion of the auditory nerve
The cochlear makes 2.5 revolutions

What are the three chambers of the cochlea of the inner ear?
- Scala vestibuli - filled with perilymph
- Scala media - filled with endolymph
- Scala tympani - filled with perilymph

What are the two membranes in the cochlea, describe their locations
Both membranes are located between the scala tympani and the scala media
- Basilar membrane is located just above the scala tympani
- Tectorial membrane is fixed in place and is located just under the scala media (on top of the basilar membrane

How are the basilar membrane and tectorial membrane involved in sound reception?
The movement of fluid through the cochlear moves the basilar membrane in relation to the tectorial membrane and this relative movement is detected by hair cells, which transduce it into a mechanical signal.
Describe the anatomy of the basilar membrane
The basilar membrane is like a flipper
- It is wider at the apex (the ‘tip’) of the cochlear and narrower at the base.
- This arrangement means that the base is stiff and the apex is very floppy

What does this difference in physical properties between the apex and base of the basilar membrane mean for the response to sound of each part?
The Base is stiff and thus will require more energy to move it (only responds to high frequency)
The Apex is more floppy/thick and thus requires less energy to move it (only responds to low frequencies)
All sounds can be encoded on the basilar membrane based on the anatomy and location. What is important about this organisation?
It is retained throughout the whole auditory system (a tonotonic map/topography).

What is the organ of Corti
The sensitive element in the inner ear situated on the basilar membrane: it contains rows of hair cells protrude from the surface, it is responsible for the transduction of electrical signals
Where do the auditory receptors/hair cells lie?
They are sandwiched between the basilar membrane and the reticular lamina of the tectorial membrane.
Hair cells are embedded in the basilar membrane with sterocilia projections in the tectorial membrane

What are the different types of hair cells? What are their locations?
- Inner hair cells: sit in a row closer to the afferent axon fibres of the cochlea nerve and feed directly into them
- Outer hair cells: sit further away from the afferent axons and receive efferent information from the brain for modification of sound pathways

Each hair cell has about 100 sterocilia projecting from it. What is the significance of this?
They extend over the top of the hair cells and insert into the tectorial membrane. They are what detect movement and direction of movement/oscillation.
The bending of sterocilia causes neuronal signalling
Describe the arrangement of sterocilia on the hair cells
The sterocilia are not all the same length. They are arranged in length/height order with the longest one called the kinocilium

Describe how travelling waves through fluid initiate auditory transduction
Sound induced vibration causes a particular end the basilar membrane to move up and down in response.
This movement creates a shear force of the hair cell sterocilia on the tectorial membrane. Oscillation in one direction causes the sterocilia to bend towards the kinocilium, oscillation in the other direction will have the opposite effect.
The frequency of this movement and the amplitude of it is converted into neural signals

Describe the normal state of a hair cell in terms of potassium channels
Potassium channels are open all the time in hair cells (this is opposite to other cells of the body)
What happens when deflection of the hair bundle occurs towards the tallest sterocilium (kinocilium)?
This causes a further opening of K channels leading to an influx of potassium (opposite to other cells) and causes a depolarization

What happens when movement is away from the tallest sterocilium (kinocilium)?
There is a closure of the K channels leading to reduced intracellular K and thus a hyperpolarization of the hair cell
How is the depolarization or hyperpolarization of the hair cell converted into a neural signal?
Depolarisation of the cell by K influx leads to an opening of voltage gated calcium channels allowing influx of calcium and subsequent release of vesicles containing glutamate. Glutamate then binds to the afferent nerve and this is read as an electrical signal to the brain.

The displacement of the hair bundle in either direction causes alterations in the membrane potential (depol. or hyperpol.), is this response symmetrical between the two?
No.
There tends to be larger depolarizing signals that hyperpolarisations (a tendency to depolarize)
Potassium is important in depolarizing and hyperpolarizing the hair cells. How are levels of potassium maintained during transduction processes?
- The scala media has high K concentrations
- The scala tympani has low concentrations
Potassium is recycled through potassium channels via the stria vascularis back into the scala media to keep this potential

Which hair cell type is more numerous?
The outer hair cells
What is the majority of nervous communication between the hair cells and brainstem nuclei?
95% of hair cells project information about sound to the brainstem nuclei from the inner hair cells while the remaining 5% are efferent inputs to outer hair cells
Where do the efferent connections to the outer hair cells come from? What is their significance?
The efferent inputs come from the superior olivary complex and they in turn receive input from higher auditory areas. They feedback from high areas and modify the signal by modifying how hair cells work
Describe the outer hair cell response to sound
Outer hair cells change length during low intensity stimuli
What is the function of the outer hair cell response?
By changing length to low frequency stimuli, they accentuate the movement of the basilar membrane and thus amplify the signal received by the inner hair cells
Outer hair cells receive either depolarization or hyperpolarization signals. How does it respond to these?
They have proteins called prestins that react to these electrical signals.
- Depolarisation causes contraction of the cell
- Hyperpolarisation causes elongation of the cell
What would happen to a person’s sense of hearing if they had a loss of outer hair cells?
What situations could cause this?
They would have no amplification of signals and this would lead to a loss of hearing. This is because without them, the basilar membrane movement is decreased 100x
This can be caused by the use of several types of ototoxic antibiotics (aminoglycosides) especially if used systemically, high doses of aspirin
Describe the auditory pathway from the hair cells to the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe
- Hair cells transmit information to the spiral ganglion of the CNVIII
- CNVIII nerves project ipsilaterally to the cochlear nuclei in the brainstem (medulla)
- Information is sent to the superior olive and then to the lateral lemniscus
- Fibres travel through the lateral lemniscus towards the inferior colliculus of the midbrain
- From here nerve fibres travel to the medial geniculate nuclei of the thalamus
- The thalamus then relays the information to the auditory cortex of the temporal lobe
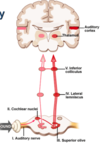
How is information integrated from both ears?
Many pathways flow from the synapse at the cochlea nuclei in the brainstem to the auditory cortex. There is the anteroventral coclear nucleus and above this level (particularly at the level of the superior olive) there is extensive crossing over of information.

What are the relay nuclei in the brainstem important for?
The localization of sound (comparing information from both ears) – horizontal localization particularly
What does the superior olivary complex consist of?
Lateral and medial superior olives and the trapezoid body
Describe the function of the lateral superior olives and the medial superior olives in relation to the duplex theory
The duplex theory is the dual means of horizontal localization of sound, depending on frequency. This is done in two ways done by 2 anatomical regions:
- MSO: Localisation of sound by measuring time delay
- LSO: localization of sound by sensing intensity differences
Describe how the medial superior olives localize sound
They are only able to do this for low frequency sounds because they take longer to travel (and thus time difference is easier to measure)
The time it takes for a neural signal to reach an neuron in one side of the medial superior olive is different it will take for the same neural signal (from the other ear) to each that same neuron. This time delay is sensed by that neuron and sent to higher areas for interpretation.

Describe how the lateral superior olives localize sound
They recognise high frequency sound because these high pitched sounds cannot travel through the head (the head acts as a thick solid barrier preventing travel). Thus the sound will definitely be louder in one ear compared to the other.
It involves an inhibitory nuclei acting on the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body that inhibits activity in the opposing lateral superior olive

Describe the auditory cortex
(also called herschls gyrus and Brodman’s area 41)
- Located in the temporal lobe
- Neurons are sharply tuned in this area to sound frequency
- There is a columnar organisation of cells (with the topography set up in the basilar membrane)
- Alternating regions of input from both ears is also set up (excitatory input from one ear and inhibitory from the other)

What is meant by the asymmetrical representation of complex sounds?
- Speech sounds: left hemisphere
- Environmental sounds: both
- Music: right hemisphere
It is not this clear cut in every individual

Describe the higher order of auditory processing in terms of “where” and “what”. Is it as organised as the optic processing pathway?
Moving down the temporal lobe of the cortex are areas that process what the sound type is
Moving towards the parietal lobe are areas that process where the sound is located
This is not as organised as the visual pathway is

What would cause a sudden loss of hearing?
Only 10-15% of cases are of known cause
- Peripheral causes: meningitis, Guillain-Barre, Acoustic neuroma, metastasis
- Central: MS
- Cochlear causes: trauma, infection, metabolic, vascular, ototoxicity


