Intracellular Membrane Traffic Flashcards
What is the secretory pathway?
Delivers new proteins, carbs, lipids, etc to extracellular space or plasma membrane. Exocytosis

Where do cells move plasma membrane components to in endocytosis?
Endosomes (endocytotic pathway)

Where can cells bring stuff from endosomes?
Lysosome (degradation) or rest of the cell

Where does the secretory pathway start and where does it move towards?
Starts in ER, goes out to golgi and cell surface (side route to lysosomes)

What’s the role of retrieval pathways?
Balance membrane flow (same # of lipids in sending / receiving areas)

How do vesicles know where to go?
Specific combination of molecular markers on cytosolic surface of membranes to differentiate them

What are vesicle coats for?
Getting specific molecules and going too specific places

What are the three types of coats on vesicles?
COP1, COPII, and Clathrin

Which vesicle coat buds from Golgi compartments?
COP1

Which vesicle coat buds from ER?
COPII

Which vesicle coat transports stuff from the plasma membrane and between endosomal/golgi compartments?
Clathrin

What are Clathrin subunits called? Where are they?
triskelions, outer coat
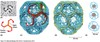
What type of proteins are on the inner layer of the clathrin coat?
Adaptor proteins

What are cargo receptors?
Transmembrane receptors that capture soluble cargo molecules inside the vesicle. Adaptor proteins trap them

How many subunits to the best characterized adaptor proteins have?
4; others are single chain

What is the purpose of multiple types of adaptor proteins?
To be specific for a different set of cargo receptors

What are the light chains of a triskelion for?
Link to the actitn cytoskeleton, generating force for membrane budding / vesicle movement. Phosphorylation regulates coat assembly

What are heavy chains of triskelions for?
Fom an outer shell that binds to adaptor proteins
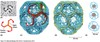
What on the membrane do adaptor proteins bind to? Why?
Phosphoinositides (lipids). So that cargo receptors can come bind

What gives phosphoinositols their name?
They’re phospholipids with inositol sugars at the top

How are PIPS regulated?
Phosphorylation / dephosphorylation by kinases / phosphatases

What assembles at bud necks as clathin-coated buds grow?
Dynamin

What on Dynamin regulates how fast vesicles pinch off from the membrane?
Its GTPase domain

How is Dynamin recruited?
PIPs in the neck





























