Cell Cycle Flashcards
(27 cards)
When does centriole replication ocur?
S-phase

What do motor proteins do in terms of mitotic spindles?
Pull them apart

What do motor proteins do in centriole replication?
Pull them apart. Dynein-14, kinesin-5. Tug-of-war.
Kinesin-14 is + end directed

Are chromosomes simply pushed into formation in mitosis without helping?
No, they help organize/form spindle

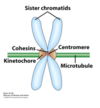
What protein structure is buillt on the heterochromatin at the centromere?
Kinetochore, microtubule attachement sites.

What complex is attached to the microtubule?
Ndc80 complex

What would be an example of unstable centrosome arrangements?
Two centrosomes attached to the same microtubule

When in mitosis do lateral kinetochores attach to microtubules?
early prometaphase

What does tubulin addition / removal do to microtubules in metaphase?
Makes microtubules flux. Overall length staying constant

If you cut a microtubule arm with a laser to remove kinetochore, what will happen?
It will move away from the pole

During what phases does cohesin resist pulling to pulls?
Prometaphase, metaphase

What happens to cohesin to cause chromosomes to pull apart?
Gets degraded through a big process (don’t need to know for quiz)
Protein that binds to unattached kinetochores

What are the components of cytokinesis? What proteins are involved?
Cleavage furrow > contractile ring
Actin / myosin filaments
After ring, actin is on the outside, myosin by the ring

What generally happens in prophase?
What forms around centrosomes in prophase?
Chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope intact, spindle starts to form, kinetochores there. Basically spindle forms, chromosomes condense.
Forms around: Mitotic asters form around centrosomes

What’s important about prometaphase?
Where are the centrosomes in prometaphase?
Nuclear envelope breaks down, chromosomes attach to microtubules
Centrosomes at spindle poles

Where are centrosomes in metaphase?
Where are chromatids?
Centrosomes at spindle pole
Chromatids aligned at spindle equator

What important events happen in anaphase?
Chromatids break apart, microtubules shorten, spindle poles separate

What’s happening to chromosomes in telophase?
What other events are happening?
Chromosomes decondensing
Contractile ring starts to form
Nuclear envelope appears again

What surrounds decondensing chromosomes in cytokinesis?
What is the valley the contractile ring makes called?
Nuclear envelope surrounds decondensing chromosomes
Valley called the cleavage furrow
What do cohesins look like?
What is their role?
When do you see them?
Rings that surround sister chromatids
Bind sister chromatids together
See them at the end of S phase, they dissolve in anaphase
What ends of microtubules are spindle sites anchored to?
Plus ends project away from spindle pole
minus ends are anchored at spindle poles

What are the three classes of mitotic microtubules in metaphase?
What are they for?
astral microtubules: Go into cytoplasm
kinetochore microtubules: Connect spindle poles
interpolar microtubules: go all the way through to the other spindle pole

When does the centriole replicate?
What is the matrix inside centrosomes called?
S-phase
Pericentriolar matrix

How does kinesin-5 push microtubules apart?
Two head motor domains
Each domain goes towards + end
Because motor domains are connected, movement pushes microtubules






