Human Development (Ch5) Flashcards
Period of natal development: grasp reflex appears
second trimester
Which reflexes begin at 4-6 months and integrate at 5 years?
neck and body righting (NOB, BOB)

palmar-supinate grasp

Which reflex begins at 4 months and persists?
downward parachute/protective extension downward
Which reflex begins at birth-2mo and persists?
labyrinthine/optical head righting
Release: involuntary release
1-4 mo
Stimulus: place infant in supine Response: increased extensor tone
tonic labyrinthine supine
In supine: holds head in midline chin is tucked and neck lengthens in back legs come together lower back flattens against floor
3-4 mo
when does a radial-palmar grasp typically develop?
6 mo
Release: presses down on surface to release
7-10 mo
Standing: rotates trunk over lower extremities lower extremities are more active in pulling to a standing position pulls to standing by kneeling, then half-kneeling
8-9 mo
Jumping and hopping: hops on one foot, few steps
2.5 yr
Period of natal development: responds to tactile stimuli
first trimester
Stimulus: rapidly lower infant toward supporting surface while suspended vertically Response: extension of the lower extremities
downward parachute/protective extension downward
Period of natal development: sleep states occur
second trimester
at what age do we expect to see palmar-supinate grasp?
1-1.5 yr
Which reflex begins at 28 wks gestation and integrates at 3 months?
rooting
Sitting: Supports self in sitting Sits alone momentarily Increased extension in back Sits by propping forward on arms Wide base, legs are bent Periodic use of “high guard” Protective responses present when falling to front
5-6 mo
Stimulus: stroke the corner of the mouth, upper lip, lower lip Response: movement of the tongue, mouth, and/or head toward the stimulus
rooting
Creeping: creeps on hands and feet
10-11 mo
Stimulus: grasp infant’s forearms and pull to sit Response: complete flexion of UE
traction
Sitting: Sits well without support Legs are closer, full upright with knees straight Increased variety of positions, including “w” sit and side sit Difficult fine motor tasks may prompt return to wide base of support
8-10 mo
Stair climbing: walks down stairs, alternating feet
3-3.5 yr
What age is this child?
- Child can build involved structures combining various planes, along with symmetrical designs
- Child is able to utilize spatial awareness, cause-and-effect, and mental images in problem-solving
48-60 mo
What kind of play is this?
- Participates in play with rules, competition, social interaction, and opportunities for development of skills
- Begins to participate in cooperative peer groups with a growing interest in competition
- Friends become important for validation
Games
In supine: equilibrium reactions are present
7-8 mo
What kind of play is this?
- Engages in sensory, motor, cognitive, and social play experiences
- Explores combinations of actions on multiple objects
- Begins to master skills that promote performance of school and work related activities
Creative play

radial-digital grasp
Stair climbing: walks up stairs, alternating feet
2-3 yr
In prone: pivots in prone moves to prone position to sit
7-8 mo

inferior pincer grasp
Release: Clumsy release into small container hand rests on edge of container
10-14 mo
What age is this child?
Child links schemes into a complex script
36-42 mo
Walking: seldom falls runs stiffly with eyes on ground
18 mo
At what age do we expect symbolic play?
2-4 yr
What age is this child?
- Child attends to shapes of things and uses them appropriately
- Child begins to think before acting
- Child uses tool to obtain a favored object
- Child begins to replace trial and error with a thought process in order to attain a goal
- Child can operate a mechanical toy
- Child can predict effects and assume causes
18-21 mo
Walking: cruises around furniture, turning slightly in the intended direction
9-10 mo
Walking: takes independent steps, falls easily
9-17 mo
What age is this child?
- Child recognizes operations of several mechanisms
- Child matches circles, squares, triangles, and manipulates objects into small openings
21-24 mo
Which reflex begins at 3-4 months and integrates at 12-24 months?
landau
Creeping: crawls forward on belly
7 mo
Stair climbing: walks up and down stairs without support, marking time
2-2.5 yr
Walking: walks with 2 hands held
8-18 mo
Stair climbing: creeps backwards down stairs
18-23 mo
Creeping: reciprocal creep
7-10 mo
Jumping and hopping: hops in straight line
5 yr
Which reflexes begin at 37 wks gestation and integrate at 6 months?
tonic labyrinthine supine and prone
Which reflex begins at 28 wks gestation and integrates at 4-6 months?
moro
Standing: pulls to standing with legs only, no longer needs arms stands alone momentarily
9-13 mo
Vestibular system is functioning at the end of this trimester
first trimester
What kind of play is this?
- Child engages in play experiences through which the child formulates, tests, classifies, and refines ideas, feelings, and combined actions
- Associated with language development
- Objects that are manageable for the child in terms of symbolization, control, and mastery are preferred
- Mostly parallel play with peers
Symbolic play
In prone: turns head side to side lifts head momentarily bends hips with bottom in air lifts head and sustains in midline rotates head freely when up able to bear weight on forearms attempts to shift weight on forearms, resulting in shoulder collapse
0-2 mo
Release: mutual fingering in midline
4 mo
age of a fetus or newborn in weeks since conception
conceptual age
Walking: walks with one hand held reaches for furniture out of reach when cruising cruises in either direction, no hesitation
11 mo
What age is this child?
- Child discriminates sizes
24-27 mo
In supine: lifts head independently brings feet to mouth brings hands to feet able to reach for toy with 1 or both hands hands are mainly open
5-6 mo
when does a radial-digital grasp typically develop?
8 mo
At what age do we expect exploratory play?
0-2 yr
Scissor skills:
cuts circles
3.5-4.5 yr
at what age do we expect to see complex rotation?
6-7 yr
when does bilateral integration emerge?
9-12mo
Stimulus: suddenly tip infant forward toward supporting surface while vertically suspended Response: sudden extension of the UE, hand opening, and neck extension
forward parachute/protective extension forward

inferior scissors grasp
What age is this child?
Child links multi-scheme combinations into a meaningful sequence (putting food in bowl, scooping food with spoon, feeding doll)
24-36 mo
Stimulus: fully rotate infant’s head and hold for 5 seconds Response: extension of extremities on the face side, flexion of the extremities on the skull side
asymmetric tonic neck
Sitting: Gets to sitting from prone
6-11 mo
Stair climbing: walks up and down stairs while holding on
18-24 mo

fine pincer grasp
What age is this child?
- Child finds an object after watching it disappear
- Child uses movement as a means to an end
- Child anticipates movement of objects in space
- Child attends to consequences of actions
- Child repeats actions to repeat consequences
6-9 mo
Scissor skills:
cuts complex figure shapes
6-7 yr
Standing: bears some weight on legs, but must be held proximally head is up in midline, no chin tuck pelvis and hips are behind shoulders legs are apart and turned outward
3-4 mo
when does a palmar grasp typically develop?
5 mo
Jumping and hopping: jumps over objects
3-5 yr
Stimulus: place infant in supine, flex one hip and knee toward the chest, and hold briefly Response: segmental rolling of the upper trunk to maintain alignment
body righting (BOB)
Rolling: Rolls from prone to supine Rolls from supine to side with right and left leg performing independent movements Rolls from supine to prone with right and left leg preforming independent movements
5-6 mo
Jumping and hopping: jumps down from step
2 yr
Stimulus: quickly but firmly tip infant off-balance backward Response: backward arm extension
backward parachute/protective extension backward
Rolling: Rolls segmentally with roll initiated by head, shoulder, or hips
6-14 mo
when does primitive self-feeding emerge?
6-12mo
Which reflex begins at 4-6 months and integrates at 8-12 months?
symmetric tonic neck
What age is this child?
- Child can use tool after demo
- Child’s behavior becomes more goal-directed
- Child performs an action to produce a response
9-12 mo

dynamic tripod posture
Sitting: Rises from supine by first rolling to side then pushing up into sitting position
11-24 mo +
What age is this child?
child combines objects in relational play, such as objects in containers
8-9 mo
What age is this child?
child notices the relation between complex actions and consequences (opening doors, placing lids on containers) and differential use of schemes based on the toy being played with (roll a ball vs. push a train)
9-12 mo
What age is this child?
- Child begins to relate experiences to one another, based on logic and knowledge of previous experiences
- Child can make a mental plan of action without acting it out
- Child can see relationships between experiences
27-30 mo
Jumping and hopping: hops on one foot
3.5-5 yr
Sitting: Held in sitting Head bobs in sitting Back is rounded Hips are apart, turned out, and bent Head is steady Chin tucks, able to gaze at floor Sits with less support Hips are bent and shoulders are in front of hips
0-3 mo
Sitting: Trunk control and equilibrium responses are fully developed in sitting Further increase in variety of positions possible
11-12 mo
when is handedness considered stable?
age 5
Stimulus: rapidly drop infant’s head backward Response: first, arm extension/abduction, hand opening; second, arm flexion and abduction
moro
how far from a newborn’s face should objects of high contrast be held?
10 in
Rolling: Rolls from prone position to side accidentally Rolls from supine to side
3-4 mo
at what age do we expect to see in-hand manipulation with stabilization?
6-7 yr
Scissor skills:
shows an interest in scissors
holds and snips with scissors
opens and closes scissors in a controlled fashion
2-3 yr
at what age do we expect to see dynamic tripod posture?
4.5-6 yr
when does a fine pincer grasp typically develop?
12 mo

pincer grasp
In prone: airplane posturing in prone position chest and thighs lift off surface
5-8 mo
What age is this child?
Child focuses on action performed with objects (banging, shaking)
3-6 mo
What kind of play is this?
- Engages in play experiences through which the child develops a body scheme
- Sensory integrative and motor skills are developed
- Plays mostly with parents/caregivers
exploratory play
Release: volitional release
7-9 mo
at what age do we expect to see palm-to-finger translation?
2-2.5 yr
Period of natal development: primitive motor reflexes appear
third trimester
Stimulus: hold infant in horizontal prone suspension Response: complete extension of head, trunk, and extremities
landau
Oral-motor development: Prior to this age, infant is fed by non-oral means
33 weeks gestation
Stimulus: apply pressure with thumb on the infant’s ball of the foot Response: toe flexion
plantar grasp
Walking: able to start and stop in walking
15 mo
In supine: head held to one side able to turn head side to side
0-3 mo
What age is this child?
Child explores characteristics of objects and expands the range of schemes (poking, pulling, turning, tearing)
6-9 mo
Standing: equilibrium reactions are present in standing
12 mo
Which reflexes begin at 28 wks gestation and integrate at 2-5 months?
suck-swallow and traction
the turning or rolling of an object held at the finger pads approximately 90 degrees or less
simple rotation
Sitting: Protective extension backwards Able to move in and out of sitting into other positions
10-12 mo
Stair climbing: creeps up stairs
15 mo
In supine: head lag is gone when pulled to sitting hands are together in space
4-5 mo
Standing: stands while holding onto furniture
5-10 mo
the persistence or reemergence of primitive reflexes is indicative of dysfunction in what system?
CNS
Stimulus: hold infant in prone suspension, gently scratch or tap alongside the spine with finger, from shoulders to buttocks Response: lateral trunk flexion and wrinkling of the skin on the stimulated side
galant
What age is this child?
- Child can build a tower of 9 cubes
- Child can organize objects by size and build a structure from a mental image
36-48 mo
Stimulus: place infant in crawling position and extend head Response: flexion of hips and knees
symmetric tonic neck
Release: transfers object from hand to hand
4-8 mo
At what age do we expect to see a child participate in games?
7-12 years
Stimulus: place infant in supine and fully turn head to one side Response: log rolling of the entire body to maintain alignment with the head
neck righting (NOB)
hemispheric specialization for specific tasks (ex: handedness)
laterality
What age is this child?
Child links schemes in simple combinations (placing a baby in carriage and pushing carriage)
12-15 mo
Release: two-stage transfer (taking hand grasps before releasing hand lets go)
5-6 mo

radial-palmar grasp
when does a primitive squeeze grasp typically develop?
4 mo
Which reflex begins at 7 months and persists?
sideward parachute/protective extension sideward
Jumping and hopping: skips on alternating feet, maintaining balance
5-6 yr
Which reflex begins at 6-9 months and persists?
forward parachute/protective extension forward
when do midline skills emerge?
9-12mo
at what age do we expect to see simple rotation?
2-2.5 yr
at what age do we expect to see finger-to-palm translation?
12-15 mo
Which reflex begins at 9-10 months and persists?
backward parachute/protective extension backward
Sitting: Equilibrium reactions are present Able to rotate upper body while lower body remains stationary Protective responses are present when falling to side
7-8 mo
when does an inferior pincer grasp typically develop?
9 mo
Period of natal development: visual processing occurs
second trimester
at what age do we expect to see static tripod posture?
3.5-4 yr
when does a scissors grasp typically develop?
8 mo
Scissor skills:
cuts simple figure shapes
4-6 yr
age of the fetus or newborn, in weeks, from first day of mother’s last normal menstrual period
gestational age
Standing: when held in standing, legs may give way
2-3 mo
Sitting: Sits alone steadily, initially with wide base Able to play with toys in sitting
5-10 mo
at what age do we expect to see digital-pronate grasp?
2-3 yr
Which reflex begins at 32 wks gestation and integrates at 2 months?
galant
several objects are held in the hand and manipulation of 1 object occurs, while simultaneously stabilizing others
in-hand manipulation with stabilization

static tripod posture
Scissor skills:
manipulates scissors in a forward motion
coordinates the lateral direction of the scissors
cuts a straight forward line
cuts simple geometric shapes
3-4 yr
Walking: stoops and recovers in play
10-14 mo
Release: one-stage transfer (taking hand and releasing hand perform actions simultaneously)
6-7 mo
a linear movement of an object on the finger surfaces to allow for repositioning of the object relative to the finger pads
shift
Standing: When held in standing, takes some weight on legs
0-3 mo
child is driven to challenge sensorimotor competencies through roughhouse play, playground activitivies, games, sports, music, etc. Developmental age?
3-7 yr

digital-pronate grasp
Sitting: Rises from supine position by first rolling over to stomach then pushing up into 4-point position
9-18 mo
Release: Releases into a container with wrist straight
9-10 mo
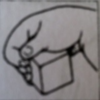
palmar grasp
Jumping and hopping: gallops, leading with one foot and transferring weight smoothly and evenly
3-4 yr
Walking: cruises sideways
8 mo
Standing: increased capability to bear weight decreased support needed legs are still spread apart and turned outward bounces in standing
5-6 mo
Release: precise, controlled release into small container with wrist extended
12-15 mo
symbolic gesturing and vocalization promotes ideation, indicating the ability to conceptualize. Developmental age?
13-24mo
What age is this child?
- Child recruits the help of an adult to achieve a goal
- Child attempts to activate a simple mechanism
- Child turns and inspects objects
- Child uses trial and error approach to new challenges
12-15 mo
Which reflex begins at 28 wks gestation and integrates at 9 months?
plantar grasp
At what age do we expect to see creative play?
4-7 yr

scissors grasp
Jumping and hopping: jumps off floor with both feet
3 yr
Creeping: creeps well
11-12 mo
Stimulus: place examiner’s finger in the infant’s palm Response: finger flexion; reflexive grasp
palmar grasp
the rotation of an object 360 degrees (e.g. turning a pencil over to erase)
complex rotation
In prone: begins to dislike prone
9 mo
In prone: shifts weight on forearms and reaches forward bears weight and shifts weight on extended arms legs are closer together and thighs roll inward toward natural alignment hips are flat on surface equilibrium reactions are present
5-6 mo
Stimulus: hold infant suspended vertically and tilt slowly to the side, forward, or backward Response: upright positioning of the head
labyrinthine/optical head righting
Release: releases above a surface with wrist flexion
8 mo

primitive squeeze grasp
Release: no release grasp reflex is strong
0-1 mo
Stimulus: place examiner’s index finger inside the infant’s mouth with head in midline Response: strong, rhythmical sucking
suck-swallow
Stimulus: place infant in prone Response: increased flexor tone
tonic labyrinthine prone
when does a inferior scissors grasp typically develop?
7 mo
Stimulus: Quickly but firmly tip infant off-balance to the side while in the sitting position Response: arm extension and abduction to the side
sideward parachute/protective extension sideward
Period of natal development: touch is functional
third trimester
when does a pincer grasp typically develop?
10 mo
Standing: pulls to standing at furniture
6-12 mo
Which reflexes begin at 37 wks gestation and integrate at 4-6 months?
asymmetric tonic neck and palmar grasp
Oral-motor development:
jaw and tongue movements are strong enough to allow for feeding
35 weeks gestation
Oral-motor development: rooting reflexes, gag and cough reflex are present
40 weeks gestation
Oral-motor development: munching occurs consisting of a phasic bit and release of a soft cookie
4-5 months
Oral-motor development: strong up and down movement of the tongue
6 months
Oral-motor development: beginning of mastication of soft and mashed foods with diagonal jaw movement
7-8 months
Oral-motor development: lateral tongue movements make mastication of soft and mashed food effective, able to drink from cup
9 months
Oral-motor development: jaw is firm; there is rotary chewing allowing for a good bite on a hard cookie
12 months
Oral-motor development: able to chew most meats and raw veggies
24 mo
Eating and feeding: takes cereal or poured baby food from spoon
5-7 mo
Eating and feeding: attempts to hold bottle but may not retrieve it if it falls; needs to be monitored for safety
6-8 mo
Eating and feeding: holds and tries to eat cracker but sucks on it more than bites it; consumes soft foods that dissolve; grabs at spoon but bangs it or sucks on end
6-9 mo
Eating and feeding: finger-feeds a portion of meals consisting of soft table foods
9-13 mo
Eating and feeding: dips spoon in food, brings spoonful to mouth, but spills food by inverting spoon
12-14 mo
Eating and feeding: scoops food with spoon and brings it to mouth
15-18 mo
Eating and feeding: demonstrates interest in using fork; proficient with spoon
24-30 mo
How old am I? Cooperates with dressing, pulls off shoes, removes socks, pushes arms through sleeves and legs through pants
1 yr
How old am I? removes unfastened coat, removes shoes if laces are untied, helps pull down pants, finds armholes in pullover shirt
2 yr
How old am I? removes pull-down pants with elastic waist, assists in pulling on socks, puts on front-button coat or shirt, unbuttons large buttons
2.5 yr
How old am I? puts on pullover shirt with min A, puts on shoes without fasteners (may be on wrong feet), puts on socks, independently pulls down pants, zips and unzips jacket once on track, needs assist to remove pullover shirt, buttons large front buttons
3 yr
How old am I? finds front of clothing, snaps or hooks front fastener, unzips front zipper on jacket, puts on mittens, buttons series of 3-4 buttons, unbuckles shoe or belt, dresses with supervision
3.5 yr
How old am I? removes pullover garment independently, buckles shoes or belt, zips jacket zipper, puts on socks correctly, puts on shoes with help tying, laces shoes, identifies front and back of garment
4 yr
How old am I? puts belt in loops
4.5 yr
How old am I? ties and unties knots, dresses unsupervised
5 yr
How old am I? closes back zipper, ties bows, buttons back buttons, snaps back snaps
6 yr
How old am I? indicates discomfort when wet or soiled, has regular BMs
1 yr
How old am I? sits on toilet when placed there and supervised
1.5 yr
How old am I? urinates regularly
2 yr
How old am I? achieves regulated toileting with occasional daytime accidents, rarely has bowel accidents, tells someone that he or she needs to go, may need reminders, may need help getting on toilet
2.5 yr
How old am I? goes to bathroom independently, may need help wiping, may need help with difficult clothing
3 yr
How old am I? is independent in toileting
4-5 yr
How old am I? imitates housework
13 mo
How old am I? picks up and puts toys away with reminders, copies parents
2 yr
How old am I? carries things without dropping them, dusts with help, dries dishes with help, gardens with help, puts toys away with reminders, wipes up spills
3 yr
How old am I? fixes dry cereal and snacks, helps with sorting laundry
4 yr
How old am I? puts toys away neatly, makes a sandwich, takes out trash, makes bed, puts dirty clothes in hamper, answers telephone correctly
5 yr
How old am I? does simple errands, does household chores without redoing, cleans sink, washes dishes with help, crosses street safely
6 yr
How old am I? begins to cook simple meals, puts clean clothes away, hangs up clothes, manages small amounts of money, uses telephone correctly
7-9 yr
How old am I? cooks simple meals with supervision, does simple repairs with appropriate tools, begins doing laundry, sets table, washes dishes, cares for pet with reminders
10-12 yr
How old am I? does laundry, cooks meals
13-14 yr
what does an Apgar score indicate?
newborn’s well-being
Behavior checklist and scale that assesses infant’s pattern of developing behavioral organization
Assessment of Preterm Infant’s Behavior (APIB)
rating scale including brief neurological exam incorporated into routine assessment; can be used with newborns in an incubator or on ventilator
Neurological Assessment of Pre-term and Full-term New-born Infant (NAPFI)
Standardized task performance and observation screening tool for early identification of children at risk for developmental delays in 4 areas, including personal-social, fine motor-adaptive, language, and gross motor
Denver Developmental Screening Test II
Standardized rating scales that assess cognition, language, motor, social-emotional, and adaptive skills; Age 1-42 months
Bayley Scales of Infant Development
Checklist and rating scale that identifies preschool students at risk and in need of more comprehensive evaluation
First STEP Screening Test for Evaluating Preschoolers
Non-standardized scale of developmental levels that assesses 6 areas of function, including cognitive, language, gross and fine motor, social-emotional, and self-help
Hawaii Early Learning Profile
Screening tool that assesses sensory and motor abilities cognitive abilities, and complex tasks
Miller Assessment for Preschoolers
Assesses capabilities and detects functional deficits to determine developmental level, monitor child’s progress
Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI)
index of overall motor proficiency, including speed, duration, and accuracy
Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency (BOT-2)
Assesses involuntary arm-hand patterns, voluntary movements of approach, and prewriting skills
Erhardt Developmental Prehension Assessment (EDPA)
Standardized rating scales of gross and fine motor development, birth to 6 years old
Peabody Developmental Motor Scales
Assesses quality of movement in children 0-3.5 yrs
Toddler and Infant Motor Evaluation (TIME)
Assesses visual-motor integration, ages 2-100
Beery-VMI
Assesses visual perceptual skills and visual motor integration; includes 8 subtests
Developmental Test of Visual Perception (DTVP-2)
Assessment of visuomotor development, including eyelid reflexes, pupillary reactions, voluntary patterns
Erhardt Developmental Vision Assessment (EDVA)
quick evaluation of visual perception (excludes motor components)
Motor-Free Visual Perception Test (MVPT-3)
Evaluation of spatial deficits, due to hemi-field visual neglect or abnormal visual saccades
Motor-Free Perception Test-Vertical (MVPT-V)
Assesses eye-hand coordination skills for copying geometric designs
Test of Visual-Motor Skills (TVMS)
Measures reactions to daily sensory experiences
Sensory Profile
Determines severity of autism and distinguishes children with autism from those without
Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS)
Assesses functional performance in order to promote participation in a school environment
School Function Assessment
opacity, clouding of lens due to changes in lens proteins; results in gradual loss of vision; central first, then peripheral; increased problems with glare; surgery is effective
cataracts
increased intraocular pressure with degeneration of optic disc and atrophy of optic nerve; early loss of peripheral vision; surgery and medication are effective if diagnosed early
glaucoma
loss of central vision associated with increased sensitivity to glare; may progress to total blindness
macular degeneration
damage to retinal capillaries leads to retinal scarring and finally detachment; central vision is impaired; vision is blurred; complete blindness is rare
diabetic retinopathy
loss of 1/2 visual field in each eye; corresponds to side of sensorimotor deficit; result of CVA
homonymous hemianopsia


