Howden - IBD Flashcards
What is the standard for determining abnormal bowel movements?
- Compare to the pt’s normal -> a change in bowel mvmts is what is important, rather than a variation from the “normal”
20-yo man with 3-4 months of bloody diarrhea.
What is the differential diagnosis?
- IBD: ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s
- Infectious disease: bacterial or parasitic -> kind of a long history (recent foreign travel would move this higher up)
-
Cancer could also present like this, but usually toward constipation -> unlikely in this young guy
1. 2nd-degree relative w/colon cancer, esp. if developed later on in life, probably has no real impact (grandfather at 70 in class example)
20-yo man with 3-4 months of bloody diarrhea.
What tests does he need?
- STOOL STUDIES: exclude infectious cause of bloody diarrhea (dysentery)
1. Can be bacterial (e.g. Shigella) or parasitic (i.e. amebic) - ENDOSCOPIC EVAL OF COLON: helps to establish presence of mucosal inflammation
1. May help to make diagnosis of IBD and to distinguish UC from Crohn’s disease
2. Can address concern about cancer in specific pts, although not major concern with young guy - REMEMBER: potentially giving CCS to pt with UC -> don’t want to give these w/o ruling out infection
What is going on in these 2 images?

- LEFT: normal-appearing colon
1. Vascular pattern: should be able to distinguish these submucosal blood vessels very clearly - RIGHT: ulcerative colitis (endoscopic features) -> edematous, inflamed, so more stuff b/t blood vessels and surface
1. Can see margin in top right-hand corner here; distinctive of UC to have abrupt change from abnormal to normal
What are the endoscopic features of ulcerative colitis?
- “Always” involves the rectum
- Loss of vascular pattern
- Erythema, granularity, friability, exudates, bleeding
1. Don’t expect to see a bunch of ulcers; usually don’t with UC - Contiguous involvement –> no “skip” lesions
- Variable amount of colon involved
How does smoking affect UC risk?
- UC typically occurs in non-smokers
- Strong, consistent relationship; we don’t know why
How does family history of colorectal cancer in a second-degree relative above the age of 60 effect an individual’s personal risk of colorectal cancer?
This has minimal effect on this person’s risk
What do you see here?
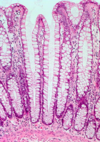
- Normal colonic epithelium: irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) can present like this
- IBS is characterized by chronic, relapsing abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits
- Despite very real symptoms, gross and microscopic evaluation is normal in most IBS patients
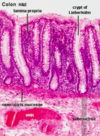
What do you see here?

- Ulcerative colitis: isolated islands of regenerating mucosa often bulge into the lumen to create PSEUDOPOLYPS
What is this?
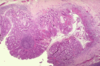
- Ulcerative colitis: isolated islands of regenerating mucosa often bulge into the lumen to create PSEUDOPOLYPS
- Biopsy is going to be much smaller than the image shown here (and more superficial)
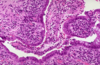
What is going on here? Arrows?

- Active colitis: crypt rupture + neutros attacking crypts + crypt abscesses
- Both UC and Crohn’s can have acute inflammation
- Crypt abscesses can rupture, making granuloma: this could be Crohn’s OR UC
- All you can dx from this image is ACTIVE COLITIS
What is going on here?

- Active colitis: ruptured crypts + crypt abscesses
- Chronic active colitis is consistent with IBD: could be UC or Crohn’s -> architectural changes indicate chronicity
- In UC, inflammatory process diffuse and generally limited to mucosa and superficial submucosa
- If granulomas are seen, and not associated with crypt rupture, can say this is suggestive of Crohn’s
What is this?

- Toxic megacolon: inflammation and inflammatory mediators can damage the muscularis propria and disturb neuromuscular function in ulcerative colitis
- Leads to colonic dilation and toxic megacolon, which carries a significant risk of perforation
This is acute colitis in a UC patient; what else is present (arrow)?
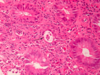
- CMV: pts with UC or Crohn’s are essentially immunocompromised via tx, so they can get CMV, which can also cause acute colitis
- Can do immunostain for CMV too
- CMV likes vessel walls/endothelium

What are the risk factors for dysplasia arising from UC and Crohn’s?
- Long-term complication: colitis-associated neoplasia
- Risk of dysplasia is related to several factors:
1. DURATION of the disease: risk INC sharply 8-10 years after disease onset
2. EXTENT of disease: pts with pancolitis are at greater risk than those w/only left-sided disease
3. Nature of the inflammatory response: greater freq and severity of active inflam (characterized by presence of neutrophils) confers INC risk
What is going on in this box? How can you tell? Arrows?

-
Dysplasia in a case of long-standing UC:
1. LEFT: active colitis
2. RIGHT: dysplasia via chronic architectural changes and distortion -> hyperchromasia, and cigar-shaped, long nuclei - Surveillance biopsies to identify dysplastic epithelium, which is a precursor to colitis-associated carcinoma
20-yo man with 3-4 months of bloody diarrhea. Dx’d with UC. Tx?
- Start on mesalamine (5-aminosalicylic acid; 5-ASA) orally and rectally: anti-inflammatory effects in colon
- Can stop rectal mesalamine when symptoms improve (no more rectal bleeding)
- Continue taking oral mesalamine only
20-yo man with 3-4 months of bloody diarrhea. Dx’d with UC. What does the future hold?
- Likely to be a chronic process with relapses and remissions
- If diagnosed as left-sided, likely to stay that way; only a minority develop pancolitis
- Should stay on oral mesalamine: safe, and likely to control inflammation in the colon
1. Could do short-dose of CCS if disease was severe to put patient into remission - Risk of colorectal cancer starts to INC above that of age- and sex-matched population after 8-10 yrs of dx; surveillance
When is a colectomy indicated in pts with UC?
- With very severe symptoms (don’t really do partial colectomies: all or nothing)
1. Absolute indications: cancer or dysplasia
2. Relative indications: failure of med therapy, fed-up with UC, or worried about cancer - Not an easy decision, and has to be discussed in detail
- Surgery rarely an issue for people with left-sided disease
What is likely going on here?

- Air-fluid levels: shouldn’t see more than a couple of these in a normal, healthy person (and shouldn’t be this well-defined)
- Multiple is suggestive of some OBSTRUCTIVE PROCESS (characteristic appearance)
- This is taken in upright position
Young woman. Hx of abdominal pain and diarrhea. Now presents with worse pain, abdominal distension and vomiting.
What is going on? Tests?
- Picture of small intestinal obstruction
1. Crohn’s usually starts in teens, 20’s, 30’s in terminal ileum - Give IV fluids (nothing by mouth), nasogastric tube for decompression, gradually advance diet if symptoms resolve
- Dr. H presented the following tests:
1. Enterography
2. Colonoscopy
3. Biopsy
What is going on here? Arrows?

- Abnormal appearing, thickened and narrowing of distal small bowel (small bowel enterography: special type of CT)
- Arrows: ascending colon, small intestine, and narrowing in distal ileum (stricture)
What do you see here?

- Ulceration of the terminal ileum: similar to apthous ulcers seen in the mouth
What is going on here?
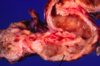
-
Crohn’s disease: intestinal wall is thickened and rubbery as a consequence of:
1. Transmural edema,
2. Inflammation,
3. Submucosal fibrosis, and
4. Hypertrophy of the muscularis propria, all of which contribute to stricture formation - Note the dilatation proximal to the stricture
- Compare to normal (attached)
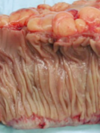
What do you see here?

- Crohn’s disease: FISSURES
- Develop between mucosal folds, and may extend deeply to become:
1. Fistula tracts or
2. Sites of perforation: image on the left (outside view of colon) - Transmural inflammation: way too blue in submucosa
What is going on here?
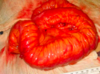
- Crohn’s disease: CREEPING FAT -> mesenteric fat extends around the serosal surface (2o to extensive transmural disease)
- Compare to normal (but ischemic) bowel attached here

What are the microscopic features of Crohn’s disease?
- Abundant neutrophils that infiltrate and damage crypt epithelium
- Clusters of neutros in a crypt called crypt abscesses and are often associated with crypt destruction
- Ulceration common, and may have abrupt transition between ulcerated and adjacent normal mucosa
- Active colitis in the attached image: can’t really tell difference between UC and Crohn’s here

What is going on here?
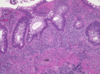
- Micro features of active Crohn’s disease: repeated cycles of crypt destruction and regeneration lead to architectural distortion (UC can present like this too)
- CHRONICITY due to repeat cycles of inflammation and destruction
- Dilated, torturous, and almost spreading horizontally

What is this?

-
Non-caseating granuloma: hallmark of Crohn’s disease (usually “loose,” and giant cells help confirm diagnosis)
1. Found in approximately 35% of cases - May occur in areas of active disease or uninvolved regions
- Absence of granulomas does NOT preclude a dx of Crohn disease
- Histiocytes loosely aggregated together
Before diagnosing a pt with Crohn’s, what meds do we need to ask about?
- NSAID’s
- Can cause ulcers throughout GI tract, including in small intestine
- Can also cause scarring and narrowing
- These meds can also make pts with Crohn’s go from remission to relapse
What might you also need to think about in a pt with sm intestinal obstruction if they had been raised in Pakistan, and just moved to the US?
Intestinal TB
Long-term expectations for young woman with Crohn’s affecting terminal ileum and no evidence of colonic or prox small intestinal involvement?
- Can expect course of relapses and remissions
- May initially be treated with CCS (short and sharp), but ultimately will probably need immunosuppressant (Azathioprine) and/or disease-modifying biological agent (anti-TNF Mab’s) to maintain remission
- No need for surgical intervention at this stage
1. Will never be cure for Crohn’s, but tx options exist for people with localized complications like fistulas and/or strictures
How can you distinguish UC from Crohn’s (table)?
- Smoking
- GI tract involvement
- Distribution
- Distribution of inflammation
- Granulomas on biopsy
- Fistual formation
- Stricture formation
- Risk of colon cancer



