Histology: Nerve Tissue Flashcards
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
- Cranial Nerves
- Spinal Nerves
- Ganglia
Neuron
- Functional unit of nervous system
- Specialized to receive and transmit electrical impulses
3 Main Parts:
- Cell body
- Dendrites
- Axon
Classified Based on Shape:
- Multipolar
- Bipolar (one axon and one dendrite)
- Pseudounipolar (one process that divides into two)
Cell Body

- Nucleus and organelles
- Prominent nucleolus
- Highly developed RER and many free polyribosomes (Nissl substance)
- Basophilic staining
Dendrites

- Shorter, smaller process
- Typically immerge from soma in multipolar
- Receive information from other neurons
- Unmyelinated
- Can form dendritic trees to increase surface area
- Lack Golgi (do not secrete proteins)
Axon

- Every neuron has one axon
- Transmit stimuli to other neurons or effector cells
-
Axon Hillock
- Pyramidal-shaped region of the cell body where axon originates
- Where action potentials are generated (high concentration of Na+ ion channels)
- Lack RER or polyribosomes (all proteins must be shipped from cell body)
Bipolar Neuron
- Dendrite on one end
- Axon on other end
Unipolar Neuron
- Axons and dendrite arise from same extension of cell body
- Sensory Nerves
Multipolar Neuron
- Multiple dendrites arise from cell body and single axon
Resting Membrane Potential
- Nerve plasma membrane contains Na+/K+ ATPase pumps
- Pumps 3 Na+ ions out of the cell
- Pumps 2 K+ ions into the cell
- Creates resting potential
- Difference in voltage across the membrane
- Inside of cell is negatively charged relative to outside (-65 mV)
Action Potential
- Brief, rapid depolarization of the resting membrane potential due to rapid influx of Na+ ions
- Generated at axon hillock (rich in voltage-gated Na+ channels)
- Propagated along axon as a “wave of depolarization”
- Myelinated fibers use saltatory conduction to increase speed of propagation
Synapses

- Neuron contacts another neuron or effector signals
- Converts electrical signal into chemical signal
- Presynaptic axon terminal (terminal bouton)
- Contains vesicles with neurotransmitter
- Postsynaptic membrane
- Contains receptors for neurotransmitter and ion channels
Types of Synapses:
- Axosomatic
- Axodendritic
- Axoaxonic
Electrical Synapse
- Impulse conducted by Gap Junctions
Synaptic Transmission
- Action potential reaches axon terminal
- Depolarization of axon terminal membrane opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
- Ca2+ influx causes fusion of synaptic vesicles with presynaptic membrane
-
Neurotransmitter exocytosed and binds post-synaptic receptors
- Can cause depolarization or hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane
- Generation of action potential in posynaptic cell depends on summation of all excitatory and inhibitory impulses
Neurotransmitters
- Small molecules that bind receptor proteins
- Ionotropic receptors are ligand-gated ion channels
- Metabotropic receptors are G-protein coupled receptors (second messenger cascade)
Excitatory NTs:
- Acetylcholines (e.g. neuromuscular junctions)
- Glutamate
Inhibitory NTs:
- GABA
- Glycine
Axonal Transport
- Transport of materials between nerve cell body and axon
- Occurs along microtubules by ATP-powered motor proteins
Anterograde Transport
- Transport from cell body to axon via Kinesin
Retrograde Transport
- Transport from periphery toward cell body via Dynein
Neuroglia Cells

- Support cells
- 10x more abundant than neurons
- Occupy space between neurons (similar to CT)
-
Neuropil
- Resembles ECM of CT
Types of Glial Cells
CNS:
- Oligodendrocytes
- Astrocytes
- Ependymal Cells
- Microglial
PNS:
- Schwann Cells
- Satellite Cells
Oligodendrocytes

-
Produce myelin sheath
- Can myelinate many axons via sheet-like processes that wrap around axons multiple times
- Round, condensed nucleus; cytoplasm does not stain in H&E due to abundant golgi
Astrocytes

- Most numerous glial cells in CNS
- “Have to baby neurons”
- Star-shaped cells with radiating cytoplasmic processes
- Cytoskeleton composed of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP)
- Allows visualization via staining
Functions:
- Structural and metabolic support
- Recycle NTs
- Maintain blood-brain barrier
Ependymal Cells

- “Epithelial-like” that line ventricles and central canal
- Cuboidal or columnar cells
- Joined with junctional complexes
- No basal lamina; basal ends extend processes into neuropil
- Surround capillaries to form choroid plexus (produce CSF)

Microglia

-
Phagocytic cells of CNS
- Originate from monocytes
- Provide immune defense in CNS

Schwann Cells

-
Produce myelin in the PNS
- Each cell myelinates only one axon
- LM: appear oval nuclei within CT of nerve
Myelinated Nerves
- Multiple concentric layers of Schwann cell plasma membrane
Unmyelinated Nerves
- Axons embedded within cytoplasm of the Schwann cell
Myelin Sheath
- Plasma membrane concentric layers
- 80% lipids; 20% protein
Nodes of Ranvier

- Interface between myelin sheaths of adjacent Schwann cells
-
Axolemma exposed to ions in interstitial fluid
- High concentration of voltage-gated Na+ channels
- Saltatory Conduction


- Myelinated Axon EM

Unmyelinated Axon EM
- Small-diameter axons
- Conduction is slower
- Within surface invaginations of Schwann cell cytoplasm
Satellite Cells

- Surround nerve cell bodies in ganglia
- Maintain controlled microenvironment around nerve cells
Nerve Regeneration Step One
*Exclusive to PNS
-
Degeneration
-
Anterograde Reaction/Wallerian:
- Axons degenerates distal to injury and is phagocytosed
- Retrograde Reaction/Chromatolysis
- Cell body swells and nucleus moves to periphery
- Nissl substance diminishes
-
Anterograde Reaction/Wallerian:
Nerve Regeneration Step Two
- Regeneration
- Schwann cells form tubes around future axon growth
-
Axon sprouts enter tubes
- Axon sprouts that reach target form synapses
- Schwann cells form myelin sheath around new axons
Injury Repair: PNS vs. CNS
- No regeneration typically in CNS
- Limited ability to clean up debris in CNS (lack of macrophages due to BBB)

- Left Side: White Matter
- Mostly myelinated axons
- Right Side: Gray Matter
- Neuron cell bodies and neuropil
Meninges

- Dura Mater: Dense irregular CT
- Arachnoid Mater: loosely arranged trabeculae
- Pia Mater: flattened cells closely related to surface of CNS

Brain: Cerebral Cortex

- Gray Matter
- 6 Layers of Neurons
Brain: Cerebellar Cortex

- Gray Matter
- 3 Layers of Neurons
Spinal Cord

Gray Matter:
- Dorsal Horns
- Ventral Horns
White Matter:
- Myelinated axon tracts
Peripheral Nerve Coverings
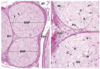
Endoneurium:
- Loose CT surrounding each axon and its Schwann cell
- Mostly reticular fibers
Perineurium
- Squamous perinueral cells
- Surrounds bundles of axons and Schwann cells
Epineurium
- Dense, irregular CT layer that surrounds nerve
Peripheral Nerve Longitudinal Section

- Wavy appearance
Ganglia

Collections of cell bodies in PNS
Autonomic Ganglia
- Multipolar neurons with eccentric neurons
Sensory Ganglia
- Pseudounipolar neurons with central nucleus
- Surrounded by satellite cells


