Histology Flashcards
what type of epithelium is Bowmans capsule
simple squamous epithelium
what are the 2 layers of Bowmans capule
parietal (outer) and visceral (inner) - podocytes

what are the 3 layers that separate the blood from the glomerular filtrate
- capillary endothelium - has pores
- basal lamina
- podocytes (Bowmans capsule) -

describe the structure of podocytes
have interdigitating cell processes forming filtration slits

what is special about the basal lamina in renal corpuscle
- thicker than usual
- forms a major part of the filtration component
mesangial cells
- scattered mesangial cells produce a connective tissue core called a mesangium
- these cells have several functions: support and removal of debris
- have contractile properties - resemble smooth muscle cells


what is the function of the renal corpuscle
production and collection of glomerular filtrate
what is the basal lamina like in the proximal convuluted tubule
large BL invaginations to increase surface area

proximal or distal convuluted tubules

proximal - they have an indistinct apical border

function of the loop of Henle
- create hyperosmotic environment in medulla - salts lost into interstitial spaces between tubes
- permeability to ions varies in differenet areas
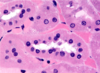
describe the histology of the loop of henle
- simple squamous epithelium in the thin limb, with nuclei protruding into the lumen (tl)
- simple cuboidal epithelial cells in the thick limb, with abundant mitochondria (TAL)

vasa recta
- thin walled blood vessels taht dip down into the medulla from cortex, and then climb back into cortex
- collectively called vasa recta
- branch from efferent arterioles
- run parallel to the loop of Henle

proximal or distal convuluted tubule
distal - no brush border

medullary rays
in the cortex, groups of straight tubules (straight segments of proximal and distal tubules and collecting ducts) run perpendicular to the surface of the kidney



what are the collecting ducts lined by
simple columnar epithelium
describe the epithelium changes in the nephron
- bowmans capsule - simple squamous
- proximal convuluted tubule - simple cuboidal with brush border
- loop of Henle - simple squamous
- thick ascending loop of Henle - simple cuboidal with mitochondria
- distal convuluted tubule - simple cuboidal
- collecting duct - simple columnar

what is the duct of Bellini
also known as papillary duct

describe the collecting and papillary duct drainage
- medullary collecting ducts form papillary collecting ducts
- these converge to form a central duct near the apex of each renal pyramid
- the papillary duct exits the renal pyramid at the renal papilla
- renal filtrate is drained into minor calyx as urine
- major calyx etc

what does the juxtaglomerular apparatus compose of
- macula densa
- juxtaglomerular cells
- extraglomerular mesangial cells

macula densa function
sense sodium ions
juxtaglomerular cell function
secrete renin, modified smoth muscle cells
what are Extraglomerular mesangial cells also called
lacis cells






