Anatomy of Lower Renal Tract Flashcards
outline the false pelvis

from iliac crests to pelvic inlet
which cavity is the false pelvis in
the abdominal cavity
outline the true pelvis
pelvic cavity
from pelvic inlet to pelvic floor

which muscles forms the pelvic floor
levator ani


coccygeus
which muscles form the pelvic floor
the levator ani and coccygeus
where do the ureters enter the pelvic cavity
at the area of the sacroiliac joints wehre they cross the pelvic brim
before they were in the retroperitoneal area

ischial spine
describe the course of the ureters in the pelvic cavity, and the effects of this
- run down the lateral pelvic walls
- at the level of the ischial spines, enter the bladder wall in an inferiomedial direction (oblique)
- this helps to prevent the reflux of urine back into the ureters when the bladder contracts - ureters collapse


pouch of Douglas
recto uterine pouch in females


how does the ureter run in relation to the uterine tubes and uterine artery
inferiorly - water under the bridge

how does the ureter run in relation to the vas deferens
inferiorly

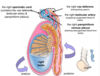
what are the functions of the bladder
- Temporary storage of urine
- Assists in the expulsion of urine


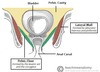
trigone
formed by the 2 ureteric orifices on the base and the internal urethral orifice on the floor

what is the muscle that forms the main bulk of the bladder wall
detrusor muscle
how do the bladder muscles prevenet reflux of urine superiorly into the ureter
detrusor muscle fibres encircle the ureteric orifices, these tighten when the bladder contracts

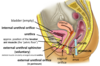
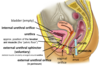
internal urethral sphincter
- in males, the detrusor muscle forms a sphincter around the necl of the bladder
- this contracts during ejaculation to prevent retrograde ejaculation of semen back into the bladder

in females, what is the weight of the uterus born by
the bladder



which surface of the bladder does peritoneum cover
superior
where does the bladder extend to
- can extend out of the pelvis - superior part lies superior to the pubic bone