Anatomy 3 Flashcards
(41 cards)
which muscles do somatic motor nerve fibres stimulate
skeletal muscles
how many pairs of spinal nerves are there
31
what is a ganglia
a bundle of nerve cell bodies outside CNS
how do sympathetic nerve fibres reach the body
within splanchnic nerves: cardiopulmonary and abdominopelvic

how do nerve fibres reach the body wall
- sympathetic within the spinal nerves - post synaptic fibres can enter any of the 31 pairs of spinal nerves
- no parasympathetic
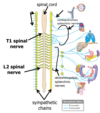
how do sympathetic nerve fibres reach the head
follow arteries which supply the same structures eg superior, middle and inferior cervical ganglia

describe the origin of the spinal nerves
- posterior ramus nerve fibres supplies deep muscles of back, intervertbral joints and overlying skin
- anterior ramus nerve fibres supply most of body - both motor and sensory

how do sympathetic nerve fibres get from CNS to kidneys, ureters and bladder
- leave the spinal cord between T10 and L2 and enter the sympathetic chains (bilaterally)
- leave the sympathetic chain in the abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves and synpase at the abdominal sympathetic ganglia which are located around the abdominal aorta
- post synaptic sympathetic nerve fibres pass from the gangllia onto the surface of the arteries which are heading towards the organs they will innervate

what is a periarterial plexus
collection of nerve fibres found on the outside of arteries
- sympathetic
- parasympathetic
- visceral afferent

which nerves are involved in the parasympathetic system
CN III, VII, X and IX
briefly sacral spinal nerves S2-4
how do parasympathetic nerve fibres get from CNS to kidneys, ureters and bladder
- parasympathetic nerve fibres for kidney and ureter are carried in CNX (down to splenic flexure)
- those innervating bladder are carried in pelvic splanchnic nerves

pelvic splanchnic nerves
- parasympathetic fibres reach the body structures of hind gut and pelvic organs through these
- carried in sacral spinal nerves briefly


which parts of the renal system are innervated by somatic motor fibres

those within the perineum eg the urethra (distal to pelvic floor) and its sphincter (external urethral sphincter and levator ani)
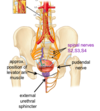
where is pain from the kidney itself felt
in the loin area - posterior aspect of flank region

where is pain felt from a calculus obstructing the ureter
radiate from loin to groin

where is pain from the bladder felt
suprapubic region - midline

where is pain from the perineal part of the urethra felt
usually quite localised in the perineum

how do visceral afferent fibres get from kidneys to CNS
- visceral afferents from the kidneys run alongside sympathetic fibres back to the spinal cord and enter between T11 and L1
- this is why pain is felt in these dermatomes

what is the main differential diagnosis of loin pain
muscular pain
how do visceral afferent fibres get from ureters to CNS
- run alongside sympathetic nerve fibres and enter spinal cord between T11 and L2
- pain felt anywhere along this path

DD of groin pain
hernia
lymphadenopathy
testicular pathology
how do visceral afferent fibres get from bladder to CNS

- visceral afferents carrying pain from the superior part of the bladder which touches the peritoneum run alongside sympathetic nerve fibres back to the spinal cord. enter between T11 and L2. pain is percieved in the midline
- visceral afferent fibres from the rest of the bladder that is not touching the peritoneum run alongside parasympathetic fibres back to spinal cord levels S2-4

how do visceral afferent and somatic sensory fibres get from urethra to CNS
- visceral afferent fibres from the proximal urethra (above levator ani and in pelvis) run alongside parasympathetic nerve firbes back to spinal cord levels S2-4
- somatic sensory from the remaining urethra are carried within the pudendal nerve back to spinal cord levels S2-4
- pain from this part of the urethra will present as localised pain in the perineum















