Hematopathology Review Flashcards
(11 cards)

B = aka atypical lymphocyte (seen in reactive lymphocytosis like mono)
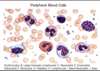

reactive/atypical lymphocyte (viral or infection)

normal bone marrow aspirate

essential thrombocythemia (larger platelets, more of them)

acute myeloid (more cytoplasm, auer rod)
acute Lymphoid leukemia (lots of blasts, but less cytoplasm in them indicate lymphoid origin)
which leukemia is associated with phildelphia chromosome presence?
9;22 is associated with CML. Phildelphia chromosome must be confirmed in order to diagnose with CML.

seeing some basophils, some granulation, most likely a myeloid issue. basophilia is indicative of CML.
a person presents with abnomrla megakaryocytes, tear drop cells, and is anemic with leukocytosis and has a lot of thrombocyte. JAK2 positive. Dx?
primary myelofibrosis– often occurs after polycythemia vera. scarring of bone marrow is occurring.

what is a leukoerythroblastic picture
lots of immature RBC and WBC– occurs when there is severe marrow stress and has increased RBC, increased WBC (thrombocytosis)

neoplastic hyperlobed megakaryocytes.
seen in essential thrombocythemia.

smudge cells present, soccer ball cell on the other side.
- indicates chronic lymphoblastic leukemia


