CPC: Pathology of the Esophagus Flashcards
(34 cards)

normal tissue of the esophagus
what is the normal epithelium of the esophagus
squamous eptihelium (stratified)
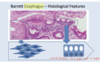
Columnar cells are more resistant to acid and pepsin and the metaplasia may be a defense against refluxed acid. In Barrett’s, the cells are usually of a type referred to as specialized columnar epithelium (a distinctive type of intestinal metaplasia). They include mucus cells, and have a tendency to resemble cells found in the small intestine.
Squamous epithelium, seen in the esophagus and skin, consists of layers of flat cells. Columnar epithelium, characteristic of the rest of the gut, consists of a single layer of tall, rectangular cells. In Barrett’s esophagus, the normally squamous epithelium of the lower esophagus becomes replaced with various types of columnar cells, that may predispose to a type of cancer known as adenocarcinoma.

stratified squamous epithelium non-keritinized

normal stomach– see all the ducts
what cells of the stomach?

mucous cells– see goblets
what part of the GI?

small intestine– tons of villi and microvilli have a brush boarder

what cells of the GI?

large intestine. less villous and more gladular.
what part of the GI?

appendix–see the galt– lymphoid tissue.
T/F anal epithelial looks the same as esophageal
true. they are both stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium.

barretts esophagus involves the change from normal ____ epithelium in the esophagus to ____.
squamous to cuboidal. can become a carcinoma.
a person suffering from severe heart burn that is now affecting his ability to swallow had a biopsy and esophagus is found to look like this. what is going on?

neoplasia– change into cuboidal. there are also more ducts and goblet cells. cuboidal cells are more ersistant to acid and can secrete their own mucus.

Columnar cells are more resistant to acid and pepsin and the metaplasia may be a defense against refluxed acid. In Barrett’s, the cells are usually of a type referred to as specialized columnar epithelium (a distinctive type of intestinal metaplasia). They include mucus cells, and have a tendency to resemble cells found in the small intestine.
Squamous epithelium, seen in the esophagus and skin, consists of layers of flat cells. Columnar epithelium, characteristic of the rest of the gut, consists of a single layer of tall, rectangular cells. In Barrett’s esophagus, the normally squamous epithelium of the lower esophagus becomes replaced with various types of columnar cells, that may predispose to a type of cancer known as adenocarcinoma.
note the pathophysiological concepts of carcinoma:
– Metaplasia in response to chronic inflammation
• Esophagitis Barrett Esophagus
– Inflammation-dysplasia-carcinoma sequence
• Inflammatory Bowel Disease Dysplasia Colonic
Adenocarcinoma
– Polyp-cancer sequence
• Colon adenoma Colonic adenocarcinoma

what is metaplasia
the reversible change in which one differentiated cell type (epithelial or mesenchymal) is replaced by another cell type. usually in response to injury. in the esophagus, chronic GERD can results in squamous epithelium being replaced with cuboidal because it’s better with dealing with acid.
4 broad causes of ESOPHAGITIS
- Chemical (Gerd, pills/medication without sufficient fluids, irradiation, caustic/corrosice/acidicc material)
- infectious (CMV, Herpes, EBV, fungal like candida)
- graft vs host
- immunoallergic (eosinophilic esophagitis)

esophagitis
Gross: Hyperemia (redness) +/- ulceration (loss of epithelium) Location: ex. GERD - lower; Infectious - anywhere Severity: Ulceration more common with more severe injury
what white cells might you see in someone with esophagitis
neuotrophils, eosinophils.
might see basal cell apoptosis, atrophy and fibrosis
- if it’s due to an infectious cause, you might see ulceration adn the cause of the infectious agent (like hyphae of the fungal infection)
which part of the esophageal epithelum is normal?


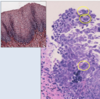
herpes esophagitis

a person with CMV esophagitis will most likely have ___ chromatin and ulceration with reactive ___ eotihelium. inclusions on the tissue will show ___ ____ ___
a person with CMV esophagitis will most likely have SMUDGED chromatin and ulceration with reactive SQUAMOUS eotihelium. inclusions on the tissue will show VIRAL CYTOPATHIC EFFECTS

risk factors fo GERD
obesity, pregnancy, alcohol and tobacco use, hernia, delayed gastric emptying can decrease the function of LES and allow acid to affect the esophagus.

outline what is going on with these 3 biopsies of different esophagus’s

- normal
- GERD– there is more metaplasia– mild basal zone expansion in yellow area and. abnormal squamous maturation, with som e intrapeithelial inflammatory cells (occasional eosinophils, more lymphocytes)
- eosinophilic esophagitis (inflammation and way more eosinophils)
treatment of GERD
PPIs, H2 receptor antagonists, lifestyle changes.
watch for stricture, progrssion to barrets esophagus through metaplasia, bleeding etc.
what demographic is affected more by eosinophilic esophagitis?
children–usually young men like teenagers. it is now being recognized in younger adults.