Blood Lab 2 Flashcards

normal BM aspirate smear
67 yrs. old woman, presented with 2 months history of weakness, weight loss (20 Lbs ), fever, night sweats and “knots” in her neck.
Which ONE of the following will be most helpful in the diagnosis.
A-CT scan B-Chest X-ray C- Lymph node biopsy D- Bone marrow biopsy
C.
Should do bone marrow biopsy for staging, not a starting poiint for lymphoma.
histological features of celiac disease
lymphocyte infiltration
villous blunting

Hodgkins lupmhoma– there are reed sternberg cells

reed-sternberg cells
Q: Diagnosis and subtyping of Lymphoma require which of the following laboratory techniques
A-Tissue biopsy H&E & Immuno- peroxidase staining
B-Flow-cytometry
C-Molecular techniques like PCR and flourescent in-sity hybridisation (FISH).
D- All of the above
D
What does the peripheral blood smear on this patient show?

rouleaux formation (hyper igG and IgM)– look for multiple myeloma
which one is most likely to be multiple myeloma (you saw rouleaux on the PBS)

A= plasma cells
B= neutrphils– neutrophilia– reactive vs neoplastic (hematological malignancy due to myeloproliferative (CML, PV, ET , Primary myelofibrosis vs metastatic acute leukemia)
C= lymphocytes
D= more plasma cells
multiple myeloma was confirmed on a patient wiht rouleaux. Serum protein electrophoresis was ordered. what do you expect to see on SPEP?
monoclonal banding– all th eB cells producing the same (but random and not functioning) immunoglobulin.

62 year old man, presented with pancytopenia. what is the most concerning on the blood report?

presence of blasts. big red flag. acute leukemia until proven otherwise.

B= it’s a blast. not a lymphocyte
a person with this cell on the PBS most likely has:
AML– multiple auer rods.
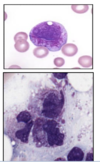
which bone marrow aspirate most likely represents a patient with AML?

B. more homogenous. tons of myeloid lineage progenitors. A has a bunch of different types of cells/
What is the most likely diagnosis?
An 81 yrs. old woman presented with pallor & petechial hemorrhages and lymph node enlargement. Examine CBC repor

CLL– chronic lymphocyte leukemia. Lymphocytes are high and smudge cells are characteristic with CLL. Probably due to B cell hyperproliferation.
what are smudge cells and whcih cell represents a smudge cell?

they are fragile degenerated CLL cells. A represents a smudge cell.

after looking on the PBS and seeing smudge cells and a lot of lymphocytes, what is the next investigation that should be done to confirm CLL?
chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- flow cytometry (can see B vs T cell)
B cell function– immunoglobulin levels and vaccine titers
- bone marrow biopsy?

C represents CLL.
- soccer ball cell lymphocytes
- smudge cells.
A is a normal blood smear
B= super huge cells. idk what this is. blasts? myeloid immature cells? acute leukemia
C= plasma cells. more likely to be hodgkins ( b cell with reed-sternberg cells) or DLBCL non-hodgkins.
52 yrs. old man,, presented with pallor, weakness and bulge in left upper belly. Examine CBC report
what is the most likely diagnosis?

there is a really high platelet count and a high WBC count. Neutrophilia is present– could be reactive or neoplastic causes CML, PV, ET, Primary myelofibrosis, or acute leukemia.
blasts are present but the percentage is low compared to WBC. probably is not as acute as we think.
Not CLL because lymphocyte count is normal
chronic myeloid leukemia: neutrophila.
what tests to run to confirm CML
PBS + CBC
FISH for philedelphia chromosome. (9;22)–> required for CML diagnosis
OR BCR-Abl1 detection PCR studies.
which is most likely suggestive of chronic myeloid leukemia?

A= some degree of maturation, lots of stippling and basophils as well as banded neutrophils
B= normal. neutrphils, dividing cells, mixed and non-homogenous. normal bone marrow
C. lots of lymphocyte or blasts. most likely an acute leukemia because of immaturaty.

42 yrs. old woman, with pallor, weakness and splenomegaly
what does this CBC data support?

- anemic
- low platelets: thrombocytopenic.
tear drop cells– trying to squeeze out of the bone marrow.
- myelocytes = immature myloid cells.
nucleated red cells. immature rbc.
supports bone marrow stress/bone marrow cancer, infiltrates, or a leuko-erythroblastic features
what is a leukoerythroblatic picture
- increase in immature RBCs and WBC seen in differential and on blood film…caused by marrow infilitartion, severe marrow stress.
often due to cancer of the bone marrow.
label the following cells

- tear drop cells.
- nucleated red cell
- abnormal platelet
- tear drop cell
- blast or atypical lymphocyte
- giant platelet.


