Final Exam - Urinary System Flashcards
(76 cards)
Identify the tissue.
kidney
The functional unit of the kidney is the __________
nephron
The __________ includes the glomerulus and all tubule segments through the connecting segment
nephron
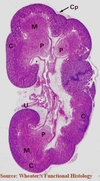
Identify the structures labeled ‘G’ in this H&E section of the renal cortex

glomeruli
Identify the structrures indicated by the arrows in this section of the kidney

renal corpuscles
**These are a distinctive feature of kidney cortex
_____________: network of capillaries that perform the first step in filtering blood
glomerulus
_____________: functional unit of the kidney; site of osmoregulation via filtration of small molecules from blood plasma to form a filtrate and selective reabsorption of most of the water and other molecules from the filtrate; = glomerulus + all tubule segments
nephron
_____________: end of the glomerular capsule where the afferent arteriole enters and the efferent arteriole exits
vascular pole
_____________: end of the glomerular capsule opposite the vascular pole where the proximal convoluted tubule begins
urinary pole
_____________: specialized cells of the distal convoluted tubule adjacent to specialized smooth muscle cells (juxtaglomerular cells) of the afferent and efferent arterioles
macula densa
_____________: specialized smooth muscle cells of mainly afferent and to a lesser degree efferent arteriole; detect variations in blood pressure (baroreceptors) and secrete renin into vessel lumen
juxtaglomerular cells
__________: aa. and vv. within the kidneys
arcuate vessels
__________: arteriole bringing blood to glomerulus
afferent arteriole
__________: arteriole draining blood from glomerulus
efferent arteriole
__________: phagocytic, contractile cells that have receptors for angiotensin II and ANP and provide some structural support to capillaries
mesangial cells
_________: first portion of proximal tubule; numerous twists and turns in cortical area; high level of microvilli on epithelium
proximal convoluted tubule
_________: ducts into which collecting tubules drain; lumen contains urine of varying concentration; terminal portions are papillary ducts which empty at area cribosa of the renal crest of papilla
collecting ducts
Describe the effect of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) on collecting ducts
ADH stimulates aquaporins in the ducts to allow reabsorpbtion of water and other molecules
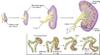
Explain the action of renin/angiotensin following substantial hemorrhage
activated in response to a substantial drop in blood pressure in an effort to restore normal blood pressure
What are the 2 components of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
macula densa and juxtaglomerular cells
macula densa cells are chemoreceptors that sense Na+ concentration in the filtrate
juxtaglomerular cells are baroreceptors that secrete renin into the lumen of the afferent (and somewhat into the lumen of the efferent) arteriole
List the principal cells associated with the renin-angiotensin cascade.
kidney – secretes renin; inc. Na+ reabsorption in response to aldosterone
liver – stores angiotensinogen
lungs – site of action of angiotensin I and conversion to angiotensin II
bloodstream – circulates and transports angiotensin II to adrenal glands
adrenal cortex – secrete aldosterone
Kids Like Leron Breathe Air
What are the two main regions of the kidney?
cortex & medulla
Identify the structures indicated by the arrows in this cross-section of the kidney.

Renal Corpuscles
Renal corpuscles are a distinctive feature of kidney cortex.
Identify ‘A’ in this section of the kidney

Podocyte cell body & nucleus