Final Exam - Respiratory System Flashcards
What are the three components of the respiratory system?
- Conductive system
- Transitional system
- Gas exchange system
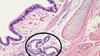
These are thin-walled structures enveloped by a rich network of capillaries: the pulmonary capillaries.
alveoli
Identify.

alveoli
Identify the H&E section pictured here.

The respiratory portion of the nasal cavity
lined by ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells
What structure is indicated by the arrow in this H&E section of the nasal cavity?

tubulo-alveolar glands
mainly serous, with lesser numbers of mucous and mixed glands.
Which region of the nasal cavity is pictured here?

The vestibular region.
This is the initial, external part of the nasal cavity with cutaneous mucous membrane, hairs and skin glands. It is lined with stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
Goblet cells produce _________ granules.
Goblet cells produce mucinogen granules.
Identify the structures indicated by the arrows in this H&E section of the trachea

goblet cells
Identify the structures indicated by the arrows in this H&E section of the trachea
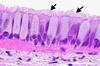
cilia
Identify the type of epithelium labeled ‘A’ in this H&E section of the nasal cavity

respiratory epithelium
Identify the type of epithelium labeled ‘B’ in this H&E section of the nasal cavity
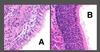
olfactory epithelium
Located in the dorsal part of nasal cavity (olfactory region). Olfactory epithelium is much thicker than respiratory epithelium. NO GOBLET CELLS ARE PRESENT
Identify the structures indicated by the arrows in this H&E section of the olfactory region of the nasal cavity

swell bodies
Swell bodies are venous plexuses found in both olfactory and respiratory regions. Swell bodies are distended with blood.
Identify ‘A’ in this H&E section of the larynx

laryngopharynx
Identify ‘B’ in this H&E section of the larynx

thyroid cartilage
What tissue are we looking at in this image?

trachea
The trachea is lined by ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. In the trachea, the lamina propria and the submucosa are not clearly demarcated. Serous glands are seen in the lamina propria/submucosa.
What are we looking at in this image?

trachea
rings of cartilage support the tracheal wall
a connective tissue adventitia completes the wall of the trachea
What type of cell is indicated by arrow A in this diagram of tracheal mucosa?

goblet cell
What type of cell is indicated by arrow B in this diagram of tracheal mucosa?

Ciliated cell
What is indicated by arrow C in this diagram of tracheal mucosa?

L. muscularis mucosae
What is indicated by arrow D in this diagram of tracheal mucosa?

Serous glands, loose CT vessels
What is indicated by arrow E in this diagram of tracheal mucosa?

Cartilage
What structure is indicated by arrow ‘A’ in this H&E section of the trachea?

goblet cell
What structure is indicated by arrow ‘B’ in this H&E section of the trachea?

cilia
What structure is indicated by arrow ‘C’ in this H&E section of the trachea?

basal cells