Exam II Osteology Flashcards
Pectoral girdle consists of:
Scapula
Clavicle
Brachium consists of:
Humerus
Antebrachium consists of:
Radius
Ulna
Palpable parts of the scapula
- Spine
- Acromion
- Medial border
- Inferior border
- Coracoid process
Palpable areas of the clavicle:
- Superior border
Palpable parts of the humerus:
- Medial and Lateral epicondyle
- Greater and Lesser tuburcle
Palpable parts of the radius:
(thumb side)
- Head
- Styloid process
Palpable parts of the ulna:
(pinky side)
- Head
- Styloid process
- Posterior border
What joint deals with shoulder displacement?
Gelnohumeral joint; Shoulder joint
What join is involved with complete shoulder separation?
Acromioclavicular joint


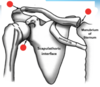
Label Joints















Muscle Attachment sites of the os coxae
Inferior Gluteal line
Anterior Gluteal line
Posterior Gluteal line
Palpable sites of the os coxae
Iliac crest
PSIS - posterior superior iliac spine (dimple)
Ischial tuberosity
Muscle attachment site(s) in the sacrum
Lateral sacral crest
Palpable sites of the posterior and anterior sacrum
Median sacral crest
Coccyx
Muscle attachment site(s) of the femur
Greater trochanter
Palpable part(s) of the tibia and fibula
Tibia: Medial condyle, Anterolateral tibial tubercle (Gerdy), Anterior border, Medial malleolus, Medial tuberosity
Fibula: Head, Lateral malleolus
Bones of the Os Coxae
Ilium
Ischium
Pubis

Muscles of the Gluteal Region


Muscles of the gluteal region; medial


Muscles of the gluteal region; posterior


Muscles of the gluteal region; anterior


Muscles of the gluteal region; Anterior


Muscles of the gluteal region; posterior


Musculature of Posterior thigh; lateral and medial


Musculature of the posterior thigh


Musculature of the posterior thigh;


Musculature of the posterior thigh;


Musculature of the anterior and medial thigh; lateral aspect


Musculature of the anterior and medial thigh; medial aspect


Musculature of the anterior and medial thigh; posterior


Musculature of the anterior and medial thigh; anterior


Musculature of the anterior and medial thigh


Musculature of the anterior and medial thigh; posterior


Musculature of the anterior and medial thigh; anterior


Associated with foot and leg; anterior


Associated with foot and leg; posterior





Movements allowed in cervical vertebrae
Rotational
Flexion and Extension
Lateral flexion
Movements allowed in thoracic vertebrea
Rotational
Lateral flexion = limited
Movements allowed from lumbar vertebrae
Flexion and Extension
Some lateral flexion
No rotation
Central Stenosis
Osteophytes of the centrum
Bony outgrowth of the centrum into the spinal cord

Foraminal Stenosis
Narrowing of the cervical disk space caused by enlargement of a joint in the spinal canal, impinging on a nerve root

Bone Spur
Bone growth due to inflammation of the zygapophysis joints
Stenotic Vertebral Foramen
Narrowing of the vertebral foramen; impinging on spinal column
Limited movement
Congenital

Causes of thoracic region disc herniation
Sudden and forceful twisting of the midback region
Wear and tear; disc degeneration
Kyphosis (Scheuermann’s Disease)
Causes of Lumbar region disc herniation
Frequent bending, twisting and improper lifting
Acute or sudden injury (falling on ass)
Spondylolysis
“Scottie dog”
Broken vertebrae; Pars Interarticlaris = b/w inferior and superior articular facets, b/w lamina and pedicles
Spondylolisthesis
Anterior/Ventral displacement of one vertebra on adjacent; common progression from spondylolysis or congenital
Typically lumbar due to weight bearing

Compression Fracture
Fracture of the centrum; turns convex = kyphosis(?)
Trauma or degenerative (Dr. Wright)
Sacralization
Fusion/partial fusion of L5 to sacrum
Congenital; may not cause problems
Osteopenia
Thinning/decrease in bone mass
Degenerative
Osteoporosis
Diminished bone density
Prone to fractures
Degenerative
Burst fracture/Jefferson Fracture
Fracture or dislocation of Atlas (C1)
Fracturing anterior/posterior arches of C1 or transverse ligament resulting in dislocation
Sudden, forceful compression of C1 (car accidents, diving)
Hangman’s Fracture
Hyperextension of neck; Fracture of vertebral arch
Fracture of pars interarticularis (traumatic spondylolysis of C2)

Fracture of Dens
Or dislocation of Axis (C2)
Fracture at base of dens or along body
Horizontal blow to the head
Soft Tissue Injury in Cervical Region
Acceleration/Deceleration syndrome
Whiplast; severe can cause fracture
Torn anterior longitudinal ligament
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Blood vessels/Brachial plexus in between collarbone and first rib (thoracic outlet) become compressed
Causes: Supernumerary ribs (lower cervical rib), poor posture, baseball pitchers, extra muscle/scar tissue in scalene muscles


