EXAM II Cole Flashcards
What is a herniated disc?
Protrusion of nucleus pulposus, may compress spinal nerves

What are the 3 types of Congential Scoliosis?
Hemivertebrae caused by failure to form
Block Vertebrae and Unsegmented Bar due to failure of segmentation
Unsegmented bar with Hemivertebrae

What are the subtypes of Hemivertebraes under Congenital scoliosis?
Semisegmented (not a full wedge that’s inserted)
Fully segmented
Wedge Vertebrae (full wedge)
These occur due to a failure in the formation of vertebrae

What condition is seen here?

Semisegmented vertebra caused by a failure of formation of the vertebrae.
Congenital scoliosis
Where are ribs derived from?
Condensed mesenchyme lateral to the body of the vertebra (from sclerotome)

What forms during axial skeletogenesis?
Vertebral column
Thorax
Ribs and Sternum
All derived from sclerotome
Where is the sternum derived from and what’s it developed from?
Derived from sclerotome
Develops from cartilaginous sternal bars in ventral body wall and fuse in cranial-caudal direction

What are 3 defects of the sternum?
Pectus carinatum
Pectus excavatum
Sternal cleft

What is Pectus carinatum?
Overgrowth of cartilage causing sternum to protude
Most common in males; esp during growth spurt
Can occur congenitally or genetic disorders

What is pectus excavatum?
Possibly caused by an overgrowth of costal cartilage which restricts the expansion of ribs and pushes sternum inward
More common in males

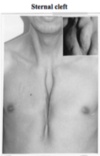
What is a sternal cleft?
When the sternum doesn’t fuse at the midline causing a sunken chest
What is a sternal foramen?
A hole found in the sternum; caused by an anomaly of ossification
Mistaken for a bullet wound
Common acupuncture point, directly over the heart

Which set of genes regulates the positioning of limbs along the craniocaudal axis?
HOX genes
Which gene initiates the outgrowth of limbs in the forelimb?
TBX5 and FGF factor
Top
Both are secreted by lateral plate mesoderm cells

Which gene initiates limb outgrowth in the hindlimb?
TBX4 and FGF
Both are secreted by lateral plate mesoderm cells
Define meromelia, what is it caused by?
Part of limb is missing
Caused by arrest or failure of development due to TBX4,5 genes

Define amelia
When a complete limb is missing

Define phocomelia
Where the feet and hands arise close to the trunk
Problem with TBX4,5 gene expression

Define Mesomelia
Shortened forearm or leg elements
The forearm (radius/ulna, tibula/fibula) is shortened compared w/ humerus
Problem with expression of TBX4,5 signals

Define radial club hand
Congenital absence or hypoplasia of radial structures of forearm and hand
Treatment includes stretching exercies and casting

What is AER and how is it initially formed?
Apical Ectodermal Ridge - thickened ectoderm on apex
Induced by BMPs after limb outgrowth is initiated
SLPM - somatic lateral plate mesoderm

Which regions control limb tissue differentiation?
Apical Ectodermal Ridge (AER)
Zone of Polarizing Activity (ZPA)
….and Progress Zone (PZ) = mitosis and limb lengthening

What does the AER express once it’s established?
AER = initial part of limb formation
FGF signals that maintain the Progress Zone (proliferating/motitic mesenchyme cells adjacent to the ridge)
SHH (secreted by ZPA) controls the signaling patterns of FGFs

What initiates expression of SHH?
Retinoic Acid
What cells produce retinoic acid? (limb formation)
Mesodermal cells located at the base of limb bud

Which areas do the following control during limb development
AER
SHH and RA
AER = proximal/distal, dorsal/ventral
SHH and RA = preaxial/postaxial
Which signals direct organization of limb bud and patterning of digits?
SHH
Define Polydactyly/Supernumerary digits
Extra digits; usually medial or lateral
In foot: lateral
Dominant trait; genetics
Caused by misexpression of RA/SHH or duplication of AER
What are the effects of Thalidomide?
Disrupts AER signaling the FRG signal
Causes a small amount of limb growth that ends once a hand or foot develops
Define Syndactyly
Webbed fingers/toes
Most common limb abnormality
Failure of programmed apoptosis to separate the digits
Simple dominant or simple recessive
More frequent b/w 3,4 fingers and 2,3 toes
Define Brachydactyly
Short digits
Uncommon
Cleft Hand/Foot
Lobster-claw (fusion of digits or loss of middle digit)

Sirenomelia
“Mermaid Syndrome”
Fusion of either the skin or limbs
Achondroplasia
Most prevalent form of dwarfism
Mutation of FGF gene
Abnormal cartilage that’s laid down, pathologic changes at epiphyseal plate, zones of proliferation and hypertrophy are narrow and disorganized
Autosomal dominat
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Brittle bone disease
Mutation on collagen that’s laid down
Kids can be misdiagnosed

Talipes Equinovarus
Club foot - most common type
Sole of foot turned medially and is inverted
Flexible Talipes Equinovarus
Abnormal positioning or restricted movement of lower limbs in utero
Feet are structurally normal
Usually correct spontaneously
Usually due to in-utero crowdness
Rigid Talipes Equinovarus
Abnormal development of the ankle and foot joints during 6th and 7th week
Bony deformities, usually in talus
Usually during bone development


