Embryology Flashcards
Which period during embryogenesis is where the most congenital defects can occur?
Embryonic period; weeks 2-8
What occurs during the pre-embryonic period?
(first 2 weeks) Zygote becomes multicellular and turns into the morula
What stages occur during the embryonic period?
Cleavage (morula) Gastrulation (3 germ layers) Organogenesis (organ formation)
What are the 8 possible teratogens that can produce development malformations?
Temperature extremes Mechanical forces Recreational drugs Dietary supplements/Prescription drugs Radiation Maternal malnutrition/diseases Environmental toxins Prenatal infections
What are the 4 variations in teratogen responsiveness?
- Timing of exposure (remember critical period = organogenesis) 2. Genetic variation; i.e. mom’s ability to metabolize 3. Method/Concentration of teratogen 4. Synergistic interactions; i.e. health medication (i.e. hypertension)
At what stages during the cell cycle can non-disjunction occur?
A) Meiosis I where they are homologous chromosomes resulting in all abnormal daughter cells B) Meiosis II where they are sister chromatids resulting in one daughter cell that has normal chromosome #
What is cleavage?
Zygote division and blastocyst formation (zygote -> 2-cell stage -> 4-cell stage -> 8-cell stage –> morula)
What does the trophoblast differentiate into during implantation?
Cytotrophoblast (lines blastocyst) and Syncytiotrophoblast (outer; lines/invades uterine wall)
What does the embryoblast differentiate into during implantation?
Epiblast (contains amniotic sac cavity) and Hypoblast (contains yolk sac cavity)
What is the inner and outer cell mass also known as?
Inner = embryoblast Outer = trophoblast
What major events occur during the embryonic period? (5)
- All major body systems develop
- 2D disk to 3D cylinder
- Folding of the embryo
- Craniocaudal folding - CNS
- Lateral folding - amnion/body wall
What are the 3 main functions of the notochord?
- Structure: rigid axis around which the embryo develops.
- Skeletal: foundation upoin which the vertebral column (vertebral bodies) will form.
- Induction: brings about the formation of the neural tube (future nervous system)
What are the locations the placenta can be in? (3 normal)
- Anterior 2. Posterior 3. Fundal

Where is the extraembryonic mesoderm (XE) layer derived from?
Epiblast and yolk sac
What events occur during embryogenesis?
Oogenesis and Spermatogenesis via Meiosis
What is organogenesis?
The differentiation of the 3 germ layers
Amniotic cavity functions (6)
- Allows symmetrical external growth
- Allows fetus to move freely
- Barrier to infection
- Normal fetal lung development
- Prevents adherence of amnion to embryo/fetus
- Helps maintain homeostatsis
Partial and total placenta previa
Implantation over the cervical os (opening)

Placenta accreta and 2 types
Trophoblastic invasion where placental roots grow deeply into uterine muscular wall.
- Placenta increta - invades muscular tissue
- Placenta percerta - invades other organs, i.e. bladder

Placental Calcification
Placental aging (precipitation of Ca2+ hydroxyapatite)
RF = smoking
Can occur if one has a post-date delivery (after 38 weeks)
Lithopedion
Stone baby - too large of a fetus that the body cannot reabsorb
Oligohydramnios
Low amniotic fluid
- Can result in renal agenesis (1/both kidney malformation) and obstructive uropathy
- Pulmonary hypoplasia and limb defects
Potter Syndrome
Via renal agenesis
lack of urine –> lack of amniotic fluid –> pulmonary hypoplasia = death due to underdeveloped resp. system (lung distention)
- Fetal compression; altered faces, breech presentation, abnormal hand and feet postions
Polyhydramnios
High volume of amniotic fluid
- CNS anomalies and esophageal atresia
Amniotic Band Syndrome
Tears in the amnion detach and surround fetus or adhesions between amnion and affected structures.
Ring constrictions or limb/digit amputations

Types of umbilical cord clinical malformations (4)
- Bilobed
- Circumvallate (towards edge)
- Succenturinate (extra)
- Velamentous (blood vessels travel abnormally, longer distances)

Caudal dysplasia
- Germ layer disorder
- Lower extremities abnormality; spine, kidneys, GI & genitourinary tracts
- Total/partial failure of lower vertebrae & sacrum development
- Mesoderm migration is disturbed
- Could be associated with maternal diabetes

When does the primitive streak develop and what does it eventually turn into?
- When epiblast begins to develop multiple cells
- Eventually turns into the craniocaudal axis of the embryo

State what the cranio and caudal ends end up developing into
- Cranio - Buccopharyngeal/Oropharyngeal membrane = mouth (anterior)
- Caudal - Cloacal membrane = anus (posterior)

What is the connecting stalk?
A yolk sac diverticulum, derived from the XE mesoderm and eventually forms the umbilical cord.

What is the role of the notochord?
Induces formation of the CNS via signaling ectoderm above it to form the neural plate which folds upon itself to form the neural tube which eventually turns into the brain and spinal cord.

What is neurulation?
The transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube which will eventually form the CNS (brain & spinal cord)

What does the ectoderm turn into during neurulation?
- Epithelial/surface ectoderm - organs & systems that maintain contact w/ the environment; epidermis, hair, nails, tooth enamel, cutaneous glands, mammary glands, etc.
- Neural ectoderm = neural tube (CNS, retina, pineal body, posterior pituitary) & neural crest (sensory ganglia & PNS nerves, separation of aorta & pulmonary trunk, etc.)

Chordoma
CNS clinical malformation - remnant of the notochord.
Onset is typically later in life (49 skull base and 69 for spine)

Ectodermal dysplasia (ED) syndrome
Affects of the ectoderm (hair, nails and teeth)
What are the 3 pigmentary disorders and what is it a disease of?
- Disease of the melanocytes
- Piebaldism - cogenital white forelock & multiple symmetrical hypopigmented or depigmented areas.
- Albinism - global reduction or absense of pigment in skin, hair and eyes; or eyes only nystagmus. Melanin necessary for fovea development
- Vitiligo - loss of melanocytes, autoimmune disorder
Anencephaly/Craniorachischisis
A neural tube defect when the forebrain doesn’t develop normally resulting in skull sitting above head.
Iniencephaly
Neural tube defect causing extreme retroflexin of the head, hyperextended spine, short and absent back.

Enchephalocele (2 types)
Cranium bifida, herniation of intracranial contents (anterior and posterior)
- Meningoencephalocele - meninges and brain
- Meningohydroencephalocele - meninges, brain, and ventricular system

Caudal Dysgenesis
Germ layer disorder where there is complete absence of the sacrum and lower vertebrae, multiple congenitial anomalies and associated with maternal diabetes.

Characteristics of the placenta (6)
- Temporary organ that exchanges blood, nutrients, etc.
- Produces some immunoglobulins
- Forms when trophoblast forms the chorion (chorion frondosum and decidua basalis)
- Synthesizes glycogen, cholesterol, fatty acids
- Removes waste products
- Synthesizes hPL (human placental lactogen) or chorionic somatomammotropin
- Induces lipolysis, eleveating free fatty acids in mother, “growth hormone” of the fetus, progesterion (maintain endom. lining & prevents smooth muscle contraction and estrogens (mammary gland dev)
Arnold-Chiari malformation
Herniation of cerebellar vermis or tonsil through foramen magnum blocking CSF flow

Caudal Neuropore (4)
- Spina bifida - failure of neural arche formation
- Spina bifida occulta - arches absent, normal tube
- Spina bifida meningocele - dura and arachnoid protruding
- Spina bifida meningomyelocele - neural tissue protruding
- Prevented by folic acid and B12, choline, and homocysteine

Triple Marker Screen Test measurs what?
- AFP (alpha-fetoprotein), HcG and Estriol
- AFP = open NTDs indicator
- HcG and estriol = trisomy 18, 21
What is the embryonic portion of the placenta?
Chorion frondosum - chorionic (fetal) blood vessels
- Eventually develops villi
- In contact with the decidua basalis

What are the villi developed from the villious chorion?
- 1º chorionic villi - outgrowths of cytotrophoblast into syncytiotrophoblasts. Intervillous space allows for O2 & nutrients & CO2 & waste products to be exchanged
- 2º Chorionic villi - contain a core of loose CT that grows into the 1º
- 3º Chorionic villi - contains embryonic blood vessels that develop. In chorion & connecting stalk and circulate embryonic blood @3 weeks

Tertiary chorionic villi formation

Maternal portion of the placenta (3 types)
- Decidua basalis - endometrium lining that is underlying implantation site
- Decidua capsularis - encapsulates the implanted embryo
- Decidua parietalis - lines the remainder of the endometrium
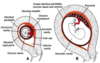
What beneficial substances can cross the placental membrane?
Oxygen, CO2, glucose, free fatty acids, vitamins
What harmful substances can cross the placental membrane?
- Rubeulla, measles, HIV, Varicella, herpes, poliomyelitis, cytomegalovirus
- Cat D drugs: (Questionnable harm) some Ab, Valium, Librium, Xanax, Lithium
- Cat X drugs: (definitely harmful) thalidomide, warfarin, isotetinoin (acene treatment; vit A derivative), nicotine, OH, phenytoin (seizure med)
Erythroblastosis fetalis (Rh factor) and Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN) causes:
Brain damage and severe edema (hydrops fetalis), enlarged liver/spleen, newborn jaundice, anemia
- Treatment; RhoGAM (Ab against Rh factor)

What is a technique used to test for familial genetic disorders? What are the two ways to do so?
Chorionic Villus Sampling - can occur at 10-12 weeks; results found in weeks
- Transcervical procedure
- Transabdominal procedure
What is another technique used to test for familial genetic disorders?
Amniocentesis

Wharton’s Jelly
Placental/umbilical cord gelatinous CT
- Potential source of stem cells
- Assists in closure of placental blood vessels
- Named after English physician
What are the two ways that vasculature can develop?
- Vasculogenesis - arise from coalescence (joining to form one) of hemangioblasts (that arise from blood islands) by major vessels
- Angiogenesis - forming from preexisting vessels by smaller vessels
Definitive Hematopoietic SC (AGM)
- Arise from mesoderm around aorta
- SC colonize and can colonize spleen, thymus and then bone marrow



