Congenital diseases Flashcards
What chromosomal trisomy is seen in Patau syndrome?
Trisomy 13
What chromosomal trisomy is seen in Edwards syndrome?
Trisomy 18
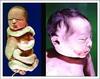
A prominent occiput, low-set ears and clenched fists is associated with which trisomy?
Edwards syndrome

What are these?

Rocker-bottom feet
Seen in Edwards and Patau syndromes
Microcephaly, microphthalmia and polydactyly are characteristic of which trisomy?
Patau
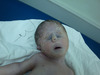
{ } is a congenital GI disorder characterised by megacolon due to a lack of ganglion/enteric nervous plexuses as a result of failed neural crest cell migration
Hirschsprung disease
{ } is a trisomy disorder associated with duodenal atresia and Hirschprung disease
Down syndrome
{ } is a congenital duodenal malformation that results in early bilious vomiting and proximal stomach distention due to failure of the duodenum to recanalise
Duodenal atresia
The double bubble sign is characteristic of which condition?
Duodenal atresia/stenosis
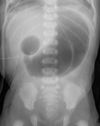
What is the most common congenital anomaly of the GI tract?
Meckel diverticulum

{ } is a GI diverticulum that is 2 inches long and found 2 feet from the ileocecal valve in 2% of the population
Meckel diverticulum
What causes Meckel’s diverticulum?
Partial failure of the vitelline duct/omphaloenteric duct to obliterate

What is the most common cause of congenital adrenal hyperplasia in infants?
21ß-hydroxylase deficiency
Enzyme required for cortisol production
What is the main problem in children with a congenital diaphragmatic hernia?
Pulmonary hypoplasia
Compression by the herniated viscera prevents development of the heart and lungs
Confers a high mortality if present
What is the most common cause of nasal polyps in children?
CF

What is the VACTERL association?
A combination of congenital diseases associated with mesodermal defects
V - vertebral anomaly
A - anal atresia
C - cardiac anomaly
T - tracheosophageal fistula
E - esophageal atresia
R - renal anomaly
L - limb malformation
What is the function of CFTR proteins in sweat glands?
Reabsorption of Cl-
Decreased reabsorption → increased sweat chloride
What is the role of CFTR proteins in epithelial tissue?
Facilitate the diffusion of Cl- into secretions → water follows by osmosis
In CF secretions are thick and cannot be cleared
Why can CF cause diabetes?
Retention of digestive enzymes → destruction of islet cells
What is the most common cause of urinary obstruction in the newborn male?
Posterior urethral valves
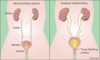
What is the most common cause of vesicoureteral reflux?
Congenitally short ureter → inadequate closure of the uterovesicular junction
Often resolves with age as the ureter grows in length
Why do children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia have hyperandrogenism?
Impaired cortisol production → high ACTH → adrenal hyperplasia + increased androgen production
How does hyperandrogenism present in females with congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
Clitoral enlargement
Precocious puberty
Virilisation (male secondary sexual characteristics)
How does hyperandrogenism in males with congenital adrenal hyperplasia present?
Precocious puberty
Do children with 21ß-hydroxylase deficiency have low or high aldosterone?
Low

Hypotension, dizziness, salt-craving, weight loss, anorexia, dehydration
What is the genetic abnormality in fragile X syndrome (Martin-Bell syndrome)?
CGG trinuclotide expansion → altered expression of FMR1 gene (fragile X mental retardation 1 gene)
How is fragile X syndrome inherited?
X-linked dominant
What are the clinical features of fragile X syndrome?
X-tra large - big ears, testes, face (long)
Intellectual disability

Which gene is affected in muscular dystrophy?
Dystrophin gene
What are the two main forms of muscular dystrophy?
Duchenne
Becker
How are Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy inherited?
X-linked recessive
What are the clinical features of muscular dystrophy?
Paresis and atrophy starting in the proximal lower limbs, later spreading to the upper body and distal areas
Weak reflexes
Waddling gait
Calf pseudohypertrophy
Gower manoeuvre (uses hands to inch-worm into standing)
Dilated cardiomyopathy
What is the most common genetic mutation in CF?
ΔF508 (chromosome 7)
Which of the following is not a feature of congenital rubella syndrome?
- Cataracts
- Deafness
- Hepatomegaly
- Hydrops fetalis
- Thrombocytopenia
Hydrops fetalis
What is a cystic hygroma?
Lymph accumulation in the jugular lymphatic sacs due to obstruction in the foetal neck

When are cystic hygromas typically diagnosed?
1st trimester ultrasound
What is the clinical significance of a cystic hygroma?
Increased risk of foetal aneuploidy and structural malformations
Most resolve throughout pregnancy and neonates and phenotypically normal
What is this?

Branchial cleft cyst
Usually presents in late childhood or early adulthood when an unrecognised cyst becomes infected
Anterior to the SCM
What are the most common congenital heart defects found in Down Syndrome?
Atrioventricular septal defect (endocardial cushion defect) (40% of patients)
VSD (30% of patients)
ASD (15% of patients
What is a complete endocardial cushion defect?
ASD, VSD, common AV valve
What is a partial endocardial cushion defect?
ASD and minor atriventricular valve abnormalities
What conditions are screened for in the newborn bloodspot screening test (NBST)?
Primary congenital hypothyroidism
Cystic fibrosis
Phenylketonuria (body cannot breakdown phenylalanine)
MCDA deficiency (body cannot breakdown fat)
Galactosaemia (body cannot process galactose)
What are 4 of the neonatal features of down syndrome?
Flat facial profile
Slanted palpebral fissures
Anomalous ears
Hypotonia
Poor Moro reflex
Dysplasia of midphalanx of fifth finger
Transverse palmar (Simian) crease
Excessive skin at nape of the neck
Hyperflexibility of joints
Dysplasia of pelvis
What condition is this?

Achondroplasia
What is the pathophysiology of achondroplasia?
Mutation in fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 gene (FGFR3) → inhibited chondrocyte proliferation → reduced endochondral ossification (bone formation)
Which TORCH infection is associated with microcephaly?
CMV
What is the most common cardiac disorder associated with fetal alcohol syndrome?
VSD
What facial abnormalities are associated with fetal alcohol syndrome?
Smooth philtrum
Thin upper lip
Small palpebral fissure
Hypertelorism (increased distance between eyes)

What is this?

Mongolian spot
How is hemophilia inherited?
X linked recessive
Which chromosomal disorder is associated with coarctation of the aorta?
Turner syndrome
Which chromosomal disorder is associated with a bicuspid aortic valve?
Turner syndrome
Which congenital disorder ipresents with ovarian dysgenesis, a shield (broad) chest, bicuspid aortic valve and horseshoe kidney?
Turner syndrome
Which congenital disorder is associated with lymphatic detects? e.g., webbed neck, cystic hygroma, lymphedema in hands and feet
Turner syndrome
What is a patent urachus?
Failure of the urachus to obliterate → urine discharge from the umbilicus

Urachus forms the median umbilical ligament in adults
What is gastroscisis?
Paraumbilical herniation of the intestine through the abdominal wall without formation of a hernial sac

What is an omphacele/exomphalos?
Congenital herniation of abdominal viscera through the abdominal wall at the umbilicus
The hernia sac is covered by the amniotic membrane and the peritoneum

What is ankyloglossia?
Tongue-tie

What is the specific genetic defect in Prader-Willi syndrome?
15q 11-13 deletion of paternal origin + maternal gene methylation (silencing)
Prader has no Paternal gene
What is the specific genetic defect in Angelman syndrome?
15q 11-12 delation of maternal origin + paternal gene methylation (silencing)
AngelMan has no Maternal gene
Normal development followed by regression and profound cognitive impairment at 6-18 months, characterises which condition?
Rett’s syndrome
Predominantly affects females
Above how many cafe au lait spots should you start being suspicious?
> 3 in a Caucasian/Chinese
> 5 African American
Which syndromes are associated with cafe au lait macules?
Neurofibromatosis
McCume Albright syndrome
Legius syndrome
Noonan syndrome
Multiple lentigines syndrome
Ash-leaf spots are characteristic of which disease?
Tuberous sclerosis

{ } is a tumour syndrome associated with Wilm’s tumour, neonatal hypoglycaemia, muscular hemihypertrophy and organomegaly (especially of the tongue)
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
Lisch nodules, neurofibromas, scoliosis and optic gliomas are characteristic of which disease?
Neurofibromatosis type 1

Bilateral vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas), cerebral and spinal tumours and meningiomas are characteristic of which disease?
Neurofibromatosis type 2
Progressive cerebellar ataxia, telangiectasias and immunocompromisation is classic of which condition?
Ataxia telangiectasia
A port wine stain birthmark is associated with which condition?
Sturge-Weber syndrome

What is sotos syndrome?
Cerebral gigantism
Overgrowth that is evident at birth with an increase in head circumference Hypotonia, mild cognitive impairment and delayed gross and fine motor milestones are typical

What is galactosaemia?
Hereditary defect in enzymes responsible for the metabolism of galactose
In which population is Canavan disease (aspartoacylase deficiency) particularly prevalent?
Ashkenazi Jews
Autosomal recessive
What are some of the clinical features of Canavan disease?
Motor regression
Hypotonia/hypertonia
Macrocephaly
Poor head control
Intellectual impairment
Seizures
Blindness
Paralysis
What is the most common abnormality associated with congenital rubella syndrome?
Sensorineural deafness
How is neurofibromatosis inherited?
Autosomal dominant
What examination findings might you find in neurofibromatosis?
Cafe au lait spots
Lisch nodules
Axillary and inguinal freckling
Neurofibromas
Scoliosis
Hypertension
Short stature
Macrocephaly
Which conditions are associated with neurofibromatosis type 2?
Bilateral vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas)
Cerebral and spinal tumours
Meningiomas
What are some of manifestations of foetal varicella syndrome?
Limb aplasia
Chorioretinitis
Cataracts
Cutaneous scars
Cortical atrophy
Hydrops + IUGR (antenatally)
What are some of the manifestations of congenital herpes simplex?
Vesicular lesions
Keratoconjunctivitis
Meningitis
Disseminated disease - multiple organ involvement, sepsis
What is the triad of McCune Albright syndrome?
- Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
- Pigmentation (cafe au lait spots)
- Precocious puberty
What is the difference between Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy?
Becker - slower progression, more heart involvement e.g., dilated cardiomyopathy
What three facial features are most specific for foetal alcohol syndrome?
- Short palpebral fissures
- Flattened philtrum
- Thin upper lip

Neonatal “snuffles” is associated with which congenital condition?
Congenital syphilis
What is defective in mucopolysaccharidosis?
Breakdown of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
What are the foetal risks of maternal Listeria infection
Severe systemic infection with disseminated abscesses (granulomatosis infantiseptica)
Respiratory distress syndrome
Skin lesions
Increased risk of premature birth and spontaneous abortion
How is maternal toxoplasmosis infection treated?
Spiramycin
Test if symptomatic (cervical lymphadenopathy), suggestive foetal US or high-risk exposure
What is neonatal varicella syndrome?
Maternal infection with varicella within 5 days before and 2 days after delivery
What is foetal varicella syndrome?
Congenital varicella from exposure in utero
What are the two major manifestations of neonatal lupus?
- Cutaneous lesions
- Heart block
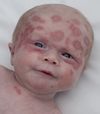
What are the features of WAGR syndrome?
W - Wilm’s tumour
A - aniridia (parital or complete absence of the iris)
G - genitourinary abnormalities
R - retardation (intellectual disability)

What is Potter syndrome?
A constellation of findings in infants exposed to severe oligohydramnios
P - pulmonary hypoplasia
O - oligohydramnios
T - twisted skin (wrinkles)
T - twisted face
E - extremity deformities
R - renal agenesis
For the most part, are metabolic diseases autosomal dominant or recessive?
Recessive
For the most part, are structural conditions autosomal dominant or recessive?
Dominant
Spherocytosis, Marfan syndrome, von Willebrand, neurocutaneous disorders, HOCM
Which conditions are associated with an increased nuchal translucency?
Down syndrome
Congenital heart defects
Abdominal wall defects
Which conditions are associated with hyperechogenic bowel on antenatal imaging?
Cystic fibrosis
Down syndrome
CMV infection
What is this abnormality and what is it associated with?

Brushfield spots - aggregations of connective tissue on the perophery of the iris
Associated with Down syndrome
What is the abnormality and what is it associated with?
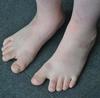
Sandal gap deformity
Down syndrome

What are the hallmark clinical features of the Pierre-Robin sequence?
Cleft palate
Glossoptosis (retraction of the tongue in the pharynx)
Micrognathia (small lower jaw)

“elfin” facies are associated with which condition?
Williams syndrome

Intellectual disability, hypersociability, supraventricular aortic stenosis
Which condition is associated with supraventricular aortic stenosis?
William syndrome


