Chapter 7 Flashcards
HSV 1 –>
HSV 2 –>
HSV 3 –>
HSV 4 –>
HSV 5 –>
HSV 6 –>
HSV 7 –>
HSV 8 –>
Oral HSV
STD HSV
VZV
EBV
CMV
?
?
Kaposi’s Sarcoma
HSV 1
Saliva or active perioral lesions
Age affects clinical presentation of symptomatic primary infections
Most commong site of latency –> Trigeminal Ganglion
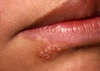
HSV 1
Recurrent (secondary, reactivated) herpes
HERPES LABIALIS
Prodrome for HSV 1
Stage of intiail presentation of HSV expression
Pain, Itching, Tingling
6-24 hrs before lesion develops

Primary Herpes Gingivostomatitis (HSV 1)
Primary HSV 1 infection before age 5
Moveable and attached oral mucosa –> YELLOW LESION WITH A RED HALO
Self inoculation – Leading infectious cause of BLINDNESS
Primary Herpes Pharyngotonsillitis
Primary HSV 1 or HSV 2 infection
Sore throat
Fever -indicative of viral infection
Headache
18+ years old
Reactivation of Herpes Simplex
Most common site –> Vermillion border, adjacent to skin of lip
HERPES LABIALIS (HSV 1)
Appearance –> Small erythematous papules
* Fluid filled vesicles
* Vesicles rupture and crust within 2 days
* Heals without scarring in 7 - 10 days
Symptoms are most sever in the first 8 hours
Herpes Labialis
Reactivation of HSV 1
“Cold Sore”

Intraoral reccurent HSV
Keratinized bound mucosa (palate, attached gingiva)
Vessicles rapidly collapse
Form a cluster of erythematous macules that coalece
Damaged epithelium is lost
Central yellowish area of ulceration
Common reasons for HSV reactivion
STRESS
pregnancy
allergies
trauma
illness,
UV LIGHT
immunocompromised

Herpetic Whitlow
HSV 1 infection of thumb and fingers
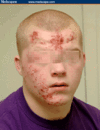
Herpes Gladiatorum
Scrumpox
Herpetic infection found in wrestlers HSV1
Contaminated abrasions

Herpes Barbae
HSV1 infection spread to bearded regions during shaving

HSV Histology
Multinucleation
Ballooning Degeneration
Tzanck Cells
HSV Histology –> Ballooning Degeneration
Acantholysis (separation of keratinocytes)
Nuclear clearing
Nuclear enlargement


Tzanck Cells
Free floating (clump of cells) epithelial cells
Cells detached
Caused by acantholysis
Pemphigous vulgaris
HSV
Two infections that involve Tzanck Cells
HSV
Pemphigous vulgaris (detached desmosomes)
How to diagnosis HSV
Clinical presentation
Cytologic smear (tzanck smear)
Tissue biopsy
Serologic testing (4-8 days after intial exposure)
Latent in TRIGEMINAL ganglion
HSV 1
Latent in DORSAL SPINAL GANGLION
VZV - “chicken pox”
HSV treatment
Acyclovir (systemic or topical cream)
Early introduction of antiviral – accelerated clinical resolution
Leading cause of infectious blindness
HSV1
Primary herpes gingivostomatitis
Varicella Zoster Virus
HSV 3
Primary infection –> Chicken Pox
Recurrent infection –> Herpes zoster (shingles)
Spread through AIR DROPLETS
Most individuals infect by 15 if not vacinnated
Latency –> DORSAL ROOT GANGLION

Chicken Pox
Primary infection of Varicella Zoster















