Chapter 4 - Cellular Metabolism Flashcards
aer-
air
(aerobic respiration)
an-
without
(anaerobic respiration)
ana-
up
(anabolism)
cata-
down
(catabolism)
co-
with
(coenzyme)
de-
undoing
(deanimation)
mut-
change
(mutation)
-strat
spread out
(substrate)
sub-
under
(substrate)
-zym
causing something to ferment
(enzyme)
enzyme
protein that catalyzes a specific biochemical reaction

cellular metabolism
the sum total of chemical reactions in the cell
What are the two types of metabolic reactions and pathways?
anabolic
catabolic
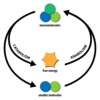
anabolism
(anabolic metabolism)
synthesis of larger molecules from smaller ones

catabolism
(catabolic metabolism)
breakdown of larger molecules

dehydration synthesis
- anabolic process that joins small molecules by enzymatically releasing the equivalent of H₂O
- forms carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and nucleic acids
monosaccharide + monosaccharide ⇄ disaccharide + water
amino acid + amino acid ⇄ dipeptide molecule + water

Are metabolic reactions reversible?
often, but different enzymes often catalyze corresponding anabolic and catabolic reactions
How do enzymes speed metabolic reactions?
lower the amount of activation energy required by straining chemical bonds in substrate
substrate + enzyme ⟶ enzyme-substrate complex ⟶ product + enzyme

substrate
molecule on which an enzyme acts

What is catalase, where is it found, and what is its substrate? Give an example.
- an enzyme
- in the peroxisomes of liver and kidney cells
- hydrogen peroxide, a toxic by-product of certain metabolic reactions
- EXAMPLE: When hydrogen peroxide is poured on a wound, cells release catalase, and the hydrogen peroxide is broken down, releasing oxygen; the foam removes debris.

active site
part of an enzyme that temporarily binds a substrate

What factors affect the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions?
- concentration of enzyme or substrate molecules in the cell; higher concentration = faster
- efficiency of the enzyme; some can catalyze only a few reactions per second, some can handle hundreds of thousands
metabolic pathway
series of linked, enzyme-controlled chemical reactions
lipase
enzyme that breaks down fat (lipid)