Chapter 2 Chemistry Flashcards
What does chemistry have to do with physiology?
- Your entire body is made up of chemicals
- Chemical reactions underline all processes that occur in the body
Your entire body is made up of what?
Chemicals
What underlines all the processes that occur in the body?
Chemical reactions
what is an example of processes in the body that are caused by chemical reactions?
- Digestion
- Muscle movement
- your heart pumping blood
What kind of reaction is cellular respiration?
Redox (reduction-oxidation)
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ———> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy + Heat
Glucose + Oxygen = Carbon dioxide + Water + ATP + Heat
What are the types of chemical bonds?
- Covalent Bonds
- Hydrogen Bonds
- Ionic Bonds
Covalent Bond
A bond formed by atoms sharing electrons
- do not conduct electricity
- do not easily dissolve in water
- tend to be gases or softer solids
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract shared electrons. Oxygen is electronegative (electron greedy). Electrons spend more time around the more electronegative atom. In the case of hydrogen and oxygenthe electrons spend more time in closer proximity to oxygen.
Polarity
The separation of charges.
ex. a polar covalent bond
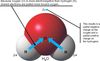
polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which the two atoms have different electronegativities, causing a separation of charges.
Nonpolar Covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the two atoms have identical or very similar electronegativities so that the charges are distributed evenly.
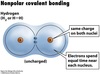
Covalent bonds are usually formed by what?
Nonmetals and metalloids
Electron shells of metals…
metals have loosley held outer electron shells, they consistantly drop electrons and become positive ions.
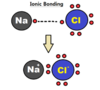
What creates an ionic bond?
When positive ions meet negative ions such as those found in the hallogen family, they are attracted to eachother, they bond to keep their energy use at the lowest possible minimum.
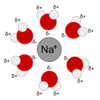
Ionic bond
A bond formed by the transfer of electronsfrom one atom to another.
- They are extremely polar; more than polar covalent bonds
- ions usually have a crystaline form
- usually dissolve in water
- ions once dissolved in water give the water the ability to conduct electricity.
Hydrogen Bonds
The attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of another molecule.

- Attraction between a positive and a negative
What are human made out of?
matter
Matter
anything that occupies space and has mass
What are the states of matter?
- Liquid
- Solid
- Gas
Energy
the capacity to do work
What are the types of energy?
- Kinetic
- Potential
Kinetic Energy
energy in motion
Potential energy
has the potential to become kinetic energy
What are the forms of energy?
- Chemical
- Electrical
- Mechanical
- Radiant
Chemical energy
Chemical enegy is stored in bonds between atoms
ex. ATP
Electrical energy
movement of charged particles
ex. nervous system, mucles
Mechanical energy
moving matter
ex. riding a bike
Radient energy
Travels in waves
ex. ultra violet radiation from the sun
Energy can be ___________ into different forms
Converted
Energy cannot be __________ or __________. It can only be __________.
- created
- destroyed
- converted
what is true of energy conversions?
They are inefficient, energy is always lost as heat.
what do chemical reactions do?
make or break bonds between atoms; they absorb or release energy
Endergonic reactions
absorb more energy than they release
Exergonic reactions
release more energy than they absorb
Endergonic and Exergonic reactions are coupled to do what?
release and provide energy
Types of reactions
- Synthesis reaction
- Decomposition reaction
- Exchange reactions
synthesis reactions
- smaller particles are bonded together to form larger more complex molecules
ex. Amino acids join together to make a protein molecule
Decomposition Reaction
- Bonds are broken in larger molecules, resulting in smaller, less complex molecules.
ex. glycogen is broken down to release glucose units
Exchange reactions
- Bonds are both made and broken (also called displacement reactions)
ex. ATP transfers its terminal phosphate group to glucose to form glucose- phosphate.
Do which types of reactions occur in cells?
All three (synthesis, decomp, and exchange)
The synthesis of molecules in a cell
Anabolism
What type of reaction represents Anabolism?
Synthesis reaction
The decomposition reactions in a cell
Catabolism
What type of reaction represents Catabolism?
Decomposition reaction
Metabolism
- Metabolism = Anabolism + Catabolism
- Metabolism is all the chemical reactions in a cell
Redox reactions
- Oxidation-reduction reactions
- Combination of decomposition and exchange reactions
- Break a molecule down and use the pieces to build a new molecule