Cardio - Mechanisms of Disease - Heart Failure; Ischemic Heart Disease Flashcards
Name some of the many causes of congestive heart failure.
Ischemic heart disease;
chronic hypertension;
cardiomyopathies;
infections;
toxins;
valvular disease;
prolonged arrhythmias
Systolic heart failure is associated with an S__ heart sound and _________ ventricles.
Systolic heart failure is associated with an S3 heart sound and dilated ventricles.
(3 = SYS-tolic
4 = DIAS-tolic)
Diastolic heart failure is associated with an S__ heart sound and _________ ventricles.
Diastolic heart failure is associated with an S4 heart sound and hypertrophic ventricles.
(4 = DIAS-tolic
3 = SYS-tolic)
_________ heart failure is associated with an S3 heart sound and _________ ventricles.
Systolic heart failure is associated with an S3 heart sound and dilated ventricles.
(3 = SYS-tolic
4 = DIAS-tolic)
_________ heart failure is associated with an S4 heart sound and _________ ventricles.
Diastolic heart failure is associated with an S4 heart sound and hypertrophic ventricles.
(4 = DIAS-tolic
3 = SYS-tolic)
Systolic heart failure is also known as heart failure with _________ ejection fraction (HF__EF).
Systolic heart failure is also known as heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
Diastolic heart failure is also known as heart failure with _________ ejection fraction (HF__EF).
Diastolic heart failure is also known as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Name three categories of compensatory mechanisms used by the heart to prevent complete failure:
Ventricular ___________
Neuro_________ activation
___________-__________ mechanism
Name three categories of compensatory mechanisms used by the heart to prevent complete failure:
Ventricular remodeling
Neurohormonal activation
Frank-Starling mechanism
What are the two main forms of ventricular remodeling?
- Myocardial hypertrophy
- Chamber dilatation
The hypertrophy or dilatation seen in congestive heart failure are compensatory mechanisms used to decrease what?
Ventricular wall tension
Concentric myocardial hypertrophy is to place the myocytes in _________.
Concentric myocardial hypertrophy is to place the myocytes in parallel.

Eccentric myocardial hypertrophy is to place the myocytes in ______.
Eccentric myocardial hypertrophy is to place the myocytes in series.
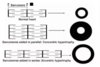
________ overload leads to concentric cardiac hypertrophy.
Pressure overload leads to concentric cardiac hypertrophy.

________ overload leads to eccentric cardiac hypertrophy.
Volume overload leads to eccentric cardiac hypertrophy.

Which form of cardiac hypertrophy (eccentric or concentric) sometimes occurs under normal physiologic conditions?
Eccentric
Via what two mechanisms can cardiac hypertrophy lead to myocardial ischemia?
- Increased O2 requirement
- Myocardial growth compresses the coronary arteries
Ventricular remodeling typically results in the heart taking on a more __________ shape.
Ventricular remodeling typically results in the heart taking on a more globular (spherical) shape.
The Law of LaPlace indicates that wall tension is proportional to what two internal chamber factors?
(1) radius (r)
(2) pressure (P)
(Tension = P*r /2h)
The Law of LaPlace indicates that wall tension is inversely proportional to what factor?
Wall thickness (h)
(Tension = P*r /2h)
Is left ventricular hypertrophy more associated with systolic or diastolic heart failure?
Diastolic
Is ischemic heart disease more associated with systolic or diastolic heart failure?
Systolic
Is cardiac fibrosis/amyloidosis more associated with systolic or diastolic heart failure?
Diastolic
Is hypertension more associated with systolic or diastolic heart failure?
Systolic
Which form(s) of natriuretic peptide arise(s) from the atria?
Which form(s) of natriuretic peptide arise(s) from the CNS?
ANP, BNP;
CNP














































