Cardiac Masses & Tumors Flashcards
What is the most common primary benign cardiac tumor found in adults? (80% of all tumors)
myxoma
etiology of myxoma
- most are idiopathic
- 10% genetic
- more common in female
- patients often young (~20 yrs old)
characteristics of myxoma
- most are pendunculated in the IAS
- different texture than myocardium; myxoid, gelatinous, smooth, lobular, friable (increased embolos risk
- often hinders diastolic filling
- if mobile, secondary valvular stenosis likely
signs & symptoms of myxoma
- asymptomatic
- arrhythmia
- arthralgia (joint pain)
- CP
- clubbing of fingerprints
- cough
- dizziness/fainting
- embolism and associated fingings
- fever/flu-like symptoms
- HF
- regurgitation
- Raynaud’s phenomenon (blood vessel spasm, usually in the fingers/toes
Treatment of myxoma
If the patient is a surgical candidate, immediate surgical removal of the myxoma is recommended.
*_entire myxoma must be removed t_o decrease the risk of reoccurrence
What are the primary benign intracardiac tumors?
myxoma
papilary fibroelastoma
fibroma
lipoma
rhabdomyoma
What is the most common benign valvular tumor?
papillary fibroelastoma (papilloma)
What is papillary fibroelastoma?
believed to originate from a small thrombus that attaches and grow into a sense, mobile mass
highly mobile and life-threatening, complication may arise due to embolism, stroke
*resemble chordae tendineae
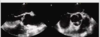
In adults, which part of the body does papillary fibroelastoma affect most?
AoV
LVOT
anterior MV leaflet
What is fibroma?
- bulky tumor that is frequently embedded in the myocardial wall of the ventricles or the IVS
- typically presents during childhood
- heart transplant may be indicated if children with a vary large LV fibroma
Fibroma is associated with ________
ventricular arrhythmia
LVOT
HF
sudden death
What is lipoma?
- an encapsulated tumor composed of mature fat cells that is usually soft and may become large
- usually asymptomatic and found incidentally *appear echogenic
- most lipomas do not require treatment unless if symptoms are present (arrhythmia, embolus, coronary artery compression)
What are these?

LHIS (lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum
a fatty infiltration of the interatrial septum sparring the fossa ovalis (gives dumb-bell shape); most prevalent in elderly and/or obese patients
What is the most common fetal cardiac tumor?
rhabdomyoma
many are diagnosed within a year of life and greater than 90% are diagnosed by the age 15
primary cardiac malignant tumors are rare; the majority are _______
sarcoma
________ is the most common type of sarcoma; usually begins with in the _____ or on the ______.
Angiosarcoma
RA
pericardium
*Note: A carcinoma forms in the skin or tissue cells that line the body’s internal organs, such as the kidneys and liver. A sarcoma grows in the body’s connective tissue cells, which include fat, blood vessels, nerves, bones, muscles, deep skin tissues and cartilage.
RA angiosarcoma tends to create _____ and/or _____ obstruction and associated findings.
inflow
outflow
____ % metastasize, so the treatment depends on patient’s age, health, the degree of metastasis, and the location and size of sarcoma
80
what is autotrasplantation?
the heart is removed, the tumor is removed, and the heart is put back into the patient.
secondary tumors are more common than primary ones; they often appear in the terminal phase of an ongoing disease (poor prognosis).
Most secondary cardiac tumors are (metastasized from):
lung, breast, renal carcinoma
malignant melanoma
The patient with secondary cardiac tumors may present with:
P.E
tamponade
HF
arrhythmia
*treatment depends on the primary malignancy and usually palliative care
carcinoid heart disease is the result of a metastasizing carcinoid tumor, usually from _____ or _____ that secrets _____
appendix
ileum
serotonin
*Note: Carcinoid syndrome occurs when a rare cancerous tumor called a carcinoid tumor secretes certain chemicals into your bloodstream, causing a variety of signs and symptoms. A carcinoid tumor, which is a type of neuroendocrine tumor, occurs most often in the gastrointestinal tract or the lungs.
if the tumor metastasizes to the liver, the serotonin is deposited on the ________ of the right heart. Serotonin does not travel to the left heart because serotonin is inactivated in the _______
endocardial linings
lungs
extracardiac tumor is anywhere within the vicinity (the area near or surrounding a particular place) of the heart such as (7) :
- mediastinal cyst: a mediastinal tumor can be caused by an enlarged lymph node, or a gland such as the thymus, thyroid, or parathyroid. It can also be caused by a cyst originating from the pericardium, the bronchus, or the esophagus.
- hematoma:
- thymoma: is a tumor originating from the epithelial cells of the thymus that is considered a rare malignancy.
- teratoma: is a rare type of germ cell tumor that may contain immature or fully formed tissue, including teeth, hair, bone and muscle. Teratomas may be cancerous or noncancerous, and they can affect people of all ages.
- infradiaphragmatic tumor
- pancreatic cyst
- pleural tumor
a thrombus usually forms in the areas of akinesis or dyskinesis; typically associated with _______ and found in the ventricular apex.
anterior MI
If the patient is in Afib, it is very important to rule out
____ and/or _____ thrombus prior to cardioversion
LA
LAA
left atrial thrombus is usually associated with: (3)
MS
LA enlargement
Afib
Echo steps to interrogate possible thrombus: (5)
- improve resolution (possible high frequency) and focus on the apex
- utilize CFD to see if it fills the apex or travel around the thrombus
- use different depth to differentiate artifact vs thrombus
- use various windows
- document the thrombus or mass in at least two views
What is missiles?
a foreign body such as a bullet, knife, nail
The patient is rushed to the ED after accidentally shooting a nail from a nail gun into his chest; echo is ordered to rule out: (7)
- P.E/tamponade
- coronary artery trauma
- myocardial rupture
- ASD
- VSD
- WMA
- valvular disruption/regurgitation (new murmur)
A detailed knowledge of cardiac anatomy and normal variants is not required for the recognition of structures that may mimic a cardiac mass.
T or F ?
F
A detailed knowledge of cardiac anatomy and normal variants allows recognition of structures that may mimic a cardiac mass.
Myocardial Trabeculations are differentiated from thrombi by their linear shape with an echodensity similar to and attachment to the myocardium.
T or F ?
T

Thrombi never form on permanent pacer leads in the right atrium or ventricle.
T or F ?
F
Thrombi also may form on permanent pacer leads in the right atrium or ventricle.
Echo can identify the etiology of a cardiac mass based on appearance. A differential diagnosis for the echocardiographic finding is based on the location, appearance, size , mobility, physiologic effects, and other findings associated with the mass.
T or F ?
F
Echo cannot identify the etiology of a cardiac mass based on appearance. A differential diagnosis for the echocardiographic finding is based on the location, appearance, size , mobility, physiologic effects, and other findings associated with the mass.
- The first step in evaluation of a cardiac mass on echocardiography is to determine whether the findings are due to an ultrasound artifact or an actual anatomic finding.*
- T or F ?*
T
The first step in evaluation of a cardiac mass on echocardiography is to determine whether the findings are due to an ultrasound artifact or an actual anatomic finding
Right-sided echo contrast is helpful in identifying thrombus when image quality is suboptimal.
T or F ?
T

List 4 structures that may be mistaken for an Abnormal Cardiac Mass in the Right Atrium.
crista terminalis
chiari network
pacer wire, Swan-Ganz catheter, central venous line
trabeculation
atrial suture after cardiac transplant
*CVC (central venous catheter/line) also known as a central line(c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for more reliable vascular access.

List 4 structures that may be mistaken for an Abnormal Cardiac Mass in the Left Ventricle.
papillary muscles
left ventricular web (aberrant chordae)
prominent apical trabeculations
prominent mitral annular calcification
Transesophageal imaging is not sensitive for diagnosis of LV apical thrombi, because the apex is in the far field of the image and the true apex may not be included in the image plane.
T or F ?
F
*Transesophageal echocardiography is required to exclude left atrial thrombi within clinically indicated. (TEE is more sensitive than TTE)
A careful examination for cardiac thrombi, tumors, valvular vegetations, and aortic atheroma, often with TEE, is needed when a cardiac source of embolus is suspected.
Echocardiography can definitively determine tissue type; diagnose a cardiac mass is based on location, attachment, appearance, and any associated abnormalities.
T or F ?
F
Ultrasound has limited utility for determination of tissue type; diagnosis of cardiac mass is based on location, attachment, appearance, and any associated abnormalities.
Lambl’s excrescences and nodules of Arantius are structures that may appear as abnormal attached to the ___________________ valve.
AoV
*The nodule of Arantius is a nodular thickening at the central portion of the free edge of each leaflet. During systole, each leaflet is pushed aside by the flow of blood leaving the left ventricle.
*Lambi’s excrescences: may exist on either native and prosthetic cardiac valves 1-4. Typically, they form at the lines of valve closure, most commonly of the mitral and aortic valves, with the right heart valves affected in less than 10% of all cases

List 4 extra cardiac pericardial benign masses.
mediastinal cyst
hematoma
thymoma
teratoma
infradiaphragmatic tumor
pancreatic cyst
pleural tumor
*usually distort (give misleading impression) the right heart
List 4 of the most common non primary cardiac tumors.
*in order of frequency
- lung carcinoma
- lymphoma
- breast carcinoma
- leukemia
- stomach tumor
- melanoma
- liver
- colon
Nonprimary cardiac tumors are______ more common than primary cardiac tumors.
20 times
Nonprimary cardiac tumors most often involve the ________ but also may invade the ________. They rarely appear as intracardiac masses.
pericardium
myocardium
Nonprimary (secondary) tumors are more common. They rarely appear as ______
intracardiac masses
List 4 ways that nonprimary tumors can involve the heart.
- direct extension
- metastatic spread of disease
- production of biologically active substances
- side-effects related to treatment of the primary tumor
The most common primary cardiac tumors in adults, in order of frequency, are:
- myxoma
- pericardial cyst
- lipoma
- papillary fibroelastoma
- Angiosarcoma (malignant)
- Rhabdomyosarcoma (malignant)
Benign cardiac tumors result in adverse clinical outcomes as a result of :
obstruction of blood flow
embolization
Primary cardiac tumors most often present on echocardiography as ____________.
an intracardiac mass
A prominent normal cardiac structure or a normal anatomic variant may be mistaken for an abnormal mass.
T or F ?
T
Structures that may be mistaken for an Abnormal Cardiac Mass found in
AoV
Nodules of Arantius
Lambl’s excrescences
Base of valve leaflet seen en face in diastole
Structures that may be mistaken for an Abnormal Cardiac Mass found in
MV
Redundant chordae
Myxomatous mitral valve tissue
Structures that may be mistaken for an Abnormal Cardiac Mass found in
LA
- Dilated coronary sinus (persistent left superior vena cava)
- Raphe between left superior pulmonary vein and left atrial appendage
- Atrial suture line after cardiac transplant
- Beam-width artifact from calcified aortic valve, aortic valve prosthesis, or other echogenic target adjacent to the atrium
- Interatrial septal aneurysm
Structures that may be mistaken for an Abnormal Cardiac Mass found in
pericardium
Epicardial adipose tissue
Fibrinous debris in chronic organized pericardial effusion
Structures that may be mistaken for an Abnormal Cardiac Mass found in
PA
Left atrial appendage (just caudal to pulmonary artery)
Describe 4 of the 6 key techniques utilized to diagnose a cardiac mass.
- echocardiography is to determine whether the findings are due to an ultrasound artifact or an actual anatomic finding (*A prominent normal cardiac structure or a normal anatomic variant may be mistaken for an abnormal mass).
- Highest transducer frequency for adequate tissue penetration
- acoustic access adjacent to the structure of interest
- visualization of the motion of the mass with the cardiac cycle
- use of a narrow sector and zoom mode once a mass is identified
- careful gain and processing adjustments
- off-axis views from standard image planes
*Clinical data and other echocardiographic findings often provide clues about the identity of a cardiac mass
*note: Echo cannot identify the etiology of a cardiac mass based on appearance. A differential diagnosis for the echocardiographic finding is based on the location, appearance, size , mobility, physiologic effects, and other findings associated with the mass.
Discuss the appearance of a vegetation in the RA (Location, appearance, and associated findings) in 30 words or less.
Location:
- Usually valvular
- Occasionally on ventricular wall, pacer lead, or catheter tip
appearance:
- Irregular shape, attached to the proximal side of the valve with motion independent from the valve
associate findings:
- valvular regurgitation usually present
- clinically, fevers, systematic signs of endocarditis with positive blood culture
Discuss the appearance of thrombus (Location, appearance, and associated findings)
location:
- LA especially enlarged or associated with MV disease
appearance:
- usually discrete (individually separate and distinct)
- somewhat spherical in shape
- laminated against LV apex or LA wall
associated findings:
- Underlying etiology usually evident
- LV systolic dysfunction or segmental WMA (except: eosinophilic heart disease)
- MV disease with LA enlargement
Discuss the appearance of tumor (Location, appearance, and associated findings)
location:
- LA (myxoma)
- myocardium
- pericardium
appearance:
- various: maybe circumscribed or may be irregular
associated findings:
- intracrdiac obstruction depending on site of tumor
Left atrial thrombi most often form in the ______, particularly in patients with atrial fibrillation
atrial appendage
Thrombi may be seen in the body of the left atrium with severe stasis of blood flow caused by ________
Mitral stenosis
What are the risk factors of thrombus formation in LA?
Afib
MS
LAA
LA enlargement
prosthetic valve
LV thrombi also are seen in patients with _______
severely reduced LV systolic dysfunction
Typical Cardiac Tumor Locations

List 2 techniques employed by the echocardiographer for the detection of LV apical thrombi.
use CFD and contrast
Highest transducer frequency for adequate tissue penetration
visualization of the motion of the mass with the cardiac cycle
use of a narrow sector and zoom mode once a mass is identified
3 Normal Intracardiac Structures that may be misdiagnosed as abnormal:
prominent eustachian valve
prominent crista terminalis
prominent pectinate muscle in LAA

List 4 intra cardiac nontumor mass like benign structures/pathologies.
crista terminalis
congenital remnants
trabeculations
moderator band
papillary muscle
redundant chordae
mitral annular calcification
chiari network
eustachian valve
catheter
pacemaker wire
A DVT may embolized to the ______________ heart and become entangled in the tricuspid valve chords or a right atrial Chiari network.
right
Eustachian valves and Chiari networks are thin filamentous structures that extend from the region of the _____1_____ toward the ______2______
Eustachian valves and Chiari networks are thin filamentous structures that extend from the region of the inferior vena cava (IVC) toward the superior vena cava (SVC)

List 3 structures that may be mistaken for an Abnormal Cardiac Mass in the Right Ventricle
Moderator band
Papillary muscles
Swan-Ganz catheter or pacer wire
Transthoracic echocardiography from the apical window is the optimal approach to detection of LV thrombi, with a sensitivity of 92% to 95% and a specificity of 86% to 88%.
T or F ?
T
The sensitivity of TTE for detecting left ventricular thrombosis ranges between 92% and 95%, with specificity of 86% to 88%
On the contrary, in TEE, midesophageal apical planes did not place the left ventricular apex in the near field, which is optimal for this purpose; transgastric views cannot always be obtained, especially in awake patients, and are often of low quality
*List 2 extra cardiac pericardial malignant masses.
Mesothelioma
Angiosarcoma

List 4 structures that may be mistaken for an Abnormal Cardiac Mass in the Left Atrium.
- Dilated coronary sinus (persistent left superior vena cava)
- Raphe between left superior pulmonary vein and left atrial appendage
- Atrial suture line after cardiac transplant
- Beam-width artifact from calcified aortic valve, aortic valve prosthesis, or other echogenic target adjacent to the atrium
- Interatrial septal aneurysm
What is this?

Angiosarcoma (malignant)
are malignant sarcomas of vascular endothelial cell origin. Endothelial cells make up the lining of vessels. Angiosarcomas can occur in any region of the body, although they are most commonly located in the skin, breast, liver, and deep tissue.
What is this?

papillary fibroelastoma
Tumor features frond-like extensions and very mobile with stalk-like attachment to Aortic valve leaflet. Most frequently attach to midportion of valve leaflets
benign but can be deadly
sometimes called cardiac papillomas. These small, noncancerous tumors develop in the heart — most often on one of the valves located between the heart chambers
95% of fibroelastomas are found in ________
the left heart.
papillary fibroelastoma has strong association with ________
systemic emboli (Stroke)
What are the benign primary cardia tumors?
- myxoma (most common tumor of the heart in adults: ~80%)
- papillary fibroelastoma (most common tumor of the heart valves & adjacent myocardium)
- Fibroma (second most common tumor in children)
- lipoma
- hemangioma (rare)
- lipomatous hypertrophy - usually spares the septum secundum, dumb-bell appearance
_________ – may be found in any of the 4 chambers. Large size and rapid/aggressive growth is not unusual. Tumor can invade the margins of the walls causing hemorrhagic pericardial effusions. They can occlude AV valves causing heart failure.
Angiosarcoma
What is this?

renal cell carcinoma
most common metastatic tumor
melanoma
Metastatic lung Cancer:
Extension of malignancy through the______ into the _______. Among the potential malignant lesions, lung carcinoma is the most common. Atypical myxomas and thrombus should also be considered in the differential diagnosis.
pulmonary veins
left atrium
Most common cardiac tumor in infants and children
Rhabdomyoma



