Anatomy: Ear Flashcards


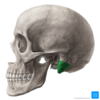
petrous part of temporal bone

zygomatic process of temporal bone

arises from squamous part and articulates wihth zygomatic bone

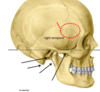
pterion
frontal, parietal, temporal and sphenoid bones
thinnest part of the skull

which part of the temporal bone is the mastoid process found on
petrous part


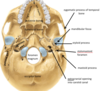
which bones form the anterior cranial fossa
frontal, ethmoid and sphenoid

which bones form the middle cranial fossa
sphenoid and temporal

which bones form the posterior cranial fossa
temporal and occipital

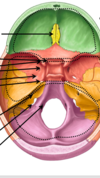
C O S F F I J H

order of cranial foraminae
“Carlos only smokes spliff since Rastaman offered skunk in indigenous Jamaica. Jamaican joint heaven”
COSFFIJH
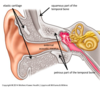
external ear
from auricle to tympanic membrnae via external acoustic meatus
collect and convey sound waves to tympanic membrane

middle ear
from tympanic membrane to oval window and esutachian (auditory) tube

amplifies and conducts sound waves to internal ear
internal ear
from oval window to internal acoustic meatus

converts special sensory information - into fluid waves, then APs which are conducted to the brain
auricle anatomy


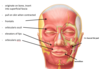
describe the innervation of the skin of the external ear
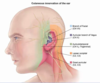
tympanic membrane and EAM sensory nerve supply
CNV3 (superior part of EAM and tympanic membrane) and CNX (inferior part of EAM and TM)

what is the lymphatic drainage of the lateral surface of the superior half of the auricle
parotid lymph nodes

what is the lymphatic drainage of the cranial surface of the superior half of the auricle
mastoid lymph nodes (purple) and deep cervical (light green)

what is the lymphatic drainage of the rest of the auricle, including the lobe
superficial cervical lymph nodes (dark green)
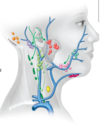
where does all lymph from the auricle eventually drain to
deep cervical lymph nodes (in carotid sheath), thoracic duct and then venous angle

what forms the skeleton of the external ear
temporal bone

is the elastic cartilage of the ear vascularised?
no - gets nutrients from the skin

where does the EAM extend from
deeper part of concha to tympanic membrane