Anatomy Flashcards
what area of the nose touches the columella, ala, and nasal tip.
soft triangle
The antihelix and helix have legs called what
crura
What are the structures that the crura of the antihelix and crura of the helix separates from anterior to pos.
cavum, cymba, triangular fossa, scapha
What is the correct term for nasolabial fold
melolabial fold
What is the correct term for marionette lines?
mentomental folds
What muscle pulls down to form marionette lines
depressor angularis oris
Muscles of facial expression arise from what?
2st branchial arch
Muscles of mastication arise from what?
1st branchial arch
what is SMAS
Superficial Musculoaponeurotic system
what is the equivalent of SMAS on the scalp
gala aponeurotica
where are motor nerves in relation to SMAS
below SMAS
where are sensory nerves and vessels located in relation to SMAS?
within SMAS or above in sub Q fat
Name the five layers of the scalp
epidermis/dermis-subQ fat-gala aponeurotica-loose areolar connective tissue, periosteum
where is it ok to undermine below SMAS
nose
where to undermine in the scalp
below the gala aponeurotica
what innervates the sensory to the lower ear?
the great auricular nerve
what innervates sensory to the cavum of the ear
cranial nerves IX and X
what innervates sensory to the top of the ear?
Lessor occipital nerve the top back, the auriculotemporal for the top front.
what does the deep peroneal nerve innervate?
great toe webspace
what does the superficial peroneal nerve innervate?
dorsum of foot
what does the sural nerve innervate
lateral malleolus and the little toe
what does the saphenous nerve innervate
medial malleolus
what are the three nerves of the posterior tibial nerve innervating the bottom of the foot
calcaneal nerve- heel
lateral plantar nerve
medial plantar nerve
where is erb’s point located?
behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle half way between the base of the mastoid and clavicle.
what nerve exits 2 cm above erb’s point
spinal accessory nerve - Cranial nerve XI
what does the spinal accessory nerve do?
innervates the trapezius muscle- leads to shoulder droop
what are the three danger zones for motor nerve injury.
spinal accessory nerve XI, temporal branch of the facial nerve VII, Marginal Mandibular branch Facial Nerve VII
what does the temporal branch of the facial nerve innervate?
The frontalis muscle.
what does the marginal mandibular branch innervate?
lip depressors, crooked smile and drooling.
what are the five branches of the facial nerve?
To Zanzibar By Motor Car (Facial nerve branches C7)
Temporal (paralysis of frontalis muscle and ptosis)
Zygomatic (snarl and nostril dilation)
Buccal (damage to stenson’s duct)
Marginal Mandibular (lower lip paralysis)
Cervical (unilateral joker smile)
P neumonic Posterior auricular (occipitalis muscle paralysis)
how does the lymphatic drainage of the face go?
down and diagonal
What forms the top of the nail plate
Proximal nail matrix Prox Top Dis-Down
what is the eponychium
the cuticle.
where is the hyponychium
under the free edge of the nail plate
what shows the distal nail matrix?
the lunula
what is a distal pterygium?
distal expansion of the hyponychium which eliminates the distal nail groove.
what causes a dorsal pterygium?
scarring which divides the nail plate into two segments.
Longitudinal erythronychia can be caused by what?
LP, Darier’s, glomus tumors, SCC & melanoma
What finger has innervation by ulnar, radial and median nerves?
The ring finger.
what nerve innervates the largest part of the palm and the distal long and index finger?
median nerve
what nerve innervates largest dorsal part of the hand.
radial nerve
what nerve innervates the lateral hand both top and bottom.
ulnar nerve.
what muscles make up the posterior triangle of the neck?
sternocleiodmastoid (anterior border)
Trapezius (posterior border)
middle third of the clavicle base (omohyoid muscle)

What are the 3 superficial nerves in the posterior triangle of the neck
greater auricular (sensory)
lessor occipital nerve (sensory)
supraspinatus (motor)
If you damage the supraspinatous nerve what can’t you do?
Shrug shoulder
raise your arm above the head
what are the four main sensory nerves of the ear top to bottom
auriculotemporal
Vagus N. auricular branch + Lessor occipital
Great Auricular N.

What is the path of Stensen duct
Parotid gland duct arises from parotid passes through the buccal fat pad and empties above second maxillary molar

what nerve has been damaged

Marginal mandibular branch of the Facial nerve can’t protrude lower lip and facial asymentry while smiling
what nerve has been damaged

temporal branch of the Facial nerve (can’t raise eyebrow ptosis) Frontalis paralysis
If you are operating on the concha and auditory meatus and the patient becomes nauseous and vomits what nerve have you hit.
auricular branch of the vagus nerve
What are the three branches of the Trigeminal nerve
Ophthalmic V1
Maxillary V2
Mandibular V3
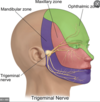
What is the “6th branch of the facial nerve that innervates the occipital muscle” that is often forgotten
posterior auricular
what nerve innervates the webspace btw the great toe and 2nd toe
deep peroneal nerve

what innervates the little toe and the lateral foot
sural nerve

what sensory innervates the top of the foot
superficial peroneal nerve

what sensory nerve innervates the sole of the foot?
posterior tibial nerve

what innervates the medial edge of the foot
the Saphenous Nerve

What are the danger zones for trigeminal nerve injury in facial surgery (sensory)
above and below midpupilary line
supraorbital and supra trochlear branches V1 (opthalmic branch)
Infraorbital branch V2 (maxillary branch) one cm below orbital rim
near 2nd pre molar
Mental branch V3 (mandibular branch)

what makes up the frontal sensory nerve
supraorbital nerve midline
Forehead, upper eyelid, scalp to vertex
supratrochlear nerve medial edge of the supraorbital margin
forehead & uppereyelid
Where do you inject for a posterior tibial nerve block
posterior to the medial malleous
numbs the center sole of the foot.
Where do you inject for the both deep and superficial peroneal nerve blocks?
junction of the foot and ankle lies over the anterior tibial artery
first web space (deep) numbs top of foot (superficial)
Where do you inject for a sural nerve block
posterior to the lateral malleolus (like the posterior tibial block but on opposite side)
numbs the little toe an lateral foot
Where do you inject for the saphenous nerve block
superior to the medial malleous
numbs the medial part of the foot.
where do you inject for a median nerve block of the hand
between the Palmaris longus (the middle one when you touch your thumb to your little finger or make a fist)
and the Flexor carpi radialis (radial to the palmaris longus)
where do you inject for a radial nerve block
ulnar to the Flexor carpi ulnaris
where do you inject for a radial nerve block
just proximal to the Radial styloid just below the anatomic snuff box
What are Sharpey’s fibers
They connect perosteum to bone
If tumor is not affecting the periosteum is it easily elevated by using tumescent technique.
yes
periosteal pain is which dull and duffuse or sharp and localized
sharp and localized.
What nerve innervates the nasal tip
external branch of the anterior ethmoidal nerve

What nerve innervates the nasal root, dorsum and sidewalls
Infratrochlear nerve

What nerves innervate the ala and lower side walls of the nose
Infraorbital nerves

If there is eyelash loss associated with the tumor what anatomic structure may be involved?
Tarsal plate
what do the medial and lateral canthal tendons connect to the orbital rim
tarsal plate
what type of suture repair should be done with a tarsal plate repair
verticle mattress suture
The tarasal plate is bigger on which eyelid?
Upper Eyelid 1cm
Lower .5 cm
what % of the eyelid can be closed with direct closure
30%


