5.6 - Intro to Radiology Pt 2 Flashcards
(20 cards)
The most common plane of dissection used to evaluate patient’s radiographically in cross sectional anatomy?
A) Coronal
B) Sagittal
C) Oblique
D) Transverse
D) Transverse
The “landmark” research project, from which cross-sectional human images were obtained, was the
A) Visible Human Project
B) Cross-Sectional Human Imaging Project
C) Cyber Human Imaging Project
D) The Tesla Project
A) Visible Human Project
The strength of an MRI’s magnet is measured in
A) Joules
B) Amps
C) Teslas
D) Volts
C) Teslas
An example of an imaging technique which uses tomography is
A) Mammography
B) Angiography
C) CT Scan
D) Ultrasound
C) CT Scan
Cross-sectional imagery is particularly helpful in assesing
A) Anatomical Compartments
B) Trigger Points
C) Inflammation
D) Bleeding
A) Anatomical Compartments
Who shared the Nobel Prize for investing the CT Scanner
A) Edison
B) Tesla
C) Hounsfield
D) Von Hagens
C) Hounsfield
Claustrophobia is a problem with
A) CT Scanners
B) Open MRI’s
C) Conventional MRI’s
D) Ultrasonography
C) Conventional MRI’s
Which of the following is not a cross-sectional technique?
A) CT Scan
B) Mammography
C) MRI
D) Ultrasound
E) Chest X-Ray
F) Histology/Microscopy slide
E) Chest X-Ray
MRI technology is based on….
Proton spin in water molecules
What units measure the density of tissue-types seen on CT scans?
A) Teslas
B) mV
C) Newton
D) Hounsfield
E) Curies
D) Hounsfield
What is the anatomical orientation when looking at CTs or MRIs?
You are looking as the patient is supine and from the feet up
What kind of image is this?
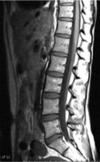
Spine MRI
What kind of image is this?

MRCP
What kind of image is this?

Breast Ultrasound
ID this
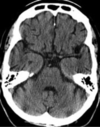
Head CT
What is the circled object?

Thyrizzle
(Thyroid, for all you non-gangstas)
What is being ID’d by the arrows

Chest CT - Pulmonary Embolism
What is this an image of?

CT Abdomen
The organ in this picture is? And the imaging technique is

Liver Ultrasound
ID this structure

Pelvic CT


