2009 Module Exam Flashcards
(91 cards)
In a patient who has a block in the anterior-interventricular septum, which is the area most susceptible to myocardial infarction?
Anterior 2/3 interventricular septum
What is the component of the fatty streak?
a. Foam cells
b. Fibro-fatty plaque
a. Foam cells
Where is the apex located?
5th intercostal space 9cm from midline
A patient with chest pain that radiated to the left arm. What is the best way to treat his condition?
Nitrates, Ca++ channel blockers, β-blockers
What are the sympathetic innervations of the heart?
T1-T6
What is the mechanism of action of nitrates?
Increase relaxation of smooth muscle cells
Weight gain is a side effect to clofibrate due to
Inhibiting lipolysis
What is the best drug for increasing HDL levels?
Nicotinic acid
What is a complication of myocardial infarctions in 3 days?
Arrhythmias
What is the feature of the post-transition state?
What changes are seen in post transition countries?
A) Low mortality, high fertility, infectious diseases
B) Low Mortality, low fertility, and chronic diseases
C) High mortality, low fertility, chronic diseases
D) High mortality, high fertility. Infectious diseases
Low mortality, low fertility – chronic diseases
How does glycosylation affect atherosclerosis?
Reduce LDL clearance
An increase of perfusion pressure increases the blood flow. What mechanism is responsible for that?
a. Neural vasoconstriction
b. Metabolic vasodilation
c. Myogenic vasodilation
c. Myogenic vasodilation
A patient has mitral stenosis due to an old rheumatic heart disease. What type of treatment is he given?
Diuretics & β-blockers
Which enzyme is seen in pheochromocytoma?
VMA
What is the mechanism of furosemide?
Inhibit Na/K/Cl pump
What is the mechanism of digoxin?
Increase intracellular Ca++
Kuwait is considered to have low hypertension percentage compared to western countries. Why is that?
Kuwait has a young population
What drug is responsible for blocking angiotensin receptors?
Losartan
What is the mechanism of action of α-methyldopa?
Stimulation of α2 receptors (agonists)
What did the drug do?

Hypotension
What is the likely cause of this condition?
a. Sympathetic dysfunction
b. Vasodilators
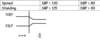
b. Vasodilators
What is the most direct cause of cardiac death?
Cardiac arrhythmias
What characterizes acute rheumatic fever?
Aschoff’s nodules
Which causes acute myocardial infarction?
Rupture of plaque




