Year 3 CAP TEST QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE (got 71%) Flashcards
Which of the following is true regarding haemoglobin? * Haemoglobin is a tetramer * All oxygen is transported bound to haemoglobin * The life span of an erythrocyte is normally 50 days * Carbon dioxide does not bind to haemoglobin * Oxygen has a greater affinity for haemoglobin than carbon monoxide
Correct answer - haemoglobin is a tetra * Oxygen is also transported by dissolving in the blood * The life span of an erythrocyte is normally 120 days * Carbon dioxide does bind to haemoglobin * Carbon monoxide has a greater affinity for haemoglobin than oxygen
The germ layers are formed during which stage of embryogenesis? Arrange the below stages of embryogenesis into order and state what happens during each stage * Cleavage * Fertilisation * Gastrulation * Morphogenesis * Organogenesis
The germ layers are formed during gastrulation
- Fertilisation - union of the sperm and oocyte
- Cleavage - earliest cell divisions of the embryo
- Gastrulation - germ layers
- Morphogenesis - formation of the body plan
- Organogenesis - development of the primordia of the body organs

An 18 year old presents following two generalised tonic clonic seizures. These occurred 2 months apart and were self limiting. She denies any illicit drug misuse or alcohol excess. Her MRI head is normal. Which of the following treatments options would you start? * Gabapentin * Sodium valproate * Phenytoin * Lamoritgine * Phenobarbitol
Correct answer is lamotrigine - least teratogenic in women of child-bearing age and there is time to titrate this up given the relatively infrequent and self-terminating events
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C837FCDF42E82767.png

Correct answer is C - * X has the same efficacy as drug Y (efficacy is the ability of an agonist to evoke a cellular response)
An 18 year-old attends a family planning clinic following her second termination of pregnancy. Her recent endocervical swab has come back positive for chlamydia infection. Select the most appropriate contraception from the options below: * Combined oral contraceptive (Microgynon) * Intra-uterine contraceptive device (Multiload Cu375) * Intra-uterine progesterone only system (Mirena) * Progesterone implant (Nexplanon) * Progesterone only pill (Cerazette)
Correct answer is D - progesterone implant Long term contraception should be encouraged to reduce the risk of unplanned pregnancy, Intra-uterine devices are contraindicated in a woman with pelvic-infection
Select the option that best fits the statement below * Anti-microbial protein(s) secreted by epithelial cells of mucosal surfaces Options * Defensin * Myeloperxoidase * Lectin * Immunoglobulin * Secretin
Correct answer - Defensins - bind to microbial cell membranes and assist in killing cells
What is the most common mode of inheritance of hereditary spherocytosis? What happens in this condition?
Hereditary spherocytosis is mainly an autosomal dominant condition that can affect the cell membrane shape In this condition, the abnormal cell membranes are spherical rather than biconcave * Affects oxygen carrying capacity * Affects ability to squeeze through small vessels -> increased destruction (splenomegaly) * Can cause pigment (bile) gallstones to due to increased unconjuated bilirubin
Which statement is true about bipolar affective disorder (BD)? * Twin studies have shown that BD has a high heritability * Several gene studies have been identified as definitely causing BD * Having a first degree relative with BD is associated with a 50% lifetime risk of unipolar depression * Patients with a strong family history of BD but no symptoms yet should be offered a mood stabiliser * Having a first degree relative with BD isn’t associated with an increased risk of schizoaffective disorder
True statement - twin studies have shown that bipolar disorder has a high heritability - heritability is about 80% People who are asymptomatic should not be offered treatment no matter how strong the family history is
Select the most appropriate treatment for a 30 year old woman, who has sudden episodes of inability to speak, associated with altered hearing and loss of spatial awareness, lasting 1-2 minutes? * Carbamezapine * Lorazepam * Phenytoin * Pregablin * Sodium valproate
This patients sound like they are having a partial seizure (simple is consciousness is maintained) 1st line treatment of partial seizures is usually Carbamezapine Or Lamotrigine
39 year old woman attends for her routine midwifery check at 38 weeks pregnant and is referred to the hospital for further assessment. She complains of frontal headache and zig-zags across her vision. The baby is moving normally and there are no signs of labour. BP is 152/98. Urinarlysis shows 3+ protein. What blood tests are essential investigations in this case? * FBC, and group and save * FBC and U&Es * FBC, U&E and LFTs * FBC, U&Es, LFTs and coag screen * FBC, U&Es, LFTs, coag screen and bile acids
Patient has developed pre-eclampsia and there is concern as to whether she has developed HELLP syndrome * (HELLP syndrome is a life-threatening condition that can potentially complicate pregnancy. Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzyme levels, and Low Platelet levels. It typically occurs in the third trimester (but can also start soon after delivery) Correct answer is C - FBC, U&Es and LFTs
A 35 year old complains of severe premenstrual pain and syparenuia caused by known severe endometriosis. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment? * Cryproterone acetate * Clomphiene citrate * Combined oral contraceptive pill * Chorionic gonadotrophin * Finasteride
Combined oral contraceptive pill is an affective treatment for endometriosis (as is any treatment that reduces menstruation)
A patient is seen in the neurology clinic, complaining of abnormal head movements and neck pain. He also notes that his head has a tendency to turn to the left and indeed he finds it uncomfortable to keep his head facing forwards. What is the most likely diagnosis? (define dystonia and spasm) * Blepharospam * Oromandibular dystonia * Cervical dystonia * Hemifacial spasm * Hemiballismus
Dystonia - sustained abnormal posture caused by persistent contraction or large trunk or limb muscles * Correct answer - Cervical dystonia (aka spasmodic torticollis) - typified by heading turning to onse side due to contraction of SCM muscle Spasm - uncontrolled contraction of a muscle * Blepharospasm - twitch of spasm of the eyelid Hemiballismus - characteristed by flailing of the limbs
Which of the following is a recognised maternal adapation to pregnancy? * Blood pressure decreases in second trimester, and returns to pregnancy level by third trimester * Cardiac output decreased by 30-50% from 6 weeks gestatinal age and then increases back to normal in the last 8 weeks of pregnancy * Erythropoiesis decreases by 25% causing anaemia * GFR stays the same throughout pregnancy * Vital capcity increases by 50%
Blood pressure decreases in second trimester, and returns to pregnancy level by third trimester - TRUE Cardiac output and GFR increase by 30-50% Erythropoiesis increases by 25% and Hb is reduced by dilution Tidal and minute volumes increase. Vital capacity is unchanged
A woman is known to carry a mutation int he factor VIII gene that causes X-linked haemophilia. She has experienced haemorrhage following surgery. Select the most likely mechanism from the options below * An X-autosome translocation causing skewed X-inactivation * A coincidental mutation in the X inactivation centre * Normal X-inactivation * She has a second mutation on her paternally inherited X-chromosome * She also has Turner syndrome
Normal X-inactivation is the most likely causes (50% of the patients liver cells will have the mutant X chromosome as the only active one - therefore reduced capcity for making factor VIII)
For each of the following language disorders, state the area responsible: * Receptive aphasia * Expressive aphasia * Nominal aphasia
Receptive aphasia - a problem with speech comprehension due to a lesion in Wernicke’s area (temporal-parietal lobe) Expressive aphasia - a problem with speech production due to a lesion in Broca’s area (frontal lobe) - patients can understand the language but unable to get their words out properly Nominal aphasia - patients unable to name familiar objects but languae otherwise preserved - suggest an inferior parietal lesion - area known as the angular gyrus
What is neuroleptic malignant syndrome? With which drug should neuroleptic malignant syndrome be treated?
NMS is a life-threatening idiosyncratic reaction to antipsychotic drugs characterized by fever, altered mental status, muscle rigidity, and autonomic dysfunction. - average onset 4-14 days after starting antipsychotic Treatment of neuroleptic malignant syndrome * DISCONTINUE ANTI-PSYCHOTIC * Then prescribe a dopamine agonist eg bromocirptine
Someone with an IQ of 45 would be described as having which severity of learning disability?
IQ 45 = moderate learning disability Borderline = 70-84 Mild = 50-69 Moderate = 35-49 Severe = 20-34 Profound = <20

An 80 year old woman with falls is found to have low serum vitamin D levels. Which of the following would you expect to see? * Low parathyroid hormone levels * High serum calcium levels * Low serium potassium levels * Low serum phsophate levels * Low serum alkaline phosphate levels
Correct answer -> D - low serum posphate levels Calcium and phosphate levels will be low with a deficiency * Phsyiologically, PTH levels increase in Vit D deficiency * Alk phos levels would increase due to osteoblastic activity early in vit D deficiency
Which of the following best describes trichomonas vaginalis? * A (true) anaerobe * A bacterium * A fungus * A protozoa (parasite) * A virus
D - a protozoal (single cell) parasite
A woman has induction of labour at 42 weeks of gestational age. Following an artificial rupture of membrane, there is a prolonged foetal bradycardia to 50bpm. Some fresh vaginal bleeding is noted and on examination the uterus is soft and non-tender. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Most likely diagnosis is vasa praevia - rare condition where unprotected foetal vessels traverse the foetal membranes over the internal os Prevents with severe foetal distress with a relatively small intrapartum bleeding following ROM (bleed in placental praevia usually starts small, then increases)

A woman is admitted at 38 weeks gestation age with severe abdominal pain and a heavy vaginal bleed. On examination her uterus is tense and the foetal heart is 50 beats per minute. What is the most likley diagnosis?
Most likely diagnosis is placental abrutpion If there is severe bleeding, uterus becomes tender, tense and there can be severe foetal distress, sometimes even intra-uterine death
For each of the following structures, select the appropriate visual field defect associated with damage to them from the options below * Lateral optic nerve lesion immediatly anterior to the chiasma * Optic chiasma * Right optic tract
Lateral optic nerve lesion immediatly anterior to the chiasma - junctional scotoma (scotoma meaning darkness, junctional meaning at optic nerve / chiasm junction) - combo of ipsilateral central scotoma and contralateral supero-temporal scotoma Optic chiasma - bitemporal hemianopia Right optic tract - left homonymous hemianopia

Necrotising enterocolitis (NEC) is a well known complication of prematurity with multiple options to reduce its incidence. Which of the following actions significantly reduces the indcidence of NEC? * Breast feeding * Use amino acid formula (hypoalergenic formula) * Use breast milk fortifier * Use preterm formula * Delay feeding
Breast feeding is the correct answer - reduces incidence of NEC
A 76 year old attended A&E following a large epistaxis. He is feeling a bit light-headed and nauseated. This bleeding has settled over the last 30 minutes with conservative management. His haemoglobin is 7.1g/dl. Select the best management plan. * Nil required * Oral iron * IV iron * IV packed red blood cells * IV O RhD negative blood
Correct answer is D - IV packed red blood cells Once the Hb is less than 8g/dl, it is reasonable to consider a blood transfusion, especially if the patient is symptomatic
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C8CAA94F36255F00.png

Case 1- D - there is pancytopenia so aplastic anaemia Case 2 - F - significant leuocytosis with increased neutrophils, eosinophils and myelocytes (normally resident in the marrow) - chronic myeloid leukaemia is the best fit Case 3 - G - marked lymphocytosis - best fit is chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
A 77 year old has a 3 month history of bilateral leg oedema Which of these results is most likely to explain her condition? * Serum albumin 54g/L (normal 35-50g/l) * Serum CRP 110 mg/L (normal
Urine protein 3.5g/day is most likely explanation Low serum albumin reduces oncotic pressure and can lead to bilateral leg oedema which can occur with a significant protein uria - can occur in patients with nephrotic syndrome where urinary protein is significant
A 29 year old labourer was moving bricks and describes feeling something going in his back. He has since noted pain down the back of his knee. On examination he has an absent knee reflex and weakness in knee extension and ankle dorsiflexion . You also find that he has decreases sensation on the inner aspect of his calf. You suspect of a disc prolapse. Which nerve root is affected?
L4 nerve roots - responsible for leg extension, patellar reflex and ankle dorsiflexion
Which of the following is least likely to happen in the first week of life for a pre-term infant born at 29 weeks of gestation: * Sepsis * Respiratory distress syndrome * Intraventricular haemorrhage * Patient ductus arteriosus * Chronic lung disease (broncho pulmonary dysplasia)
Sepsis Respiratory distress syndrome Intraventricular haemorrhage Patient ductus arteriosus Chronic lung disease (broncho pulmonary dysplasia) ALL of the above are known complications of prematurity, except for chronic lung disease which describes a condition in which the preterm infant will require O2 supplementation beyond 28days or beyond 36 weeks corrected gestation
A 74 year old presents with a haematemesis and hypotension. He is taking warfarin due to his atrial fibrillation. Which of the following is not an appropriate reaction? * Check the patients INR * Give vitamins K * Give fresh frozen plasma * Give a four factor (II, VII, IX, X) coag factor concentrate * Phone the on-call haematologist for advice
Check the patients INR Give vitamins K Give a four factor (II, VII, IX, X) coag factor concentrate Phone the on-call haematologist for advice Wrong answer - Give fresh frozen plasma - does not give sufficient coag correction when there is a life threatenting haemorrhage - slow to act
An 85 year old lady presents with incontinence. She is unable to get to the toilet in time. The very thought of the toilet makes her incontinent. What type of incontinence does she have.
Urge incontinence - typically presentation in urge where any stimulus triggers detrusor and leads to sudden voiding
A 75 year old man with a six month history of Parkonsonism and a ten year history of ischaemic heart disease presents with short term memory loss, difficulty counting money and word-finding difficulties. He has no other symptoms. A SPECT scan shows reduced attentuation throughout the brain. What is this diagnosis? * Lewy body dementia * Dementia in Parkonsin’s disease * Vascular dementia * Frontotemporal dementia * Alzhiemers dementia
Correct answer- vascular dementia Although he has Parksonism, he has no other features of LBD and his SPECT scan is indicative of vascular dementia
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpg-172C8EF310324235426.png

Neutrophil with toxic granulation
Which of the following drugs is most likely to precipitate an acute attack of gout? * Amlodopine * Simvastatin * Spironolactone * Atenolol * Bendroflumethiazide
Bendroflumethiazise - a thiazide diuretic
Which area of the brain is first affected in Alzheimer’s disease?
The nucleus basalis of Meynert is the area of the brain to bee affected by the neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease
What is the most appropriate term for each of these presentations? * A 30 year old woman with borderline personality disorder pretends to have seizures so that she can claim benefits for disability living allowance * A 30 year old woman with borderline personality disorder has episodes where she loses consciousness and appears to have a tonic clonic seizure, but her EEG is normal.
A 30 year old woman with borderline personality disorder pretends to have seizures so that she can claim benefits for disability living allowance - MALINGERING (illness faked for secondary gain * A 30 year old woman with borderline personality disorder has episodes where she loses consciousness and appears to have a tonic clonic seizure, but her EEG is normal - NON-EPILEPTIC SEIZURE (associated with a history of child abuse)
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C9135A6A545AC506.png

* Case 1 - MIGRAINES unilateral moderate/severe headaches between 4 and 72 hours of length * Associated with pulsating/throbbing, worse on movement, nasuea/vomiting * Case 2 - Benign intracranial hypertension - can be caused by taking COC - worse on any activity that further increases intracranial pressure such as coughing or sneezing * Case 3 - Acute tnesion headache - mild/moderate, non pulsatile bilateral headache
This organsim does not stain with gram stain and is a spirochaete (spiral shape) organism. It is diagnosed primarily by serological tests (or by PCR in the early stages) Select the organsim that causes a STI from the options below * Chlamydia trachomatis * Herpes simplex * Human papilloma irus * Neisseria gonorrhoea * Trepoenema pallidum
The only spirochete in the list is treponema pallidum - causative agent of syphilis
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpgpngjpg-172C91B55F661E401A5.png

In some bones, this is the location of the site of production of new blood cells - the bone marrow this is referring to which is contained within the MEDULLARY CAVITY - E Forms the outer lining of bones - PERIOSTEUM - H A bony feature seen, for example, in the internal aspect of the base of the skull - FOSSA - E
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune condition in which antibodies are directed against: * Postsynaptic calcium channels * Presynaptic calcium channels * Postsynaptic cholecalciferol receptors * Presynaptic acetycholine receptors * Postsynaptic acetylcholine receptors
Correct answer - E In myasthenia gravis, autoantibodies are directed against postynaptic acetylcholine receptors * (In Lambert Eaton Myasthenic syndrome - the autoantibodies are directed against the voltaged gated presynaptic calcium channels)
A 30 year old is breast feeding her 6 week old baby. Which of the following drugs is contra-indicated? * Warfarin * Labetaolol * Tetracycline * AMoxicillin * Amitryptilline
C - Tetracycline is contraindicated - it is abosrbed into the breast milk and may cause discolouration of the infants teeth
A 78 year old man complains of poor balance and falls. On examination you find that he as a significant sway. Which of the following is least likely to contribute to his falls? * Muscle strength * Vestibular dysfunction * Cerebellar dysfunction * Posterior spinal cord dysfunction * Carotid sinus hypersensitivity
Least likely to contribute - Carotid sinus hypersensitivity Carotid sinus hypersensitivity will cause acute sympotms of dizziness and collapses rather than increase postural sway
Which hormone can be measured to determine whether a woman has ovulated? Which hormone can be used to assess ovarian reserve prior to in vitro fertilistion treatment? Which hormone can be measured to perform serial assessment to help with the possible diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy?
* Which hormone can be measured to determine whether a woman has ovulated - PROGESTERONE - secreted by corpus luteum, peaking approx 7 days post-ovulation * Which hormone can be used to assess ovarian reserve prior to in vitro fertilistion treatment - ANTI-MULLERIAN HORMONE - predict response to supra-ovulation in IVF treatment * Which hormone can be measured to perform serial assessment to help with the possible diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy - Human chorionic gonadotrophin
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C924DC2014113002.png

Case 1 - Huntington’s disease - * presents usually in the 40s * autosomal dominant (clue with father dying young) * Presents classically with chorea (involuntary movements of the limbs) which leads to cognitive decline Case 2 - Lewy body dementia * Classic dementia, hallucinations, falls and parkonsonism * Symptoms classically fluctuate
What is the mechanism of action of memantine? Blockage of voltage sensitive sodium channels Blockage of N-methyl-d-aspartic acid (NMDA) type glutamate channels Blockage of 2-amino-3 (3-hydroxy-5-methyl-isoxazol-4-yl) propanoic acid (AMPA) - type glutamate receptors Blockage of muscarinic receptors Blockage of nicotinic receptors
Memantine - Blockage of N-methyl-d-aspartic acid (NMDA) type glutamate channels - used in severe dementia
Which artery is most likely to be the causes of bleeding during the following surgical procedures? * Insertion of a lateral adominal port, during female laproscopic sterilisation * Incision of a bartholin’s abscess * Dissection of the lower end of the ureter
Insertion of a lateral adominal port, during female laproscopic sterilisation - INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY (branch of the external iliac artery) Incision of a bartholin’s abscess - INTERNAL PUDENDAL ARTERY (technically branches from this artery) Dissection of the lower end of the ureter - UTERINE ARTERY
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C92B7E7A5CB25677.png

Correct answer - B - Chlamydia infection * Chlamydia infections are common causes of irregular vaginal and post-coital bleeding. Therefore an endocervical swab should be performed. * Although a cervical smear is due, this is not an investigation for irregular bleeding * An endometrial biopsy and ultrasound scan would only be considered to investigate post-menopasual bleeding or when examination reveals an abnormality
What is the main mechanism of action of lamotrigine?
Lamaotrigine antagonises voltage sensitive sodium channels and this reduces the release of glutamate - the main excitatory neurotransmitter
A 68 year old man who has been a smoker for over 50 years, complains of pain in his calves when walking; it comes on after about 50 metres. He is hypertensive (BP 176/94). Urinalysis shows protein ++ and no blood. His GP checks his renal function. Urea 15mmol/l. Creatinine 190 nanomol/l What is his most likely diagnosis? * Multiple myeloma * IgA nephropathy * Carcinoma of the prostate * Renal artery stensosis * Membranous nephropathy
Renal artery stenosis - causes hypertension and atrophy of the affected kidney - if caused by fibromuscular dysplasia the patient may develop claudication
Which of the following is true regarding the normal bladder function? * Production of 3L of urine in 24 hours is considered within the normal range * Desire to void usually occurs when the bladder volume is 250mls * Stimulation of parasympathetic nerves induces relaxation of the detrusor muscle * Relaxation of the urethral sphincter is under purely voluntary control * Female urethra measures 5 to 6 cm
Case 1 - B is correct - the desire to void does usually occur when the bladder volume is 250ml * Polyuria is when over 2.8L is produced in 24 hours * Parasympathetic nerve stimulation results in contraction of the detrusor muscle * Urethral sphincter is under both voluntary (striated muscle) and involuntary (smooth muscle) control * Female urethra measures 3-4cm
Which investigation should be done prior to initiation of lithium carbonate?
Urea and electrolytes -> Lithium can cause renal impairment so it is important to get a baseline measure for comparison
A 55 year old male presents with left testicular pain and swelling. His pain started approximately 2 days ago. On examination the left testis is tender, swollen, with redden skin. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? * Testicular torsion * Epidydimo orchitis * Testicular tumour * Scrotal hernia * Varicocele
Correct answer -Epididymo-orchitis - usually unilateral and presents with acute onset of pain, swelling and tendernes (there may be a urethral discharge and pyrexia) * In torsion, the presentation is usually within hours * Too acute for a tumour, that can be painless * Scrotal hernia not usually tender on examination * Varicocles are usually painless
Which of the following changes results in a right shift of the oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve? * Decreases carbon dioxide * Decreased pH * Decreased temperature * Decreased 2,3 DPG * Decreased hydrogen ions
Right shifts of the oxyhaemoglobin curve is caused by acidosis (reduced pH, or increases H+ ion concentration), increased CO2, increased concentration of 2,3BPG and increased temp Therefore the correct answer is B - decreased temp
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C946AF4A784CD5FE.png

B - Take her forgotten pill now and the next one at the usual time. Additional precuations are only required if she missed 2 or more combined oral contraceptive pills
At what stage does the embryo implant into the uterus * Pronuclear * 8 cell stage * Blactocyst * Morula * Gastrula
Correct answer C - Blastocyst An embryo develops into a blastocyst around day 5, with an inner cell mass and trophoblast. Implanatation occurs around day 6 to 10.
A 42 year old attends her GP complaining of heavy period and tiredness. Her cycle is regular coming every 28 to 32 days and lasts for 5-7 days. Her last cervical smear was 6 years ago. On vaginal examination her cervix appears healthy and her vuvla and her uterus is normal sized. What investigation is appropriate to investigate her heavy menstrual bleeding? * FBC * Cervical smear * Endomaterial biopsy * USS to determine endometrial thickness * Dilatation and curettage
FBC - first line investigation for heavy menstrual bleeding is to assess for anaemia Although a cervical smear is due, this is not an ivnestigation for heavy periods.
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C94BE087546BB66D.png

Case 1 - G - neisseria gonorrhoea Case 2 - H - patient has urethreitis as demonstrated by his symptoms and presence of pus cells in the urethral discharge. As PCR tests are negative, he would be classified as having non-specific urethreitis Case 3 - A - Bacterial vaginosis - presence of clue cells and offensive discharge
An 85 year old man is admitted with confusion. You suspect delirium. Which three features are essential for a diagnosis of delirium? * Fluctuating course, gradual onset, agitation * Fluctuating course, hallucinations, agitation * Acute onset, hallucinations, disorganised thinking * Acute onset, inattention, drowsiness * Gradual onset, inattention, drowsiness
Acute onset, inattention, drowsiness A diagnosis of delirium requires the following features * Acute onset * Inattention with fluctuating course Plus one of * Disorganised thinking or altered level of consciousness
A 34 year old is currently taking the combined oral contraceptive pill for contaceptions. Which of the following drugs is known to reduce the contraceptive efficacy of the drug? * Methyldopa * Phenytoin * Mefanamic acid * Amoxycillin * Codeine
Phenytoin reduces contraceptive efficacy as it is a liver enzyme inducer
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C9524D8751D4AA9C.png

Option C - Reassure and re-examine in 2 hours * CTG is reassuring despite there being meconium stained liquor * She is likely to have a SVD and should be reexamined in 2 hours * She requires continuous CTG monitoring throughout labour because of the meconium stained liquor
Which legal course of action should be taken in the following situation? A man with severe depression is detained on a short term certificate, which is due to lapse in 10 days time. His psychiatrist believes that he will need to stay in hospital for longer than this, but he refuses to stay as he believes he is too wicked to deserve treatment?
If a patient required treatment under the Mental Health Act after their short term order expires, a mental healthy officer must apply to the mental health tribunal for a COMPULSORY TREATMENT ORDER (section 63 of Mental Health act Scotland) Application must be accompanied from two medical practitioners
Which legal course of action should be taken in the following situation? A woman with dementia fractures her hip and requires surgery. The surgeon takes time to explain the proposed operation clearly and simply but she does not understand
Adults with incapacity Act Section 47 - can be used in a patient who does not have the capacity to accept or decline treatment themselves
Which hormone in pregnancy causes enlargement of the mammary glands of the breasts and prepares for lactation?
Prolactin
Unfractioned heparin is best dosed by performing which of the following tests * Prothrombin time * International normalised rati * Activated partial thromboplastin time * Plasma viscosity * Bleeding time
APTT - Activated partial thromboplastin time is used to monitor heparin
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C95967F2703ED1CE.png

* Case 1 - C- Iron deficiency anaemia * Case 2-H-autoimmune haemolytic disease - anaemia and jaundice should make you consider the possibility of haemolysis - bone marrow is working hard to make new red cells and reticulocyte count is very high in this case. spherocytes on the blood film could mean autoimmune or hereditary spherocytosis but the history an strong direct antiglobulin tests suggest this is autoimmune * Case 3- J - Multiple myeloma
State the most likely diagnosis A 33 year old woman who is 6 weeks post-partum develops a hot tender breast and a milky discharge. her grandmother had breast cancer at the age of 75 years. Examination reveals a 2.5cm tender lump in the upper outer quadrant of her right breast
Breast abscess - these tend to more common in lactating women and are tender
State the most likely diagnosis A 26 year old woman has a smooth mobile lump in the lower inner quadrant of her left breast. You examine her and both nipples are inverted which she says is long standing
Fibroadenoma - tend to present in younger women as mobile smooth breast lumps
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpg-172C95ECA8023E1DB10.png

D is the correct answer * Xanthochromic CSF indicates the presence of blood - likely to be seen in patietns with subarachnoid haemorrhage * CSF is clear in viral meningitis, guillian barre, Multiple sclerosis and normal samples * CSF is cloudy in bacterial and TB (usually) * Glucose is low in bacterial as it is utilised as an energy soruces * Lymphcoytes raised in viral, TB and MS
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C9613E1817A3CB36.png

D is correct Reaction A is an example of competitive inhibition. As more substrated is added, inhibitor binding at the catalytic site declines and the reaction tends towards Vmax
For each of the following scenarios, state the mechanism of action best associated with the drug used * A 70 year old man admitted to hospital with a MI. He is started on aspirin * A 65 year old woman diagnosed with a stroke is commenced on clopidogrel * A 24 year old man undergoes mitral valve replacement and is commenced on warfarin
A 70 year old man admitted to hospital with a MI. He is started on aspirin - Inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX1 and COX2) A 65 year old woman diagnosed with a stroke is commenced on clopidogrel - Antagonsit against adenosine diphosphate receptor (P2Y12 receptor inhibitors) A 24 year old man undergoes mitral valve replacement and is commenced on warfarin - vitamin K antagonist (prevents post-translation modification of vitK dependent factors II, VII, IX, X, Protein S and C)
A 29 year old woman presents with a first positive pregnancy test. She thinks she is approximately 8 weeks pregnant and is keeping well. She has no other medical conditions and is a non-smoker. The pregnancy is unplanned and she has not been taking any supplements so far. Which supplement should she continue throughout her pregnancy? * Folic acid * Folic acid and vit D * vit D * Folic acid, vit D and ferrous sulphate * Ferrous sulphate
Correct answer is vitamin D Folic acid is only beneficial in early pregnancy before neural tube closure No evidence of benefits of ferrous sulphate unless iron deficiency anaemia is present
For each of the following tendon reflexes, state the nerve root * Biceps reflex * Ankle reflex * Knee reflex
Biceps reflex - C5,6 Ankle reflex - S1(2) Knee reflex - L3,4
Which of the following statements about transport in the proximal tubule is true? * 100% of filtered glucose and amino acids are reabsorbed * About 10% of salt and water are reabsorbed * Reabsorption is by paracellular mechanisms only * Urea is secreted * Hydrogen ions are reabsorbed
The proximal tubule is involved in regulation of pH and also is where 100% of filtered glucose and amino acids are reabsorbed
A 62 year old woman has collapsed twice recently. Each time she has lost consciousness but recovered very quickly. She also complains of breathlessness on exertion. On examination her BP is 108/90 and she has an ejection systolic murmur. What valvular abnormality is the patient most likely to have?
Ejection systolic murmur and collapsing - aortic stenosis
What is the inheritance of each of the following neurological conditions * Wilson’s disease * Becker’s muscular dystrophy * Myocolonic epilepsy with ragged red fibres
Wilson’s disease - autosomal recessive - due to copper accumulation in the tissues (mutation in copper transporting protein ATP7B) Becker’s muscular dystrophy - X-linked recessive Myocolonic epilepsy with ragged red fibres - Mitochondrial
What is the enzyme that transcribes genetic material?
RNA polymerase transcribes messenger RNA from DNA that comprises the exon (coding) regions of a gene
An 18 year old student presents with an 8-week history of an enlarging lump in his neck and night sweats. On examination, he has a 4x5cm nodal mass in the right anterior triangle of his neck and right axillary lymphadenopathy. Which of the following tests is most likely to give a definitive diagnosis? * Bone marrow biopsy * Haemoglobin high performance liquid chromatography * Lymph node biopsy * Serum protein electropheresis * Peripheral blood immunophenotyping
Presentation is typical of Hodgkin’s disease - best diagnnosed by LYMPH BIOPSY (excision mrore useful than core biopsy)
What is the function of the aversive and defensives systems of the body? Which neurotransmitter is most involved in the aversive and defensive systems?
The function of the aversive and defensive systems is to promote survivial in the event of a threat. The ascending serotonin are most involved in these systems
A 28 year old attends her morning GP surgery concerned that she has forgotten to take her oral contraceptive pill the previous evening. What is the most appropriate advice?
Take her forgotten pill now and the next one at the usual time - additional contraception only required if she has missed 2 oral contraceptive pills
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C974837E1E442B9E.png

B - There is rouleax formation - when the red cells are stacked like a group of coins. * This change occurs when the charge on the surface of the cells is altered as a consequence of cell being labelled with proteins. * The proteins can be acute phase proteins (as one would find in a reactive process eg infections) or paraprotein (intact immunoglobulin) found in plasma cell dyscrasias.
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C976B1775E7BCBC4.png

Case 1 - B - imperforate hymen- usually presents approx 2 years after puberty with abdo pain Case 2 - G - premature ovarian failure - diagnosed by elevated FSH levels - important to exclude pregnancy with a urinary pregnancy test Case 3 - I - Polycystic ovarian syndrome - 2 out of 3 of * Oligo or amenorrhoea * Clinical or biochemical increase in androgens * Enlarged ovaries with multiple peripheral cysts on scan
Which cell type would typically be expected to increase in the following? Peter Smith, a 55 year old man is suddenly taken ill and admitted to hospital. Strep pneumonia is isolated from blood cultures
Neutrophil
Which cell type would typically be expected to increase in the following? John Stewart, a 62 year old man develops a rash after being started on new anti-hypertensive medication
Eosinophils are increased during allergic response (and basophils)
Which cell type would typically be expected to increase in the following? James Scott, a 23 year old foundation year doctor develops coryzal symptoms and influenza A is isolated from nsal swabs?
Lymphcoytes
Which abnormality of the hypothalamic pituitary axis is associated with depression?
- * Adrenal atrophy
- * Decreased cortisol in urine
- * Decreased production of coritsol
- * Decreased secretion of ACTH
- * Cortisol non suppression following dexamthasone administration
Major depression is associated with * adrenal enlargement, * increased secretion of cortiol and ACTH and * cortisol non-suppression following dexamtheasone administration

Which of the following drugs inhibits the action of acetylcholinesterases? * Galantamine * Amitryptyline * Mirtazapine * Aripiprazole * Phenlzine
Galantamine is a cholinesterase inhibitor
Select the causative organism that causes a STI. It does not stain with gram stain. It is an intracellular orgnaism that produces both elementary bodies and reticulate bodies during its reproductive cycle. It is diagnosed by PCR * Chlamydia trachomatis * Herpes simplex * Human papilloma virus * Neisseria gonorrhoea * Treponema pallidum
Chlamydia trachomatis is the answer - forms both elementary and reticulate bodies
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/png/pjpgpngjpg-172C981254E231C27A8.png

Haemolytic Uraemic syndrome due to E.coli 0157 * Red cell fragmentation and thrombocytopenia occurs when there is intravascular destruction of red blood cells due to overactivation of the complement system or of platelets - this is known as a microangiopathic haemolytic uraemia * Most likely causes in this case is HUS due to E.coli due to the history of diarrhoea
State which neurotransmitter is the most likely to be abnormal in the following case A 21 year old man with known elicit drug use who attends the emergency department following a suspected epileptic fit
GABA (gamma aminobutyric acid)
State which neurotransmitter is the most likely to be abnormal in the following case A 24 year old man brought to the emergency department after an episode of bizarre behaviour indicating third party auditory hallucinations. he has no previous medical history
Dopamine - appears to be inexcess in shcizophrenia
State which neurotransmitter is the most likely to be abnormal in the following case A 50 year old man attends her GP with a 3 month history of low mood and poor concentration following a relationship breakdown
Serotonin is low (5-hydroxytryptamine)
A 60 year old male presents with malaise, fever, painful erosions of his mouth a generalised erythema with desquamation which has developed over 2 days. He was recently started on an antibiotic for a chest infection. What is the most likely diagnosis? * Toxic epidermal necrolysis * Eyrythroderma * Sweet’s disease * Vasculitis * Erythema multiforme
Toxic epidermal necrolysis - involves >30% of the skin surface
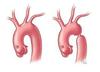
Which of the following suggests congenital cardiovascular diseases in a new born infant? * Delay in femoral pulses * Early neonatal jaundice * Polycythaemia * Peripheral cyanosis * Splitting of the second heart sound
Delay of femoral pulses - highly suggestive of coarctation of the aorta
A 70 year old patient is in an acute medical ward develops vomiting and diarrhoea. You want to test for norovirus. What is the most appropriate investigation?
Stool for polymerase chain reaction


