Integrated Specialties E - Rheumatology Assessment 4th year (82%) Flashcards
Following 2 months of joint pain, a 38 year old lady, otherwise well and fit is diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis after appropriate investigations. Which of the following treatments is recommended first? Methotrexate Azathioprine Diclofenac Anti-TNF therapy Anti- IL6 therapy
Methotrexate - 1st line DMARD for RA Give with NSAID + steroid to begin with to rapdily reduce inflammation
The Beighton score is a simple system to quantify joint laxity and hypermobility. It uses a simple 9 point system, where the higher the score the higher the laxity. What are the 5 categories used to assess joint hypermotility? (little finger, thumb, elbow, knee, palms)
Passively dorsiflex little finger greater than 90 degrees (R+L) Passively oppose thumb to volar aspect of the ipsilateral forearm (R+L) Passively hyperextend elbow greater than 10 degrees (R+L) Passively hyperextend knee greater than 10 degrees (R+L) Hands can rest flat on floor when flexing the trunk with extended knees

Select which of the following statements are true of the Beighton classification of joint Hypermobility * a. The ability to place both palms on the floor when bending with straight legs * b. A score of 2 or more confirms the diagnosis of hypermobility * c. The ability to passively touch the forearm with the thumb with the wrist in the flexed position scores one point per wrist. * d. > 10 degrees of hyperextension at the elbow * e. There are a total of 9 criteria in the scoring system
TRUE * a. The ability to place both palms on the floor when bending with straight legs * c. The ability to passively touch the forearm with the thumb with the wrist in the flexed position scores one point per wrist. * d. > 10 degrees of hyperextension at the elbow * e. There are a total of 9 criteria in the scoring system Score of 4 or more is a good indicator of hypermobility
Live vaccinations can be given during treatment with DMARDs Select one: True False
FALSE
A 32 year old man is diagnosed as having a pulmonary embolus with no clinical risk factors. Anticardiolipin antibodies are raised. What is the most appropriate treatment? a. 3 month course of rivaroxaban, with life-long rivaroxaban if he has a second thrombotic event. b. 3 month course of warfarin followed by aspirin c. 3 month course of warfarin with life-long warfarin if he has a second thrombotic event. d. life-long warfarin e. 2 year course of warfarin
d- life long warfarin
Which of the following statements about changes on X-ray is correct? Select one: a. Subchondral sclerosis is seen in psoriatic arthritis b. Punched out lesions are seen often in osteoarthritis c. Chondro-calcification is a typical feature in gout d. Pencil-in cup change is characteristic of pseudogout e. Peri-articular osteopenia and erosions are seen in rheumatoid arthritis
a. Subchondral sclerosis is seen in OSTEOARTHRITIS b. Punched out lesions are seen often in GOUT c. Chondro-calcification is a typical feature in PSEUDOGOUT d. Pencil-in cup change is characteristic of PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS e. Peri-articular osteopenia and erosions are seen in rheumatoid arthritis - TRUE
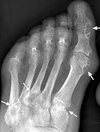
In a patient diagnosed with Polymyalgia rheumatica, the correct starting dose of prednisolone is 40mg daily Select one: True False
False- the correct starting dose is 15mg daily 15% of patients with PMR have/develop GCA pic just shows what punched out lesions on a gout xray appear as
The joints most commonly affected in ankylosing spondylitis are: (There may be more than one correct answer.) Select one or more: Spine Small joints of the hand Sacroiliac joints Temperomandibular joint Knee
Spine and sacroiliac joints
Which of the following are true? Select one or more: a. Steroids can be used to reduce inflammation in acute gout. b. Allopurinol reduces urate in gout by inhibiting xanthine oxidase c. Allopurinol should be titrated until target serum urate is achieved (below 360 micromol/L). d. Colchicine can only be used for up to 3 days in gout. e. Allopurinol should be stopped during acute gout flares.
True a. Steroids can be used to reduce inflammation in acute gout. b. Allopurinol reduces urate in gout by inhibiting xanthine oxidase False c. Allopurinol should be titrated until target serum urate is achieved (below 360 micromol/L). - 300micromol/l d. Colchicine can only be used for up to 3 days in gout. - wait 3 days between treatment e. Allopurinol should be stopped during acute gout flares
Which of the following are known side effects of corticosteroids? Select one or more: a. Muscle hypertrophy b. Adrenal suppression c. Glaucoma d. Fluid retention e. Osteoporosis
b. Adrenal suppression c. Glaucoma d. Fluid retention e. Osteoporosis
True or false: In acute exacerbations of gout, allopurinol is a useful treatment for controlling symptoms. Select one: True False
False 1st line - NSAIDs If they fail, try colcichine If that fails, try oral or intraarticular steroids
Which of the following is true of primary Sjogren’s syndrome? Select one: a. There is an increased incidence of lymphoma in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome b. The best treatment for dry mouth is total dental clearance c. There are no antibody tests to aid diagnosis d. It is commoner in males e. It has the worst prognosis of all the connective tissue diseases
a. There is an increased incidence of lymphoma in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome - TRUE b. The best treatment for dry mouth is total dental clearance - DENTAL HYGIENE c. There are no antibody tests to aid diagnosis - anti-RO & LA d. It is commoner in males - females e. It has the worst prognosis of all the connective tissue diseases - false
Which of these autoantibodies is most specific for SLE? Select one: a. Anti-smooth muscle antibody b. Anti-DNA binding antibody c. Anti-Ro antibody d. Anti-Scl-70 e. Anti-nuclear antibody
Anti-DNA binding antibody is the most specific for SLE
Which of the following is true? Select one: 1. PMR and GCA have a quick onset, within weeks 2. GCA is seen in 15% of patients with PMR. 3. Polymylagia rheumatic (PMR) is seen in 50% of patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA). 4. Prednisolone starting dose in PMR is 15 mg/day. 5. The proximal limb girdle muscles are the predominant site of symptoms in PMR. 6. ALL OF THE ABOVE
ALL OF THE ABOVE
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/jpg/ppngjpgpng-1710EB949E376D634EB.jpg

EOSINOPHILIC GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS (eGPA)
Polymyalgia rheumatica principally affects patients over the age of 50 years Select one: True False
TRUE
Select one: a. Anti-mitochondrial antibody b. ANCA c. Anti-CCP antibody d. Anti-centromere antibody e. Anti-nuclear antibody

b - ANCA Looks like Granulomatosis wiith polyangiitits Expecting c-ANCA specific for PR3, would probs do a renal biopsy to check for glomerulonephritis
Treatment in polymyalgia rheumatica is likely to continue lifelong Select one: True False
False - usually taper down over 18 months/2years
A patient has pain in their lower back and a positive anti-nuclear antibody at a titre of 1:160. This is diagnostic of SLE. Select one: True False
FALSE
Please match the following sites of pain and diagnosis Tenderness over the medial epicondyle Tenderness in the heel on walking Tenderness over the lateral epicondyle of the elbow Restricted rotation of the shoulder Tenderness over the greater trochanter * Golfer’s elbow * Tennis elbow * Trochanteric bursitis * Adhesive apsulitis * Plantar fasciitis
Tenderness over the medial epicondyle - GOLFER’S ELBOW Tenderness in the heel on walking - PLANTAR FASCIITIS Tenderness over the lateral epicondyle of the elbow - TENNIS ELBOW Restricted rotation of the shoulder - ADHESIVE CAPSULITIS Tenderness over the greater trochanter - TROCHANTERIC BURSITIS
The following medications are appropriate treatments for acute gout (under 4 weeks duration) Select one or more: a. Colchicine b. Flucloxacillin c. Prednisolone d. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (eg. Naproxen) e. Allopurinol
a. Colchicine c. Prednisolone d. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (eg. Naproxen)
Which of the following is not a recognised treatment for Osteoarthritis? Select one: a. Topical analgesics b. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (eg. Naproxen) c. Joint replacement d. Methotrexate e. Physiotherapy
d - Methotrexate
Which of the following best describes the therapeutic approach to connective tissue diseases? Select one: a. Treat symptomatically and monitor closely for major complications b. Physiotherapy and if necessary surgery to stabilise the joints c. Immunosuppression with an aim to normalise antibody levels d. Discharge to general practitioner with a request for rereferral if major organ involvement occurs e. Start high dose steroids on diagnosis
a. Treat symptomatically and monitor closely for major complications
Which of the following is an x-ray finding indicative of Pseudogout? Select one: a. Peri-articular erosion b. Loss of joint space c. Subchondral cyst formation d. Peri-articular osteopenia e. Chondrocalcinosis
e - chondrocalcinosis

Select one: a. Pulmonary fibrosis b. Stage 3b renal impairment c. Cord compression secondary to atlanto-axial joint disease d. General frailty e. Anaemia of chronic disease
c. Cord compression secondary to atlanto-axial joint disease
SLE more commonly affects males than females Select one: True False
Almost 10:1 females to males Usually black african/carribean or asian Rarely present in africa and carribean however so environmental trigger with genetic predisposition
In a patient with fibromyalgia what blood abnormalities would you expect to see? Select one: a. Raised plasma viscosity b. Raised CRP c. Positive anti-nuclear antibody d. No abnormality e. Anaemia
d. No abnormality
A patient is diagnosed in the respiratory clinic as having pulmonary fibrosis. The chest physician notes that she has Raynaud’s phenomenon, dry eyes, facial telangiectasia and puffy hands. What is the most likely diagnosis? Select one: a. Primary Sjogren’s syndrome b. Limited systemic sclerosis c. Diffuse systemic sclerosis d. Systemic lupus erythematosus e. Rheumatoid arthritis
c. Diffuse systemic sclerosis
Which of the following statements is true? Select one: a. Inflammatory markers are always normal in vasculitis. b. ANCA is always positive in small vessel vasculitis. c. Large vessel vasculitis is generally ANCA negative. d. A rise in ANCA titre always predicts a relapse of vasculitis. e. Anti-PR3 is specific for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis.
c. Large vessel vasculitis is generally ANCA negative.
Which of the following statements is false? Select one: 1. HLA B27 may be positive in reactive arthritis 2. The treatment for reactive arthritis can include intraarticular or oral steroids and DMARDs 3. The joint aspirate in reactive arthritis is usually positive for microorganisms. 4. Reactive arthritis can occur following a Campylobacter infection 5. 90% of reactive arthritis cases resolve spontaneously
- The joint aspirate in reactive arthritis is usually positive for microorganisms - FALSE
90% of cases of reactive arthritis are self limiting If symptoms persist what treatment options can be given? What is rarely used but can be given in chronic cases?
NSAIDs if symptoms persists Steroids can be given if NSAIDs dont manage to control symptoms Rarely DMARDs may be required
Fibromyalgia syndrome can be treated successfully with a reducing course of prednisolone Select one: True False
FALSE


