Week 5 - D - General Trauma (2) - Describing a fracture and the clinical signs Flashcards
(30 cards)
What are the five basic fracture patterns?
* Transverse
* Oblique,
* Spiral,
* Comminuted
* Segemental

When do transverse fractures occur?
They occur during a bending force when the cortex on one side fails in compression and the the cortex on the other side in tension
When do oblique fractures occur?
They occur due to shearing forces eg falling from height or deceleration
How are oblique fractures fixed?
They have the benefit of being fixed with an interfragmentary screw
Which between oblique and transverse fractures tend to shorten(overall bone length and angulate)
Oblique fractures tend to shorten and may also angulate.
Transverse fractures can angluate but usually not shorten
When can transverse fractures shorten?
Transverse fractures can shorten if they are completely displaced
Which fractures are most unstable due to rotational (torsional) forces?
Spiral fractures
What can potentially be used to fix both spiral fractures and oblique fractures?
Interfragmentary screws
Spiral fractures occur due to torsional forces
How many fragments must a comminuted fracture have?
Comminuted fractures are fractures with 3 or more fragments.
What are the two main causes of comminuted fractures?
They are a reflection of higher energy injury or poor bone quality
There may be substantial soft tissue swelling and periosteal damage with reduced blood supply to the fracture site which may impair healing in comminuted fractures Comminuted fractures are very unstable and how do they tend to be stabilised?
Tend to be surgically stabilised
A segmental fracture occurs when the bone is fractured in two separate places How are they treated?
Segmental fractures tend to require stabilisation with long rods or plates
Questions for which fracture
* Occurs due to a shearing force? (describe a shearing force)
* Occurs due to torsional force?
* Occurs due to a bending force?
* Fractured in two places?
* Fracture is 3 segements?
- Shearing force - this is an oblique fracture due to eg fall from a height or decelerating
- Torsional force - spiral fracture
- Bending force - would be transverse
- Fractured in two places - segemental fracture
- Fracture is in 3 segements - comminuted fracture

How are spiral and oblique fractures treated?
Uusally with interfagmentary screws
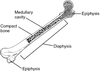
A decision regarding the optimum management of a fracture depends on the site of the fracture, whether its position is satisfactory or not and its stability (likelihood of displacing) which is related to the fracture pattern and the degree of initial displacement. What are the three separate parts of the bone? - can use to desribe the type of bone involved in the fracture
Have the epiphysis, metaphysis and diaphysis

What type of bone is in the diaphysis and epiphysis?
Diaphysis - compact cortical bone
Epiphysis - trabecular/cancellous bone
Which of the five types of fractures are very unstable?
Spiral, comminuted and segemental fractures
A fracture of a long bone can be described according to the site of the bone involved How would this be described?
Proximal, middle or distal 1/3rd of the bone
A fracture at the end of a long bone (metaphyseal / epiphyseal) can be intra‐articular (extending into the joint) or extra‐articular. Which have a greater risk of stiffness, pain and post‐traumatic osteoarthritis?
This would be intra-articular bone fractures
The position of a fracture depends on the degree of displacement and angulation What does the displacement of a fracture mean?
This refers to the direction of translation of the fracture and is described using anatomic terms eg anterior, posterior, medial and lateral
In the forearm and hand, anterior and posterior displacement are typically substituted by volar (or palmar) and dorsal How are medial and lateral displacement changed?
They are described by ulnar or radial displacement
So what is dispalcement and how is it described in the forearm/hand?
Displacement is the direction of translation of the distal fragment of bone and can be described using the terms, anterior, posterior, medial and lateral
In the forearm and hand,
anterior = volar (or palmar),
posterior = dorsal,
medial = ulnar, l
ateral = radial translation
Displacement can be estimated with reference to the width of the bone (eg 25%, 50%, 75% displacement) What is 100% displacement often referred to as?
Off ended fracture - a long bone fracture that is displaced by more than the width of the bone.

Angulation desribes the direction in which the distal fragment points towards and the degree of this deformity. Event though it is typically described as anterior, posterior, medial and lateral How is it described usually in the lower and upper limb?
Upper limb - described as volar, dorsal, ulnar and radial
Lower limb - varus (distal fragment pointing towards the midline) , valgus (distal fragment pointing away from midline)