Week 3 - G - Foot/Ankle (Tarsal coalition, hallux valgus & talipes equinovarus) and Spine problems (Scoliosis & spondylolisthesis) Flashcards
What is tarsal coalition?
Tarsal coalition is where the bones of the hindfoot (the tarsal bones) have an abnormal bony, fibrous or cartilaginous connection Between the clacaneous and navicular or talus and calcanceus

What can tarsal coalition cause to the arch of the foot and how is it treated?
Tarsal coalton can lead to a painful fixed flat foot deformity Treatment may improve with splintage / orthotics but can require surgery to remove the abnormal connection
What is hallux valgus?
Hallux valgus is where the big toe deviates laterally at the metatarsophalangeal joint Also known as a bunion

What can form over the hallux valgus?
Inflamed bursae at the metatarsal head can form in hallux valgus causing bursitis

What is talipes equinovarus colloquially known as? What is affected in this condition?
Talipes equinovarus is colloquially nown as clubfoot It is due to in utero abnormal alignment of the joints betweent he talus, calcaneus and navicular
What percentage of the cases of talipes equinovarus are bilateral? Which sex is more commonly affetced? What are predisposing risk factors for the condition?
50% of cases are bilateral Boys are twice as commonly affected than girls It is more common in breech presentation and oligohydraminois (low amniotic fluid content)
What are the features of talipes equinovarus which result from the abnormal alignment of the joints between the talus, calcaneus and navicular bones?
Cavus of midfoot - high arched midfoot
Adduction of forefoot
Varus of hindfoot - adduction and inversion
Equnius of hindfoot - plantarflexion
High arched midfoot, adducted forefoot, adducted and inverted hindfoot and plantarflexed

What is the treatment of talipes equinovarus?
Treatment of talipes equinvoarius is via a technique of splintage known as the Ponseti technique

Why is it important that the Ponseti technique splintage is started early?
It is important that this is commenced as soon as possible after birth as delayed presentation can result in fixed deformity with the child walking on the outside of their foot
The Ponseti technique requires two stages - the corrective stage and the maintenance stage to prevent recurrence - this is carried out over 5 or 6 weeks cast changes Once full correction is achieved, the child is then placed in a brace consisting of boots attached to a bar How long is this worn for and what position does it keep the feet in?
The brace is worn 23 hours a day for 3 months and then used during sleep until the age of 3 or 4 to prevent recurrence of the talipes equinovarus The brace holds the child’s feet in abduction

What percentage of children require a tenotomy of the achille tendon to maintain full correction of the talpies equinvorus?
80% of children require a tenotomy of the Achilles tendon (a minor procedure) to maintain full correction
Remember back pain in a child or adolescence is a red flag sign – have a low threshold for referral/investigation. What is lateral curvature of the spine (and also rotational deformity) known as? What is the common causes of it?
Scoliosis is the lateral curvature of the spine (and also rotational deformity) Most commonly is idiopathic But can occur secondary to neuromuscular disease, tumour, skeletal dysplasia or infection
What investigation does any painful scoliosis require and why?
Any painful scolisois requires urgent investigation - MRI for tumour or infection
What is the angle used to confirm a diagnosis of scoliosis? How is it measured?
Cobb’s angle is the angle measured to confirm a diagnosis of scoliosis It is an angle calculated between the top most displaced vertebrae to the bottom most displaced vertebrae and measures >10 degrees

The majority of scoliosis are mild and non progressive How are these treated? How are larger curves treated?
Mild, non progressive scoliosis does not require surgery Larger curves may require surgery for cosmosis or to improve wheelchair posture
What can severe cases of scoliosis cause in regards to the lungs?
Severe curves can result in a restrictive lung defect and surgery may be required to prevent breathing difficulties.
Surgery for scoliosis is complex and requires vertebral fusions and long rods connecting the posterior elements of the spine. What is important to consider as a risk when carrying out the corrective surgery?
Correction of larger curves carries a risk of spinal cord injury
What is spondylolisthesis? Which vertebral levels does it most commonly occur at?
Spondylolisthesis is the slippage of one vertebrae over another It most commonly occurs at the L4/5 or L5/S1 vertebral levels
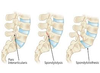
What are the causes of spondylolisthesis?
It can be causes by development defect or a recurrent stress fracture of the posterior elements which fail to heal
Describe the type of patient that commonly gets spondylolithesis?
An adolescent who has increased body weight and increased sporting activity have been implicated
How does spondylolisthesis typically present?
Patients present with low back pain and have a radiculopathy with severe slippage Also may have a paradoxical ‘flat back’ due to muscle spasm And can present acutely with a characterisitc waddling gauit
How is spondylolisthesis diagnosed?
DIagnosis is made from plain xrays

How is spondylolisthesis treated?
Minor egrees of slippage may be observed and treated with rest and physiotherapy More severe slips may require stabilisation


