Visual pathway Flashcards
(17 cards)
What is described as your visual field?
Everything you see with one eye (including in the periphery)
What is this?
What is it’s structure and purpose?

The Fovea
On the retina:
- Thinnest point (top layers pushed out)
- Highest visual acuity
- Only cones
- When we look at something, we move our eyes to focus the light directly onto it
What are the types of visual field testing?
Testing by confrontation test:
- Outpatient screening
- Doctor maps out a visual field through a series of ‘tell me when you see my hand’ sort of tests
- No equipment etc
Automated perimetry:
- Uses a spicy machine
- More accurate but needs the equipment etc
What test is this?

Visual acuity testing
(not a type of visual field testing)
Compared to the object in real life, what image of that object is projected onto our retina?
Objects are upside down and inverted
This is the visual pathway
Identify the stuff like

aye min

What is the Optic chiasma?
The part where the 2 nasal optic nerves from each eye come together/cross over before leaving through the opposite sides optic tract

What are the contents of each optic tract?
One tract contains:
- Fibres from the temporal (lateral) half of the ipsilateral eye (same side)
- Fibres from the nasal (medial) half of the contralateral eye (other side)
What is the LGB?
In which part of the brain is it located?
Lateral geniculate body
This is where the optic tract fibres synapse with the Optic radiation fibres
it is located in the thalamus
What happens to impulses once they reach the Lateral Geniculate body and have synapsed?
The optic radiation fibres pass behind the internal capsule (retro-lentiform fibres) to reach the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe (area 17)
So what visual field is processed by what visual cortex?
Opposite cortex to the visual field
Follow the colours on the diagram
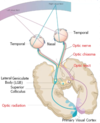
Whats this?

Optic chiasma
What structure does the optic chiasma sit on top of?
Pituitary gland
Clinically important as pathological enlargement of pituitary gland can cause/present with vision-related symptoms
Damage to which part of the visual pathway would cause this?

Right optic nerve is damaged
Stops temporal and nasal fibres from the right eye
What sight loss is this?
Where in the visual pathway is there damage?

Bitemporal hemianopia
Damage to the middle of the optic chiasma would disrupt nasal fibres but temporal fibres (which capture light from the medial half of the visual field) would be fine and continue to their visual cortexes
What is this and what caused it?

Contralateral homonymous hemianopia
This one would be caused by damage to the right optic tract or the right optic radiation
It would prevent all information from the left side of the visual field from reaching the right cortex


