Vestibular function Flashcards
(21 cards)
What is the vestibular system?
A sensory system essential in the control of posture and balance.
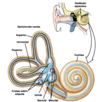
Found in the inner ear, it is a series of fluid-filled membranous tubes, (labyrinths), which are embedded in the temporal bone (petrous part)

Describe the overall structure of the vestibular system?
Vestibular apparatus consists of 3 semi-circular canals, the utricle to which the semi-circular canals all connect and the saccule
Describe the structure of the semi-circular canals found in the vestibular apparatus
3 semi-circular canals are:
- at right angles to each other (3 dimensions)
- have swellings at their bases, called ampulla
- contain sensory hair cells
The utricle and saccule also contain sensory hair cells
Do the thing

Cristae are structures found within the ampullae of SC canals
What do they do?
Sensory receptors for rotational acceleration
There are also receptors called Thermaculae for linear acceleration and head position
What parts of the vestibular apparatus make up the otolith organs?
What are their functions?
Utricle & saccule
Utricle:
- back/front tilt and horizontal acceleration
Saccule:
- Vertical acceleration
Describe the structure of the ampullae of the semi circular canals
Inside the Ampulla (swelling) at the bottom of canal:
- A flexible gelatinous structure called the cupula stretches across the entire width of the ampulla
- Hair cells are embedded into this cupulla
- Endolymph fills the space
- Nerves at bottom (vestibular nerve)
Cupula is distorted by endolymph movement within the canals (during rotational acceleration)
Identify the parts of the ampulla


What are the types of cilia (hair cells) and their differences
a single very large kinocilium and a set of progressively smaller stereocilia
Distortion of the cilia:
- in the direction of the kinocilium causes depolarisation and increased discharge of APs in the vestibular nerve.
- away from the kinocilium leads to hyperpolarization and decreased discharge of APs in the vestibular nerve
This allows the brain to determine movement in time and space
Maculae is the term for the sensory apparatus of the saccule and utricle, so the maculae sense linear movements
What is the difference between the maculae in the saccule and in the utricle?
Utricle:
- Orientated in horizontal plane
- Detects tilt of head
Saccule:
- Vertical orientation
*
Describe the structure of Maculae of the otolith organs
The maculae:
- have a set of cilia (one kinocilium and a series of stereocilium)
- The cilia protrude into a gelatinous mass called the otolith membrane
- Embedded in the otolith membrane are CaCO3 crystals called otoliths.
Label the parts of the Maculae


What feature of otolith crystals means they are useful in detecting movements such as tilt
Otoliths have a density greater than endolymph and thus are affected more by gravity.
Tilting the head moves the otoliths and the otolith membrane in which they are embedded. This distorts the jelly, and moves the cilia
Describe what happens on the macula when the head is tilted backwards
Backward tilt moves the otoliths in the direction of the kinocilium causing depolarisation and increased discharge of APs.
(Opposite for forward tilt)

Describe how the vestibular information travels in the brain
Numerous neural pathways connect the vestibular centres of the medulla, where many of the sensory afferents of the vestibular nerves terminate, and the cerebellar centres which co-ordinate the postural muscles required to maintain balance
What are the tonic labyrinthine reflexes?
Keep the axis of the head in a constant relationship with the rest of the body.
Use information from maculae and neck proprioceptors
What are the dynamic righting reflexes?
Rapid postural adjustments that are made to stop you falling when you trip.
Long reflexes, involving extension of all limbs.
Most profound in cats
What are the vestibulo-occular reflexes?
2 reflexes (static & dynamic) that work to maintain a clear focus on an object/image during movement of the head
Static:
- Lateral tilting ==> Intorsion/extorsion
- When you tilt your head, the eyes intort/extort to compensate, so that over a certain range, the image stays the right way up.
Dynamic:
- Rotation of head ==> Rotation of eye against
- direction of nystagmus is the direction of the rapid flick back. So R rotation = R nystagmus
How can induced Nystagmus be used to test vestibular function?
Caloric Stimulation:
- Test of Horizontal SCC
- Outer ear is washed with either cold or warm fluid causing convection currents in endolymph
- Warm fluid (44°C) causes nystagmus towards affected side and Cold (30°C), away
- COWS (cold = opposite, warm = same)
Post rotatory nystagmus:
- Spun in a Barany chair
- Not important
Powerful maintained stimulation of the Vestibular system can give rise to what sickness?
kinetosis = motion sickness
visual and vestibular system inputs to the cerebellum are in conflict e.g. if the vestibular system indicates rotation but the visual system does not
cerebellum generates a “sickness signal” to the hypothalamus to bring about the ANS changes – nausea, vomiting, lowered BP and dizziness, sweating and pallor
Identfy the labels of the ampulla




