Embryology and congenital Flashcards
From which germ layer does the nervous system form?
What else forms from this layer?
Ectoderm
Ectoderm also gives rise to epidermis
When does the Central nervous system appear?
(including the stage of embryonic development)
Beginning of 3rd week - during Gastrulation
Describe how the primitive CNS forms during the 3rd week of development
- Thickening of Ectoderm anterior to the Primitive node/streak - forming Neural plate
- Edges of Neural plate thicken and move upwards - forming the Neural folds
hehe xox

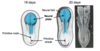
Describe what happens after the neural folds have formed
At 22 days:
- Neural folds migrate towards each other and fuse at midline forming the NEURAL TUBE
- tube initially remains open at both ends
What name is given to the openings at each end of the neural tube?
Which closes first?
Anterior (cranial/rostral) neuropore:
- Closes first - 25 days (somite stage)
Posterior (caudal) neuropore:
- Closes - 27 days
Failure of the neural tube to close causes what conditions?
- Anencephaly (+ variations)
- Encephalocoele
- Spina bifida
What is anencephaly?
Absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp
Failure of Anterior neuropore closure
Incompatible with life
What is Exencephaly?
Condition in which the embryo’s brain is located outside of the skull
This condition is usually found in embryos as an early stage of anencephaly
It is hence also caused by failure of the anterior neuropore to close
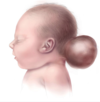
What is encephalocoele?
Condition caused by failure of the posterior neuropore (rostral neural tube) to close
Characterised by the Herniation of cerebral tissue through a defect in the skull. This forms large, sac-like protrusions
Describe how spina bifida arises
Defective closure of the caudal (anterior) neural tube - such that the vertebral arches do not fuse
This basically leaves a section of the spinal canal open at the back
What are the types of Spina bifida?
Spina bifida occulta
Spina bifida cystica:
- SB w/ meningocele
- SB w/ meningomyelocele
- Myeloschisis
What are the main features of SB occulta?
Most minor form of SB
Failure of embryonic halves of vertebral arch to grow normally and fuse - usually L5, L6
Usually no clinical symptoms - however, may have a dimple with tuft of hair at site of problem

Spina bifida cystica encompasses 3 types of spina bifida.
What characterises this class of Spina bifida?
Protrusion of spinal cord and/or meninges through the defect in the vertebral arches
What is spina bifida w/ meningocele?
Rarest form
Protrusion of meninges and CSF outwards - but Spinal cord remains where it should be
What is Spina bifida w/ meningomyelocele (MMC)?
Protrusion of sac - containing Spinal cord and/or nerve roots
This form of SB involves neurological deficits - loss of sensation and muscle paralysis
The area affected depends where the lesion is located
What other condition is associated with SB w/ meningomyelocele (MMC) and how?
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus can develop in babies with SB w/ meningomyelocele
What is myeloschisis?
The most severe form of SB
Failure of neural folds to fuse causes the spinal cord to be open in the affected area
Describe how spina bifida is prevented
Folic acid supplements - 400 µg/day –> 50-70% decrease in risk
Describe how prenatal diagnosis of spina bifida is achieved
Maternal blood screening:
- Elevated α-fetoprotein (AFP) in serum - best detected at 16-20 weeks
Amniocentesis:
- Elevated α-fetoprotein (AFP) in amniotic fluid
Ultrasound:
- Spina bifida after 16-20 weeks
- Anencephaly after 12 weeks
What are the risk factors for spina bifida etc?
Genetic predisposition
Nutritional
- (e.g. too little folate, too much vitamin A)
Environmental
- (e.g. hyperthermia; taking certain drugs – e.g. sodium valproate)


