Vertebral Column and the Muscles of the Back Flashcards
•All vertebrae have a ______ that surrounds and protects the spinal cord
vertebral foramen
cervical vertebrae have transverse foramen for the ____ ______
vertebral artery
Vertebral column in a adult typically consists of ____ vertebrae arranged in ______ regions
33; 5
spinal vertebrae regions and how many vertebrae
- Cervical (7)
- Thoracic (12)
- Lumbar (5)
- Sacral (5)
- Coccygeal (4)
thoracic vertebrae articulate with the ____
ribs
lumbar vertebrae are ____
large and massive for weight bearing
•Motion only occurs between 24 vertebrae:
7 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
•The 5 sacral vertebrae are fused in adults forming the ___
sacrum
•4 coccygeal vertebrae are fused to form the _____
coccyx (tailbone)
_____ help align our bodies center of gravity and provide shock absorption throughout the gait cycle
Curvatures


Primary curvatures are the ______ and ____ curvatures that develop during the _____…. same/opposite direction as the fetal vertebral column
thoracic and sacral; fetal period; same
Secondary curvatures are the _____ and _____ curvatures which develop _____…. same/opposite direction as the fetal vertebral column
cervical and lumbar; opposite
_______ is accentuated thoracic curvature …often a result of age related osteoporosis. Sometimes referred to as ‘hunchback’ or ‘dowager’s hump’
Kyphosis
______ accentuated lumbar curvature…often due to weight gain (i.e. during pregnancy). Sometimes referred to as ‘swayback’ or hollow back
Lordosis
_____ abnormal lateral curvature and rotation of the vertebral column- can result from limb length inequalities and/or malformation of vertebrae
Scoliosis

kyphosis

lordosis

scoliosis

scoliosis
Typical vertebrae consists of three major features:
- Vertebral body- for weight bearing
- Vertebral (neural) arch consisting of pedicles and laminae- protection of the spinal cord
- Numerous (7) processes for muscular attachment:
Spinous process (1)
Transverse processes (2)
Articular processes (4) (superior & inferior) which form joints
_____ are synovial joints between the superior and inferior articular processes of adjacent vertebrae
Facet Joints or (zygapophysial joints)
Intervertebral discs
- are cartilaginous joints designed for weight bearing and strength
- are interposed between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae
- These discs are tightly adhered to the surface of the vertebral bodies and provide a stable/strong attachment between adjacent vertebrae
Intervertebral discs consist of:
- Outer anulus fibrosus- composed of concentric layers of fibrocartilage that adheres to the vertebral bodies
- Nucleus pulposus- a gelatinous central mass (high water content) that acts like a miniature shock absorber






_____ allow passage and protection for the spinal nerve as it exits the vertebral column
Intervertebral foramen
_____ vertebrae have transverse foramina for the vertebral artery
Cervical
Majority of motion along the vertebral column occurs in the ____ and ____ …hence, this is where we tend to see herniated or “slipped” disc problems
cervical and lumbar regions
•As mentioned….the greatest range of motion is within the______…followed by the _______, both areas have significantly greater motion than the fairly ridged _____
cervical spine; lumbar spine; thoracic spine
the _____ is at greatest risk of injury purely from a mechanical prospective (least stable area)
cervical spine
•In addition…the change from mobility to rigidity within the spine creates two areas of significant stress concentration; These junctions are common sites of vertebral fractures
- Cervicothoracic junction (~C5-T1)
- Thoracolumbar junction (~T10-L2)






____ is the 1st cervical vertebra
•Atlas
_____ is the 2nd cervical vertebra
•Axis
•Distinguishing feature of C2 is a “tooth-like” process-the ______ that projects superiorly from the body
dens (odontoid process)
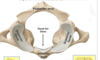
what view and what vertabrea ?

superior view of the atlas
Craniovertebral Joints:
- Atlanto-occipital Joint
- Atlanto-axial Joint
Synovial joint between the superior articular facets of the atlas (C1) and the occipital condyles at the base of the skull
Atlanto-Occipital Joint

Atlanto-Occipital Joint
Fractures of Axis (C2) often referred to as _____…others may involve the dens or odontoid process which, if displaced…can injure the spinal cord (quadriplegia)

‘Hangman Fracture’

Atlanto-Axial Joints
Actually three synovial articulations:
- One median atlantoaxial joint-between the Dens of C2 and the anterior arch of C1
- Two lateral atlantoaxial joints- are synovial joints between opposing articular facets

Atlanto-Axial Joints
Functions of the Vertebral Column
- Supports the head and trunk (torso)
- Transfers the weight of the body to the lower limbs
- Provides a flexible…yet rigid axis for our body (postural support)
- Encloses and protects the spinal cord and spinal nerves
nThe spinal cord has ____ pairs of spinal nerves:
31 pairs
- 8 cervical
- 12 thoracic
- 5 lumbar
- 5 sacral
- 1 coccygeal (relatively minor/insignificant)


______ contains axons of somatic motor (efferent) nerves that convey impulses away from the spinal cord
Ventral Root-
______ contains axons of somatic sensory (afferent) nerves that convey impulses toward the spinal cord
Dorsal Root
Both ventral and dorsal roots unite to form a _____ which conveys both motor and sensory axons
spinal nerve
spinal nerves split into ____ and ____
dorsal ramus and ventral ramus
______ conveys nerve axons to and from the muscles of the back and the overlying skin of the back
Dorsal ramus
_____ conveys nerve axons to and from the body wall (torso) and/or the upper & lower limbs
Ventral ramus


______ unites anterior surfaces of the bodies of the vertebrae- prevents hyperextension
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
________ unites posterior surface of the bodies of vertebrae- thus located inside the vertebral canal
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
______ connects the spinous processes from the sacrum to C7- expands into the Ligamentum Nuchae in cervical region
Supraspinous Ligament
_______ a broad strong ligament of the neck that provides attachment for cervical muscles
Ligamentum nuchae








______ adjoin adjacent spinous processes
Interspinous Ligament
______ elastic fibers adjoin adjacent lamina of vertebrae- help prevent hyperflexion of the vertebral column

Ligamentum Flavum- yellow,



Superficial back muscle are “extrinsic” muscles- these muscles actually produce and control limb/shoulder movements:
- Trapezius
- Latissimus dorsi
- Levator scapulae
- Rhomboids
Latissimus Dorsi
- Latissimus Dorsi- large superficial muscle positioned in the lower back region…but is actually a muscle of the upper extremity
- Insertion- intertubercular sulcus (bicipital groove) of the humerus
- Action- extends, adducts and medially rotates humerus
- From a daily activity point of view…we use our Latissimus Dorsi for climbing/rowing or pushing yourself up when you get “out of a chair”
- Innervation- thoracodorsal nerve (ventral rami of C6, C7, C8)
Trapezius Muscle
- Trapezius Muscle- large trapezoid-shaped muscle in upper back
- Insertion- clavicle, the acromion, and the spine of scapula
- Action- elevates, rotates and retracts the scapula (“shrugs shoulders”)
- Innervation- trapezius receives its motor innervation via the eleventh Cranial Nerve (CN XI) - the spinal accessory nerve
Intermediate Muscles of the Back
Intermediate muscles are small muscles aid/assist in respiratory control
- Serratus posterior superior (located deep to the rhomboids)
- Serratus posterior inferior (located deep to the latissimus)
Function of Deep back muscles are often referred to as “true” or “intrinsic” back muscles because
these muscles all act specifically on moving and/or stabilizing the vertebral column
All deep or intrinsic muscles of the back are innervated by
dorsal rami of spinal nerves
Deep Muscles of the Back
nClinicians often refer to the deep back muscles as “paraspinal” muscles because of their position along-side the spinal column
Deep muscles of the back are further divided into 3 layers:
- Superficial intrinsic layer consists of the splenius muscles- located in the cervical region
- Intermediate intrinsic layer consists of the erector spinae muscle complex
- Deepest intrinsic layer consists of the transversospinalis muscle complex (not shown well here…located deep to the erector spinae)
Erector Spinae
Complex
Intermediate layer of “intrinsic” or deep back muscles
Divided into 3 muscles masses:
- Iliocostalis- lateral column
- Longissimus- intermediate column
- Spinalis- medial column
Important postural muscles; help extend and stabilize the vertebral column
Innervated by dorsal rami of spinal nerves
Transversospinalis
Muscle Complex
Deepest layer of “intrinsic” or deep back muscles
These muscles course from transverse process to spinous processes of more superior vertebrae
Divided into 3 muscle segments
- Semispinalis- superficial (span 4-6 segments)
- Multifidus- intermediate (span 2-4 segments)
- Rotatores- deepest (span 1-2 segments)
Important postural, rotational, and proprioceptive muscles
Innervation- dorsal rami of spinal nerves
Orientation of the _____ help determine motion within the vertebral column
facet joints
Remember the close proximity of spinal nerves with facet joints AND the intervertebral disc. _______ can impinge upon the exiting spinal nerve
Arthritis or disc degeneration
Latissimus Dorsi- it is a muscle of the upper limb despite the fact that is located on the back- hence its innervated by _______
ventral rami of spinal nerves (thoracodorsal nerve C6, C7 and C8)
Trapezius –innervated by the ______
spinal accessory nerve (Cranial Nerve 11 or CN XI)
the facet joints in the lumbar spine are oriented in the ______ plane which favors flexion/extension
The facets in the thoracic region are oriented in the ______ plane and favor rotational/torsion movements
Facets joints in the cervical spine are nearly ______ which renders considerable motion/mobility in the cervical region
sagittal; frontal or coronal; horizontal
















_______ of the cervical region, as occurs in whiplash and/or football injuries, can often tear portions of the ______ ligament: These injuries can also result in compression fractures and or dislocations of the cervical vertebrae…putting the spinal cord at risk
Hyperextension; anterior longitudinal


